Введение. Стриктура уретры – это заболевание, при котором отмечается сужение мочеиспускательного канала в результате метаплазии эпителия и формирования зоны спонгиофиброза [1]. В основе развития стриктур уретры лежат локальные рубцовые изменения, возникающие вследствие избыточной продукции коллагеновых волокон. Депозиты коллагена препятствуют пролиферации, дифференцировке и миграции клеток микроокружения в стромальном компоненте тканей, что в свою очередь может стать причиной прогрессирующей склеротической деформации уретры [2]. Улучшение результатов лечения требует не только усовершенствования оперативной техники уретропластики, но и поиска методов влияния на патогенетические звенья формирования стриктуры уретры. Одним из наиболее безопасных методов служит применение плазмы, обогащенной тромбоцитами (PRP). Обогащенная тромбоцитами плазма не только обладает регенеративным потенциалом, но и уменьшает воспалительный процесс, спонгиофиброз и отек ткани [3]. Факт снижения спонгиофиброза при применении PRP имеет фундаментальный интерес к лечению стриктур уретры, как первичных, так и рецидивных.
Цель исследования: оценить изменения строения межклеточного матрикса, клеточного состава спонгиозного тела и регенеративный потенциал PRP после выполнения уретропластики на биологической модели.
Материалы и методы. Эксперимент выполнен на 18 кроликах-самцах бургундской породы массой 3,0–4,5 кг. Перед экспериментом все животные были осмотрены ветеринарным врачом с целью выявления и исключения больных особей. Содержание животных и работа над ними проводились на базе вивария ФГАОУ ВО РНИМУ им. Н. И. Пирогова Минздрава России. Во время проведения эксперимента соблюдались требования нормативных документов, регламентирующих проведение исследований с участием животных: Правилами проведения работ с использованием экспериментальных животных, утвержденными Приложением к приказу Министерства здравоохранения СССР от 12.08.1977, № 755; Европейской Конвенцией о защите позвоночных животных, используемых для экспериментов или в иных научных целях (Страсбург, 18.03.1986).
Было сформировано две равнозначные группы животных: экспериментальная и контрольная.
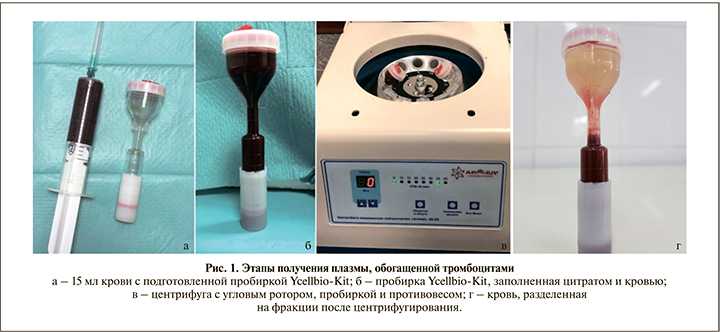
Методика получения плазмы, обогащенной тромбоцитами. В асептических условиях из ушной вены выполняли забор 15 мл крови в стерильный шприц 20 мл, содержащий 1,5 мл 3,2%-ного цитрата натрия (рис. 1, а). Кровь из шприца переливали в пробирки Ycellbio-Kit (рис. 1, б), затем кровь центрифугировали (аппарат Armed 80-2S с угловым ротором, Китай) при скорости 3500 об/мин в течение 4 мин (рис. 1, в), в результате происходило разделение крови на три фракции: плазму, PRP и эритроцитарную массу (рис. 1, г). Плазму, обогащенную тромбоцитами, набирали в 5-миллитровый одноразовый шприц. Объем PRP составлял в среднем 1,5–2 мл.
Методика уретропластики и введения плазмы. Поперечным разрезом в области промежности выполняли доступ до бульбозного отдела уретры. Циркулярно мобилизовали весь бульбозный отдел уретры в дистальном и проксимальном направлении (рис. 2, а). Ориентируясь на введенный в уретру катетер Фолея № 6, поперечно пересекали уретру (рис. 2, б). Накладывали 6 узловых швов (рис. 2, в) с анастомозированием краев уретры «конец в конец» (рис. 2, г). Затем устанавливали силиконовый уретральный катетер 8 Сh, ушивали бульбоспонгиозную мышцу и послойно ушивали рану. Кровопотеря составила около 5 мл.
