Введение. Контактная гольмиевая литотрипсия, применяемая в лечении мочекаменной болезни (МКБ), относится к разряду высокотехнологических операций, широко используемых в практической урологии. Этот способ удаления мочевых камней обладает высокой эффективностью. Однако существует также риск возникновения послеоперационных осложнений. Отсутствие последних наблюдалось лишь в 84,8% [1] или 81,9% [2] операций. В частности, количество инфекционных осложнений после контактной лазерной литотрипсии составило 8,37%, у 6.61% наблюдалась послеоперационная лихорадка, у 4,41% пациентов развился синдром системного воспалительного ответа. При этом установлено, что количество осложнений возрастает с увеличением длительности операции, кроме того, зависит и от квалификации хирурга.
К наиболее значимым осложнениям при трансуретральной пиелокаликолитотрипсии можно отнести синдром системного воспалительного ответа (ССВО) с уросепсисом до 4,5% случаев [3] и стойкую гематурию в 2% случаев [4]. Еще одним существенным видом осложнения является развитие обострения воспалительных процессов (пиелонефрита), сопутствующих МКБ. В статье [5] отмечается, что после лазерной контактной литотрипсии в почках и верхней трети мочеточника частота развития острого пиелонефрита достигает 11,5% На еще более высокую частоту (16,4%) данного осложнения после лазерной КЛТ мочевых камней всех локализаций указывают авторы [6].
В работе [7] указывается, что продолжительность трансуретральной пиелокаликолитотрипсии свыше 60 мин существенно повышает риск развития острого пиелонефрита в послеоперационном периоде. В исследовании [8] также отмечено, что наличие или отсутствие инфекционно-воспалительных осложнений в послеоперационном периоде зависело от времени оперативного вмешательства.
В частности, отмечено, что при продолжительности операции более 120 мин частота возникновения осложнений была выше по сравнению с операциями, длившимися меньше этого времени. Так, послеоперационные осложнения встречались в 11,1% случаев при продолжительности ретроградной нефролитотрипсии до 120 мин и в 37,5% случаев при длительности операции более 120 мин. С другой стороны, исследованиями того же автора выявлено, что у пациентов, имеющих нефростомический дренаж, установленный до или в момент операции, осложнений в виде острого пиелонефрита в послеоперационном периоде отмечено не было. Таким образом, автор [8] предлагает пациентам с повышенным риском развития инфекционно-воспалительных осложнений (крупные коралловидные камни, предполагающие большую длительность операции, наличие микрофлоры в моче больше чем 103 КОЕ/мл) трансуретральную контактную пиелолитотрипсию начинать с установки нефростомического дренажа. Наличие последнего обеспечивает дополнительный отток промывной жидкости, тем самым снижает давление в чашечно-лоханочной системе (ЧЛС), уменьшает риск возникновения пиеловенозных рефлюксов и развития инфекционно-воспалительных осложнений в интра- и послеоперационном периоде.
По данным литературных источников, виды и количество осложнений зависят от длительности проведения контактной трансуретральной литотрипсии. При продолжительности до 120 мин в 11,1% отмечаются различные послеоперационные осложнения. При превышение этого временного порога частота интра- и послеоперационных возрастает до 36,6%.
 Таким образом, напрашивается вывод: снижение времени трансуретральной контактной лазерной пиелокаликолитотрипсии остается весьма актуальной задачей.
Таким образом, напрашивается вывод: снижение времени трансуретральной контактной лазерной пиелокаликолитотрипсии остается весьма актуальной задачей.
Цель исследования. Оценка эффективности предлагаемой методики трансуретральной пиелокаликолитотрипсии с микродренированием по сравнению со стандартной.
Материалы и методы. Основным материалом исследования послужили результаты собственных измерений in vivo «чистого» времени фрагментации конкремента и продолжительности дополнительных временных затрат на промывание области литотрипсии, компенсацию позиционирования лазерного волокна из-за смещения камня в результате ретропульсии и дыхательной экскурсии, а также других дополнительных манипуляций.
