Введение. В структуре уронефрологических заболеваний особое место отводится мочекаменной болезни (МКБ). По современным данным, МКБ относится к полиэтиологическим заболеваниям [1] и на сегодняшний день известно более 200 факторов риска ее развития [2]. Показатели распространенности МКБ зависят от географических, климатических, диетических и генетических факторов, варьируя в пределах 20–37% [3]. Характерной особенностью МКБ является рецидивирующее течение с активацией системного воспаления, что увеличивает вероятность сердечно-сосудистого риска и ухудшения функции почек [4]. Проведенными исследованиями установлено, что МКБ часто сочетается с ожирением, смешанной дислипидемией и нарушениями пуринового обмена [5]. Данное обстоятельство повышает подверженность пациентов с МКБ риску развития острого инфаркта миокарда и инсульта по сравнению с лицами, не страдающими уролитиазом [6]. Во многих исследованиях отмечено, что число пациентов с МКБ ежегодно растет, и в повседневной практике врачу не раз приходится сталкиваться с данным заболеванием [7]. Согласно отчетам Республиканского медико-информационного центра, в Кыргызской Республике первичную медико-санитарную помощь населению в 2017 г. оказывали 49 центров семейной медицины, 29 центров общеврачебной практики, 718 групп семейных врачей и 1045 фельдшерско-акушерских пунктов. При этом ежегодно к врачам организаций здравоохранения Кыргызской Республики, оказывающим первичную медико-санитарную помощь, осуществляется более 16,5 млн визитов. Растущая популяция пациентов, страдающих МКБ, создает определенные трудности, связанные не только с лечением, но и с постановкой диагноза, а также стратификацией сердечно-сосудистого и нефро-церебрального риска. В публикации А. Б. Батько (2019) отмечено, что на Всемирном конгрессе урологов в Сан-Франциско (1980) были рассмотрены подходы к выявлению МКБ, согласно которым первым шагом является скрининг, вторым – обследование пациентов, обратившихся к врачу со специфичными жалобами [2]. Молекулярные и генетические аспекты формирования МКБ в свете персонализированного подхода к лечению и профилактике уролитиаза активно изучаются [8]. С позиции практической медицины стоит отметить, что оценка функционального состояния почек является необходимым и всесторонним условием при ведении пациентов в амбулаторно-поликлинических условиях. Приняв во внимание этот факт, целью настоящего исследования стал анализ функционального состояния почек и показателей жесткости сосудов у пациентов с мочекаменной болезнью в амбулаторно-поликлинических условиях.
Материал и методы. Набор участников исследования проводился на базе Центра семейной медицины № 7, клинических кафедрах КГМА им. И. К. Ахунбаева и КРСУ им. Б. Н. Ельцина (Бишкек). В исследование были включены 110 пациентов с диагнозом МКБ без признаков обструкции нижних мочевыводящих путей, активного воспаления чашечно-лоханочной системы и болевого синдрома. Средний возраст обследованных пациентов составил 40,4±13,2 года (минимальный взраст – 17 лет и максимальный – 72 года). Женщин было 56 (51%, средний возраст – 40,5±13,6 года), мужчин – 54 (49%, средний возраст – 40,3±12,9 года). Тип исследования – одномоментный и аналитический. При ультразвуковом исследовании почек размер конкрементов составил 2,67 (1,90–3,49) мм. Анализировали рост (см), вес (кг) всех пациентов, а также рассчитывали индекс массы тела (ИМТ, кг/м2) по методу Ketle: ИМТ=масса тела/(длина тела)2 (кг/м2). По общепринятым рекомендациям были выделены пациенты с избыточной массой тела, ожирением. Физическая активность нами была определена как любая ежедневная активность, включающая движения тела, производимые скелетными мышцами и предполагающая расход энергии. У всех участников исследования оценивали содержание мочевой кислоты, кальция, фосфора, магния и общего холестерина сыворотки крови. Повышение содержание общего холестерина >5,01 ммоль/л считали гиперхолестеринемией, фосфора >1,45 ммоль/л – гиперфосфатемией, кальция >2,55 ммоль/л – гиперкальциемией, снижение содержания магния <0,71 ммоль/л – гипомагниемией. С учетом влияния пола на содержание мочевой кислоты крови за гиперурикемию принимали повышение ее концентрации >0,36 ммоль/л для женщин и >0,42 ммоль/л для мужчин. Функциональное состояние почек анализировали по концентрации креатинина и цистатина С в сыворотке крови. Диапазон нормального значения концентрации цистатина C в сыворотке крови составлял 0,40–0,99 мг/л. Расчет скорости клубочковой фильтрации (рСКФ, мл/мин/1,73 м2) проводился по формулам CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration) и MDRD (Modification of Diet in Renal Disease) с использованием креатинина [9] и F. J. Hoek et al. [мл/мин/1,73 м2]=(80,35/цистатин С [мг/л]) – 4,32 [10] – с помощью определения уровня цистатина крови.