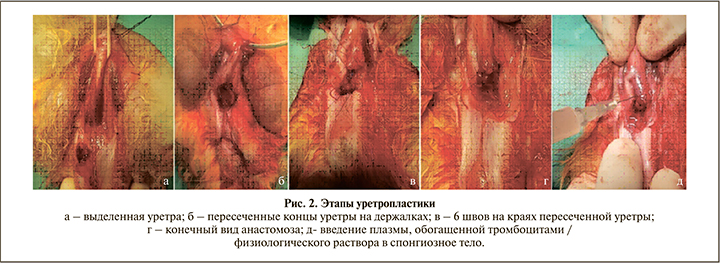
В экспериментальной группе проводили активацию аутологичной плазмы 10%-ным хлоридом кальция в соотношении 1:10. После активации в течение 10 мин выполнялось введение PRP в объеме 4 мл по периметру анастомоза (рис. 2, д). Животным контрольной группы аналогичным образом вводили изотонический раствор 0,9% NaСl.
Методика гистоморфологического исследования. Для исследования осуществляли забор образцов тканей уретры размером 1,0×0,5×0,5 см. Края резекции всех образцов были прошиты хирургической лигатурой. Забор материала осуществляли на 3-и, 7-е и 15-е сутки после оперативного вмешательства. На каждом сроке выполнялось выведение из эксперимента по три животных из контрольной и экспериментальной групп. Все образцы тканей фиксировали в растворе забуференного формалина с последующим изготовлением залитых парафином блоков и готовых микропрепаратов.
Рутинную окраску гематоксилином и эозином использовали для визуализации гистоархитектоники тканей. Также применяли окраску по Ван Гизону для выявления коллагеновых волокон и оценки правильности их ориентации (для визуализации матрикса и клеток используются три красителя: пикриновая кислота окрашивает цитоплазму клеток в желтый цвет; железный гематоксилин по Вейгерту придает ядрам черную окраску, а коллагеновые волокна окрашиваются кислым фуксином в красный цвет).
С целью объективной детализации воспалительных и регенеративных изменений проведено дополнительное иммуногистохимическое исследование со следующими антителами: CD79a, CD43, CD31(PECAM1), MMP1, MMP9.
CD79а (clone JCB117) является гетеродимерной сигнальной молекулой трансдукции, связанной с мембранным иммуноглобулином. Антитела к α-цепи молекулы служат маркером линии В-клеток, выявляющимся на всех этапах их дифференцировки.
Антитела к CD43 (clone MT1) идентифицируют муцин мембраны, известный как сиалофорин, и могут быть использованы как Т-клеточные маркеры.
CD31 (PECAM 1 – platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1) является мембранным белком семейства иммуноглобулинов и может быть использован как маркер эндотелиальных клеток.
ММР (matrix metalloproteinase) – эндопептидазы, способные разрушать коллаген и участвовать в ремоделировании различных тканей. MMP-1 – межтканевая металлопротеиназа, основным субстратом которой являются коллагены I, II, III, VII, VIII и X типов; MMP-9 – желатиназа В, разрушающая коллагены IV, V, VII, X, XIV типов.
Количественный анализ структурных изменений осуществлен посредством подсчета В- и Т-лимфоцитов, имевших позитивную мембранную реакцию с CD79a и CD43 соответственно в 10 репрезентативных полях зрения (HPF) с апертурой объектива 0,65 в участках наибольшей концентрации («горячие очаги»). Уровень экспрессии MMP1, MMP9 оценивали путем подсчета позитивных клеток в 10 репрезентативных полях зрения HPF с апертурой объектива 0,65 в подслизистом и мышечном слоях.
Для оценки ангиогенеза осуществляли подсчет сосудов в 10 полях зрения HPF (апертура объектива – 0,65).
Визуализация биопсийного материала выполнена с помощью светооптического микроскопа Carl Zeiss Lab. Al. («Carl Zeiss», Германия), совмещенного с видеокамерой AxioCam Erc5s («Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH», Германия), и программного обеспечения Zen Lite.