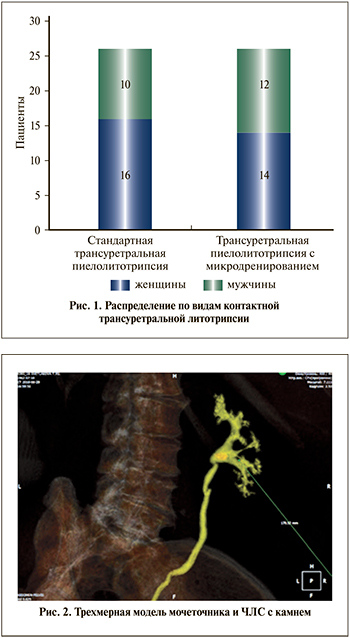
Всего были прооперированы 52 пациента. Одним из критериев включения в исследование стало соблюдение условия одномоментного доступа через мочеточник в ЧЛС. Пациентам, которым потребовалось предварительное стентирование по тем или иным причинам, из наблюдения исключались. Из них 30 женщин и 22 мужчины. Распределение по видам контактной трансуретральной литотрипсии показано на рис. 1.
В предоперационном периоде пациенты проходили КТ мочевыделительной системы. Камни располагались в доступных для ригидного инструмента отделах ЧЛС: лоханка, верхняя чашечка, что прогнозировалось по данным КТ. Объем камня и его средняя плотность определялись на основании КТ-обследования и обработки результатов с помощью программы Inobitec DICOM Viewer Professional. Доступ к камню осуществлялся по стандартной трансуретральной методике с помощью полуригидного уретероскопа (9,5 ш, Karl Storz). Объем камней колебался от 0,065 до 3,28 см3. Средняя рентгенологическая плотность составляла от 390 до 2400 HU. Реальная физическая плотность камня (ρ) рассчитывалась по формуле: ρ=1,539+0,000485×НU [г/см3] на основании рентгенплотности, предложенной в работе [10]. А физическая масса конкремента (m) определялась формулой: m=ρV. Дробление осуществлялось гольмиевым лазером отечественного производства компании Медоптотех, серии Triple с длиной волны лазерного излучения 2,1 мкм и диаметром оптического зонда 600, 400 и 270 мкм. Фрагментация камней выполнялась при энергиях импульсов от 0,6 до 2,5 Дж при частоте импульсов от 5 до 10 Гц.
Литотрипсия проводилась до дисперсного состояния и мелких осколков, которые извлекались в мочевой пузырь. При этом достигнуто полное избавление от камней в 91,2%, что подтверждалось результатами послеоперационного КТ через 3–4 нед.
Временные интервалы отдельных этапов процесса дробления оценивали в группах камней ЧЛС правой (ПП) или левой (ЛП) почки без или с дополнительным микродренированием полости операционного поля с помощью иглы. Чрескожное микродренирование выполняли по комбинированной методике. Вначале пациент проходил КТ с тремя рентген-метками, прикрепленными к коже в углах треугольника, приблизительным центром которого являлась компрометированная почка.
Перед УЗ-пункцией находили оптимальную точку вкола на построенной предварительно на основании данных КТ 3D-модели по следующей схеме. Сначала создавали трехмерную модель на базе бесконтрастной серии, включающую расположение камня, паренхиму почки, близлежащие паренхиматозные и полые органы (печень, селезенка, кишечник), костные структуры (рис. 2)
После этого «совмещали» построенные модели, взятые из разных фаз, в одну. На последней фазе создавалась оптимальная трасса к интересующему месту пункции с учетом «опасных» участков и зон. Далее программным способом устанавливали заранее внедренный макет УЗ-датчика на «кожу» в найденном оптимальном месте по созданной трассе с заранее просчитанными параметрами и углами.