Измерение артериального давления (АД, мм рт.ст.) проводили на обеих руках в положении пациента сидя по методу Короткова. Подсчет числа сердечных сокращений (ЧСС) и параметров жесткости сосудов исследовали на приборе «АнгиоСкан-01» в затемненном кабинете после 15-минутного отдыха пациента в утренние часы натощак в удобном сидячем положении с неподвижными кистями с использованием фотоплетизмографических датчиков на концевых фалангах указательных пальцев. За сутки до проведения процедуры исследования жесткости сосудов пациентам было рекомендовано исключить тяжелые физические нагрузки и курение, прием кофеина, алкоголя и других стимулирующих факторов. Оценивали следующие параметры жесткости сосудов: возрастной индекс (AGI, лет), биологический возраст сосудистой системы (VA, лет), индекс жесткости (SI, м/с), индекс отражения (RI, %), индекс аугментации (Alp, %) и альтернативный индекс жесткости (aSI, м/с). В связи с тем, что индекс аугментации (AIp) при росте ЧСС на 10 ударов в среднем уменьшается на 5%, дополнительно у всех пациентов анализировался расчетный индекс аугментации (AIp75, %) – значение AIp, приведенное к пульсу 75 ударов в минуту.
Статистическую обработку результатов исследования проводили с использованием пакета статистических программ Microsoft Excel 2010, Statistica 10.0. Количественные данные, соответствовавшие нормальному распределению, представлены в виде среднего и стандартного отклонений (М±σ), а также медианы и квартилей [Ме (Q25;Q75)]. Качественные показатели приведены в виде абсолютных (n) и относительных (%) частот. Значимость межгрупповых различий оценивалась с помощью t-критерия Стьюдента (для переменных с нормальным распределением) и теста Манна–Уитни (для переменных с непараметрическим распределением). Взаимосвязь между показателями анализировали непараметрическим методом Спирмена. Корреляционные связи признавались достоверными при уровне значимости р<0,05. Уровнем статистической достоверности считалось значение p<0,05.
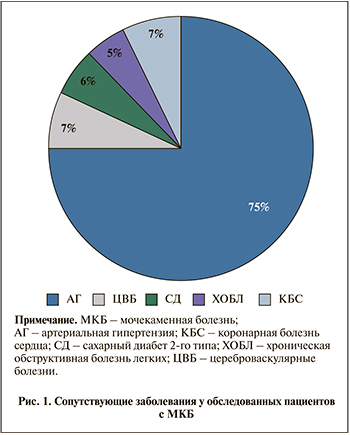
Результаты исследования. В нашем исследовании среди обследованных лиц с МКБ наиболее распространенным сопутствовавшим заболеванием оказалась артериальная гипертензия (рис. 1). Частота встречаемости цереброваскулярных и коронарных болезней сердца (стабильные формы стенокардии) были схожими. Как видно из рис. 1, доля пациентов с СД2 и хронической обструктивной болезнью легких составила 6 и 5% соответственно.