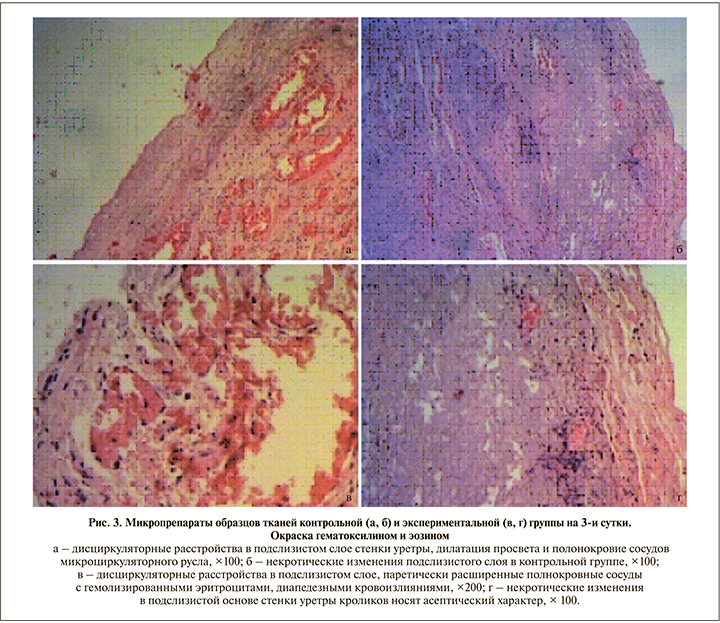
Результаты. На 3-и сутки после операции в контрольной группе были выявлены следующие морфологические изменения (рис. 3, а, б). Эпителиальная выстилка была представлена неравномерно утолщенным зрелым уротелием со слабовыраженными дистрофическими и некробиотическими изменениями в виде гомогенизации и мелкозернистости эозинофильной цитоплазмы. Количество слоев в эпителиальном пласте не превышало 10 (от 3 до 7) без нарушения стратификации ядер. Клетки эпителия с минимальным полиморфизмом округлой формы, с набухшей эозинофильной цитоплазмой, несколько гиперхромными овальными ядрами; в части клеток отмечался глыбчатый распад хроматина. В разволокненном, несколько отечном подслизистом слое стенки уретры имели место дисциркуляторные расстройства, проявившиеся полнокровием сосудов микроциркуляторного русла, а также дилатацией просвета артериол и венул с седиментацией в них форменных элементов крови (агрегацией и сладжированием эритроцитов). Эндотелий с дегенеративными изменениями на отдельных участках был десквамирован от подлежащей базальной мембраны в просвет сосуда; также обращали на себя внимание миоинтимальные утолщения стенок артериол.
В рыхлой соединительнотканной подслизистой основе уретры контрольной группы обнаружены крупные, не сливающиеся между собой зоны некроза. Ядра некротизированных клеток сморщены, с конденсацией, а также глыбчатостью хроматина, в некоторых клетках ядра не визуализировались (признаки кариолизиса). Цитоплазма клеток имела признаки коагуляционного некроза. В части клеточных элементов определялись признаки разрушения мембранных структур с гидролитическим расплавлением цитоплазмы (плазмолиз). Межклеточный матрикс в зоне некроза лизирован, представлен гомогенными эозинофильными массами. Перифокально в зоне некротических изменений отмечена полиморфно-клеточная воспалительная инфильтрация, представленная лимфоцитами, сегментоядерными гранулоцитами (преимущественно эозинофилами и нейтрофилами). В части микропрепаратов выявлена мышечная оболочка, представленная тяжами спиралевидно переплетающихся гладких мышечных клеток, образующих внутренний и наружный слои.
В экспериментальной группе на 3-и сутки (рис. 3, в, г) в уротелии также были выявлены дистрофические изменения. Слизистая оболочка выстлана зрелым многорядным, многослойным переходно-клеточным эпителием, состоявшим из уротелиальных клеток с минимальными признаками клеточного и ядерного полиморфизма. Клетки округлой или овальной формы с крупными, несколько гиперхромными ядрами (при ненарушенном ядерно-цитоплазматическом соотношении), гомогенной эозинофильной цитоплазмой. В единичных эпителиоцитах – признаки фокального колликвационного некроза. Клеточные элементы в эпителиальном пласте расположены без нарушения стратификации, зонтичные клетки прослеживались на большем протяжении. В рыхлой соединительнотканной подслизистой основе уретры обращали на себя внимание расстройства кровообращения, проявившиеся резко расширенными полнокровными сосудами микроциркуляторного русла с отеком и набуханием эндотелиальных клеток, а также наличием частично гемолизированных эритроцитов в их просветах. На фоне вышеописанных морфологических изменений выявлялены очаговые диапедезные кровоизлияния. В подслизистом слое также имели место мелкие, не сливавшиеся фокусы некрозов. Однако некротические изменения в экспериментальной группе носили асептический характер ввиду отсутствия клеточных элементов воспаления. Мышечная оболочка (представлена не на всем протяжении) образована слоями пучков гладкомышечных клеток, проходящих в разных направлениях.