Процедуру 3D-моделирования выполняли в связи с тем, что КТ позволяет получать гораздо более детализированное пространственное изображение по сравнению с УЗИ, детальную индивидуальную анатомию, а также более четкое понимание расположения камня в ЧЛС. Благодаря этому появилась возможность на КТ-модели выявить опасные участки и зоны (кишечник, сосуды, печень, селезенка) и с учетом их строить безопасную трассу. Следует отметить, что сами же производители УЗ-оборудования активно предлагают систему слияния УЗ- и КТ-изображений, однако изображения при этом получаются плоскими, а не объемными, как в нашем случае.
Следующим этапом «переносили» оптимальное положение для пункции с трехмерной модели на пациента. Эта задача решалась путем предварительного вычисления радиусов от трех рентген-маячков до места вкола на коже. Местом входа иглы было общее пространство пересечения этих трех окружностей. Непослоедственно пункцию выполняли под УЗ-контролем по вычисленной предварительно «трассе» иглой 17,5G.
Измерение временных интервалов отдельных этапов процесса дробления осуществлялось путем анализа видеозаписи операции литотрипсии, выполненной эндовидеокамерой типа ENDOCAM® Performance HD, с помощью профессиональной программы редактирования и монтажа видео- и аудиопотоков Sony Vegas 16.0. На временной оси, выведенной на экран персонального компьютера, врач, проводивший литотрипсию, на основе просмотра в специальном окне программы Vegas 16.0 хода операции ставил временные отметки, по которым измерялось время, затраченное на ту или иную процедуру. Измерение временных интервалов выполнялось с точностью до 0,1 с. При измерениях фиксировались энергия Ei и частота следования Fi импульсов литотриптера, диаметр оптоволокна, масса камня m, фактическое чистое время дробления камня Тчф и фактическое общее время литотрипсии Тлтф. Фактическое время дополнительных затрат Тдзф вычислялось как разность между общим временем литотрипсии и чистым временем дробления. Обработка данных осуществлялась с помощью табличного процессора Exel и пакета Statistics Toolbox системы Matlab.
Результаты и обсуждение. В процессе исследований авторами установлено, что на продолжительность дополнительных манипуляций при осуществлении трансуретральной контактной лазерной пиелокаликолитотрипсии (ПКЛТ) существенное влияние оказывают как анатомические особенности оперируемого, так и некоторые физико-химические свойства мочевых конкрементов. Следует заметить, что длительность дополнительных затрат, как и собственно время чистого дробления могут зависеть и от опыта, и от квалификации хирурга.
Дробление мочевых камней в чашечно-лоханочной системе существенно отличается от дробления конкрементов, находящихся в мочеточниках.
К особенностям контактной лазерной литотрипсии в ЧЛС относятся следующие факторы:
1) более сложный и продолжительный по времени доступ к камню;
2) опасность миграции фрагментов в недоступные для ригидного инструмента участки ЧЛС;
3) возможность установки (выведение) оптического зонда зачастую только под острым углом к поверхности камня;
4) когда объем ЧЛС превышает таковой камня, возможна миграция, что приводит к дополнительным затратам времен на репозиционирование уретрореноскопа;
5) возникновение замутнения области литотрипсии в моменты воздействия на камень лазерных импульсов, причем степень замутнения зависит от химического состава камня.
 Возможность установки зонда только под острым углом по отношению к поверхности камня приводит к тому, что не вся энергия лазерного импульса поглощается камнем, так как оптический луч частично «скользит» по поверхности камня. Это приводит к снижению удельной скорости расхода массы камня и дополнительной погрешности расчета чистого времени дробления.
Возможность установки зонда только под острым углом по отношению к поверхности камня приводит к тому, что не вся энергия лазерного импульса поглощается камнем, так как оптический луч частично «скользит» по поверхности камня. Это приводит к снижению удельной скорости расхода массы камня и дополнительной погрешности расчета чистого времени дробления.
Если объем ЧЛС превышает таковой камня, то под действием лазерных импульсов происходит «отскок» камня от световода, т.е. проявляется явление ретропульсии. В связи с этим требуются дополнительные затраты времени, чтобы повторно «выйти» на камень и подвести к нему конец световода.