На 7-е сутки в материале, полученном от животных контрольной группы (рис. 4, а, б), выявлены реактивные изменения эпителиального пласта в ответ на повреждение. Уротелий неравномерно утолщен с увеличением количества слоев (более 10), эпителиальные клетки с укрупненными гиперхромными несколько вытянутыми ядрами, отмечалось нарушение их стратификации в эпителиальном пласте (ядра расположены хаотично, на разном уровне). Зонтичные клетки прослеживались не на всем протяжении. Обращало на себя внимание присутствие интраэпителиальных сегментоядерных гранулоцитов в слизистой оболочке уретры. В подслизистом слое сохранялись дисциркуляторные расстройства и зоны некротических изменений в виде детрита, пропитанного фибрином и сегментоядерными гранулоцитами (в составе клеточного воспалительного инфильтрата преобладали эозинофилы). Мышечная оболочка образована тонкими веретенообразными гладкими мышечными клетками с удлиненными ядрами и гомогенной эозинофильной цитоплазмой, идущими в поперечном и продольном направлении.
В экспериментальной группе на 7-е сутки (рис. 4, в, г) после альтерации покровный эпителий был представлен уротелием с минимальными признаками реактивных изменений (клетки относительно мономорфные, с крупными округлыми ядрами, расположенными у базального края клетки). Рыхлая подслизистая основа с отеком и разволокнением межуточного вещества, мелкими фокусами некроза с наличием клеточных элементов (гистиоцитов и многоядерных макрофагов). Гладкомышечные клетки с центрально расположенными ядрами, окруженные тонким слоем цитоплазмы. Между миоцитами выявлены тонкие коллагеновые волокна.
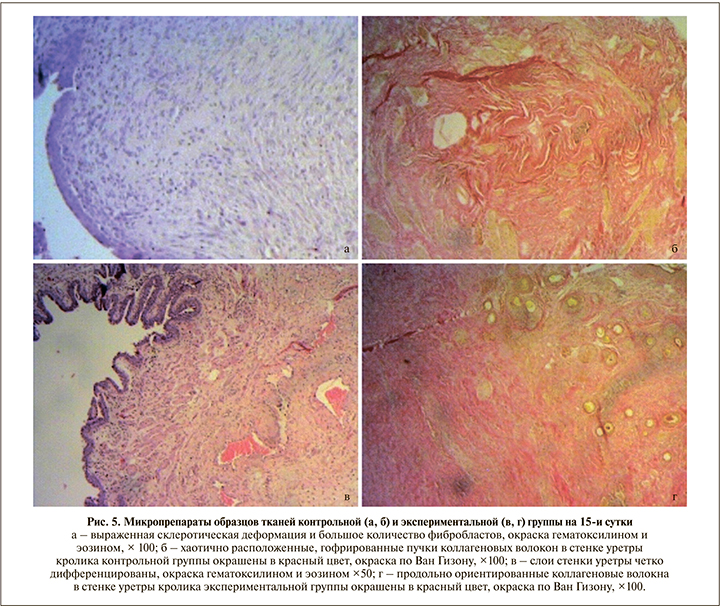
При изучении микропрепаратов контрольной группы, полученных на 15-е сутки после операции (рис. 5, а), зон некроза на всем протяжении стенки не обнаружено. Уротелий, покрывавший слизистую оболочку уретры, несколько уплощен. Собственная мышечная пластинка не прослеживалась, сливалась с подслизистой основой. В подслизистом слое имели место хаотично расположенные коллагеновые волокна с большим количеством фиброцитов и фибробластов. Мышечные волокна с вытянутыми ядрами с заметными ядрышками, межклеточные границы нечеткие.
В экспериментальной группе на 15-е сутки (рис. 5, в) ни в одном из представленных слоев стенки уретры некротических изменений не выявлено. Слои стенки уретры хорошо дифференцированы. Слизистая оболочка, представленная 6–8 слоями эпителиальных клеток, формировала множественные складки. Собственная мышечная пластинка слизистой оболочки гипертрофирована, прослеживалась на всем протяжении. Подслизистый слой с незначительным отеком. В области шовного материала замечена гистиоцитарно-макрофагальная воспалительная инфильтрация. Мышечный слой (прослеживался на отдельных участках) представлен гладкомышечными клетками удлиненной веретеновидной формы, в которых хорошо определялась центральная часть, содержавшая палочковидное ядро, и заостренные концы клеток, проникавшие в промежутки между соседними клетками. В части клеток было видно центрально расположенное ядро, имевшее округлый вид на поперечном срезе. Между миоцитами визуализировались тонкие прослойки рыхлой соединительной ткани. Краткое описание морфологических изменений представлено в табл. 1.

При окраске по Ван Гизону и при анализе данных, полученных при иммуногистохимическом исследовании, значимых различий в экспрессии коллагена между группами на 3-и и 7-е сутки выявлено не было. Однако на 15-е сутки в образцах контрольной группы (по сравнению с экспериментальной) отмечена избыточная продукция коллагена с субтотальным замещением всех структурных элементов, а также хаотичное расположение коллагеновых волокон в стенке уретры, что может свидетельствовать о выраженной синтетической активности фибробластов с последующей коллагенизацией стромы в рамках компенсаторно-приспособительных реакций (рис. 5 б, г).
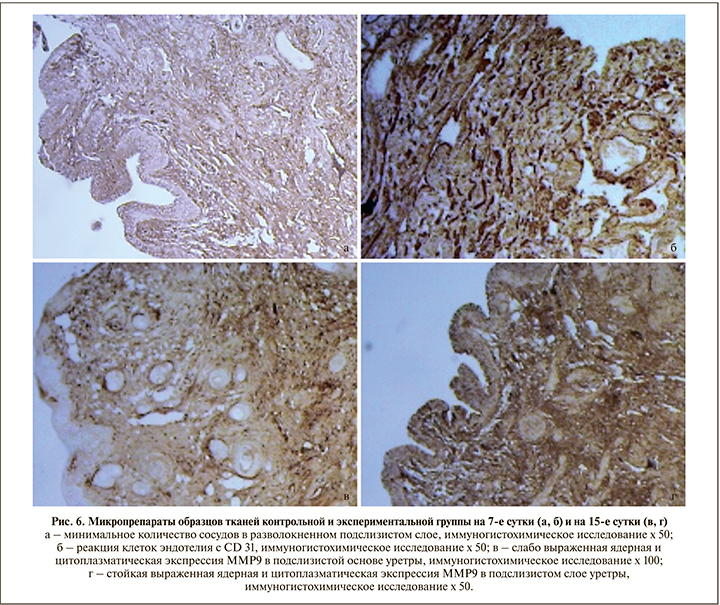
При проведении иммуногистохимического исследования (рис. 6) на 3-и, 7-е и 15-е сутки во всех экспериментальных образцах по сравнению с контрольной группой отмечено меньшее количество Т- и В-лимфоцитов, а также более интенсивная экспрессия MMP и CD31 (табл. 2).
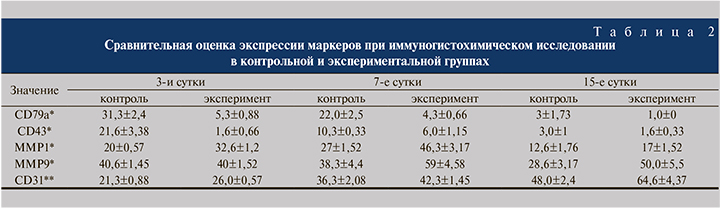
Для объективной оценки количества цинк-зависимых эндопептидаз в исследуемом материале выполнено иммуногистохимическое исследование с соответствующими антителами. Уровень экспрессии MMP1 во всех образцах, полученных от кроликов экспериментальной группы, был на 38% выше, чем в контроле.
Значимых различий в экспрессии MMP9 на 3-и сутки обнаружено не было. Однако на 15-е сутки уровень экспрессии MMP9 в образцах тканей с применением плазмы, обогащенной тромбоцитами, был примерно в 2 раза выше, чем в контрольной группе (50,0±5,5 и 28,6±3,17 соответственно, p<0,05).
Полученные результаты свидетельствуют о том, что уровень экспрессии металлопротеиназ является одним из определяющих факторов ремоделирования экстрацеллюлярного матрикса и как следствие – может коррелировать с репаративными процессами без формирования рубцовых изменений.
Обсуждение. Воспаление, развивающееся в ответ на повреждение тканей, также играет важную роль в процессах регенерации и фиброза. Воспалительные клетки, мигрирующие из кровеносного русла, проникают в ткани с последующим повреждением базальных мембран клеток, а также инициируют деградацию протеинов интерстициального матрикса с дальнейшим высвобождением их фрагментов, что способствует непрерывной активации фибробластов, гиперпродукции белков экстрацеллюлярного матрикса и развитию фиброза. Таким образом, альтерация не только индуцирует воспаление, но и активирует различные типы клеток иммунной системы, например лимфоциты, способные выделять профибротические медиаторы воспаления.