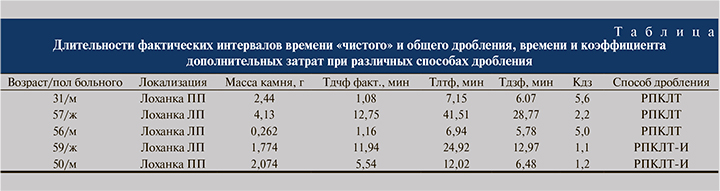
Замутнение, возникающее в момент воздействия лазерного излучения на камень и образования акустической ударной волны, связано с выбросом микрочастиц камня, вспенивающих окружающую камень физиологическую жидкость, образуя непрозрачную эмульсию, которая скрывает камень (рис. 3).
Под «пыльностью» камня подразумевается интенсивность выброса микрочастиц данного конкремента под воздействием лазерных импульсов, которые приводят к образованию мутной субстанции в области литотрипсии. К непыльным относятся твердые камни (оксалаты), к умеренно пыльным – (ураты), к сильно пыльным – (фосфаты).
Перечисленные факторы, способствующие увеличению длительности дополнительных затрат, не могут быть измерены количественно и поэтому относятся к качественным показателям. Учет этих факторов при создании модели прогнозирования длительности пиелокаликолитотрипсии может существенно повысить точность моделирования предстоящего пособия.
На основе проведенных измерений суммарного общего времени пиелокаликолитотрипсии Тлтф, отсчитываемого от момента начала дробления до его завершения, вычислялся коэффициент дополнительных затрат, определяемый отношением фактического времени дополнительных затрат Тдзф и фактического времени, в течение которого происходит собственно разрушение конкремента («чистое» время дробления) Тдчф:
Kдз = (Тлтф – Тдчф) / Тдчф . ( 1 )
Этот коэффициент рассчитывался как для пиелокаликолитотрипсии, осуществлявшейся по традиционной методике, так и по методике с применением микродренирования. В таблице в качестве примера приведена часть данных измерений in vivo фактических Тдчф и Тлтф интервалов времени, затрачиваемых на полное разрушение камня («чистое» дробление) и на необходимые дополнительные действия Тдзф, обеспечивающие процесс фрагментации камня при различных способах его дробления, а также коэффициент дополнительных затрат, вычисленный на основании формулы (1).
В связи с тем, что вид и общая продолжительность дополнительных затрат зависят от ряда случайных факторов, рассмотренных выше, коэффициент дополнительных затрат Кдз представляет собой случайную положительную величину, изменяющуюся от некоторого минимального Kmin до максимального Kmax значения. Обработка полученных при измерениях данных показала, что плотность распределения Kдз может быть аппроксимирована бета-распределением. Последнее, так же как и широко используемое нормальное распределение, задается двумя параметрами – α >0 и β >0. Однако в отличие от нормального, всегда имеющего форму колокола, бета-распределение обладает гораздо большей гибкостью. В зависимости от параметров α и β оно может принимать форму равномерного распределения, вогнутую форму (колодца) или выпуклую, близкую к нормальному распределению.
На основе вычисленного по экспериментальным данным среднего значения коэффициента дополнительных затрат Kдз и стандартного отклонения, а также минимального Kmin и максимального значения Kmax этого коэффициента по формулам, приведенным в [9], определены параметры бета-распределения α и β.