Образование новых сосудов в поврежденных тканях является естественным процессом при заживлении ран. Недостаточное количество кислорода в тканях вызывает увеличение количества HIF1α-рецепторов и инактивацию гидроксилазы, что обусловливает повышение экспрессии трансформирующего фактора роста β (TGF-β), стимулирующего образование матриксных белков с развитием дальнейшего фиброза [4].
Одним из направлений в лечении не только первичных, но и рецидивных стрикутр является подавление синтеза коллагена, воспалительного процесса и формирования грубой волокнистой соединительной ткани. С целью подавления пролиферации фибробластов после оптической уретротомии интрауретрально вводили митомицин С, который в ряде работ обеспечивал увеличение безрецидивного периода в 2 раза [5, 6], но применение данного препарата ограничено случаями только внутренней оптической уретротомии. Кроме применения противоопухолевых описано таковое различных стероидных противовоспалительных препаратов, например триамциолона, в сочетании с интермиттирующей самокатетеризацией после внутренней оптической уретротомии. Согласно данным морфологического исследования, в тканях уретры при этом достоверно снижалось число апоптозных клеток, определялось меньше отложений коллагена и имела место более легкая степень фиброза [7, 8]. В экспериментальной работе на крысах M. F. Kilinc et al. [9] оценили действие интрауретрального введения эритропоэтина. При морфологическом контроле через 14 дней отмечено снижение воспалительного процесса, выраженности фиброза в группах применения эритропоэтина по сравнению с контрольной группой. Ограничением представленных выше работ считаются использование обозначенных препаратов только после оптической уретротомии и малые размеры групп пациентов, что требует продолжения исследований.
Другим направлением в комбинированном лечении стриктур уретры является применение препаратов для стимуляции процессов регенерации и неоангиогенеза, что предотвращает рубцевание ткани после оперативного лечения. К одним из таких методов относится применение PRP.
Первые результаты применения PRP представлены в 1985 г. Knighton, применившим ее для лечения трофических язв; с 2000 г. она стала применяться в спортивной медицине, с 2006-го – во многих областях [10]. В настоящее время PRP активно применяется в травматологии и ортопедии, косметологии, челюстно-лицевой хирургии. Тромбоциты содержат в высоких концентрациях ростовые факторы, такие как PDGF-AB (тромбоцитарный фактор роста АВ), TGF-1 (трансформирующий фактор роста 1) и VEGF (фактор роста эндотелия сосудов). Эти факторы способны стимулировать клеточную пролиферацию и ангиогенез, снижать воспалительный процесс [4]. В урологии применение PRP ограничено лечением эректильной дисфункции, болезни Пейрони и пузырно-влагалищных свищей [11–13].
В. Л. Медведев et al. местно применили PRP в лечении пузырно-влагалищных свищей диаметром от 3 до 40 мм. Зафиксировано закрытие трех фистул диаметром от 3 до 7 мм.
У половины пациенток по завершении терапии наблюдалось уменьшение свища в диаметре не менее чем на 50% окружности [14].
В реконструктивной хирургии уретры эффективность применения PRP подтверждена в ограниченном числе исследований. Е. Г. Карпущенко оценил эффективность заместительной уретропластики буккальным графом без и с применением PRP. Показано, что частота рецидива в экспериментальной группе была вдвое ниже, а результатом стимуляции ангиогенеза стало увеличение числа капилляров на 80% [15]. Результаты нашей работы подтверждают положительное влияние PRP не только на процессы регенерации посредством влияния на локальный ангиогенез, но и на организацию межклеточного матрикса спонгиозного тела. Это можно рассматривать как перспективу для дальнейшего изучения и применения PRP в клинической практике пациентам с рецидивным течением стриктуры мочеиспускательного канала.
Заключение. Согласно результатам проведенного эксперимента, применение PRP способствует ускорению репаративных процессов в спонгиозном теле после уретропластики. Другим немаловажным положительным эффектом PRP является повышение экспрессии металлопротеиназ, что приводит к снижению продукции коллагена и правильной ориентации коллагеновых волокон. Это позволяет снижать количество патологической фиброзно-рубцовой ткани в зоне операции. Результаты данного исследования дают возможность применять PRP в лечении не только в первичных стриктурах уретры, но и в сложной группе рецидивных стриктур.