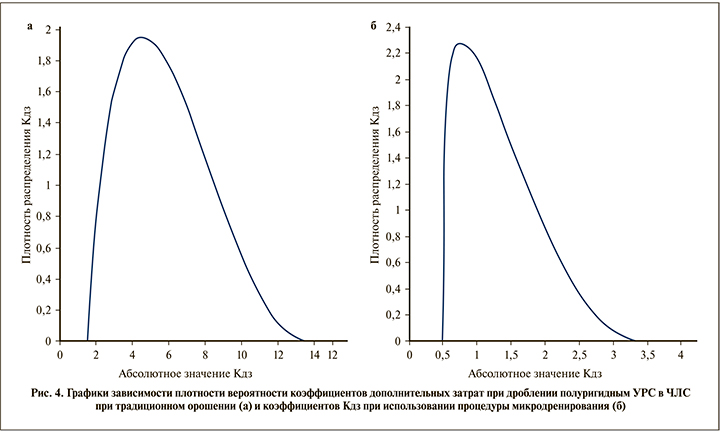
Графики зависимости плотности распределения для действительных значений Kдз при дроблении полуригидным уретерореноскопом в ЧЛС при традиционном орошении и коэффициентов Kдз при использовании процедуры микродренирования показаны на рис. 4а и 4б соответственно. Как видно из рисунков наиболее вероятное значение Кдз при гольмиевой пиелокаликолитотрипсии, выполняемой полуригидным УРС по традиционной методике, равно 4,7, при использовании дополнительного микродренирования наиболее вероятное значение коэффициента дополнительных затрат существенно ниже и составляет 0,8.
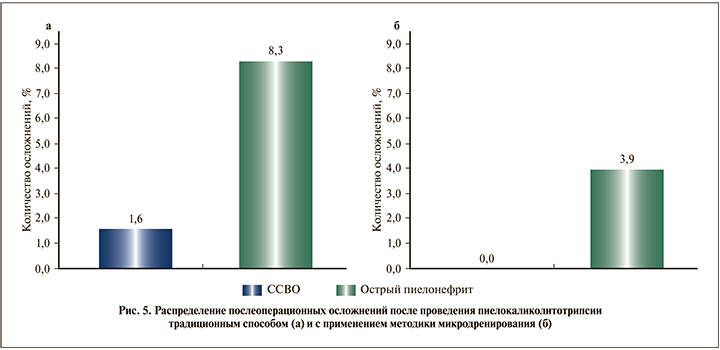
Авторами был произведен анализ группы больных, где выполнялась стандартная трансуретральная ригидная пиелокаликолитотрипсия. При этом было выявлено, что в 1,6±1,2% (p=0.05) случаев отмечался ССВО, клиническими признаками которого были гипертермия, озноб, снижение АД, тахипноэ (пациенты получали стандартную интенсивную терапию в ОРИТ в течении 1–2 сут.). Обострение пиелонефрита отмечено в 8,3±2,7% (p=0.05) случаев, которое потребовало усиления антибактериальной терапии и проведения дезинтоксикационных мероприятий.
У больных, которым выполнялась пиелокаликолитотрипсия с применением методики микродренирования, проявления ССВО отмечено не было, а пиелонефрит возникал у 3,9±1,2% (p=0,05) прооперированных (рис. 5). Статистическую значимость межгрупповых различий средних величин и дисперсий осложнений оценивали при помощи критерия Фишера.
Таким образом, микродренирование значительно улучшает видимость операционного поля и снижает компрессию ЧЛС ирригационным раствором. Через микродренаж также осуществлялась эвакуация пыли от разрушаемого конкремента, благодаря чему уменьшалась вероятность развития лоханочно-почечных рефлюксов, интра- и послеоперационных воспалительных осложнений. После окончания литотрипсии игла удалялась.
Из осложнений в группе с микродренированием отмечено одно контактное кровотечение, купированное консервативно, но приведшее к прекращению литотрипсии из-за плохой видимости. Пациенту потребовался второй этап дробления. Случай не включен в исследование. Из абсолютных противопоказаний можно отметить выраженные коагулопатии.
Заключение. Предложен способ вспомогательного промывания полости дробления, позволяющий сократить время дополнительных затрат при дроблении практически в 4 раза и уменьшить вероятность послеоперационных осложнений. Благодаря этому количество случаев острого пиелонефрита снизилось на 4,4%. Проявления синдрома системного воспалительного ответа в исследуемой группе больных не наблюдалось.