Средние значения и стандартные отклонения клинических и лабораторных показателей исследуемых пациентов отражены в табл. 1. Большинство участников исследования имели гиперхолестеринемию (53,6%) и малоподвижный образ жизни (66,3%). Отдельно следует отметить, что у 47 (42,7%) человек МКБ была верифицирована впервые. Эпизоды почечной колики в анамнезе отмечались у 19 (17,2%) пациентов. В момент обследования наличие курения подтверждено у 45 (40,9%), избыточной массы тела у 18 (16,3%) и ожирения – у 52 (47,2%) лиц с МКБ (табл. 1). При анализе пуринового и минерального обменов гиперурикемия выявлялась у 44,5%, гиперфосфатемия у 39,0%, гиперкальциемия у 26,3% и гипомагниемия у 16,3% участников исследования (табл. 1).

Оценка фильтрационной функции почек показала, что медиана и интерквартильные значение СКФ, рассчитанные с помощью формул CKD-EPI и MDRD, достоверно не различались. Однако, показатель СКФ по методике F. J. Hoek был существенно ниже по сравнению с таковым по формулам CKD-EPI и MDRD (p<0,05).
Дальнейший анализ показал (табл.2 ), что число пациентов с СКФ более 90 мл/мин, т.е. С1 категорией, составляет 73 (66,3%) по CKD-EPI и 58 (52,7%) по F. J. Hoek. Различия оказались достоверными (p<0,05). При этом снижение СКФ легкой степени выявлялено у 21 (19,0%) по CKD-EPI и 33 (30,0%) по методике F. J. Hoek (p<0,05). По CKD-EPI частота умеренного (С3а) и существенного (С3б) снижения фильтрационной функции почек отмечена у 8,1 и 2,7% соответственно. Однако по методике F. J. Hoek категория умеренного (С3а) и существенного (С3б) снижения фильтрационной функции почек составила 10,9 и 3,6%. Доля исследуемых больных С4- и С5-категориями ХБП по формуле CKD-EPI (1,8 и 1,8%) и по методике F. J. Hoek (1,8 и 0,9%) были малочисленным (рис. 2).
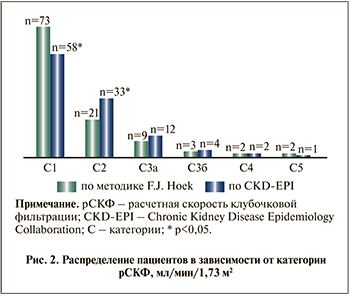
C уетом полученных данных (рис. 2) нами были сформированы две подгруппы пациентов с целью анализа состояния жесткости сосудов. Так, в 1-ю подгруппу (CKD-EPI) включили 55 пациентов с С2- и С3а-категориями снижения СКФ, определенными по методике CKD-EPI, во 2-ю (F. J. Hoek) – 55 пациентов с аналогичными категориями снижения СКФ, но определенными по методике F. J. Hoek.
У пациентов с МКБ с легким и умеренным снижением СКФ по методике F. J. Hoek индекс жесткости и индекс отражения сосудов были достоверно выше по сравнению с таковым у лиц из CKD-EPI (p<0,05). Различий по аугментационному индексу, индексу увеличения при частоте пульса 75 в 1 мин, альтернативному индексу жесткости, возрастному индексу и биологическому возрасту сосудов получено не было.
При проведении корреляционного анализа выявлены взаимосвязи между параметрами жесткости сосудов и расчетной СКФ у лиц с МКБ (табл. 3). Так, отрицательная статистически значимая корреляционная связь выявлена между СКФ (рассчитанной с помощью всех трех формул) и аугментационным индексом. Тесная взаимосвязь отмечена между СКФ по формуле MDRD и показателем индекса увеличения при частоте пульса 75 в 1 мин. Нами получена также достоверная отрицательная связь между снижением расчетной СКФ по методике F. J. Hoek и повышением индексов жесткости и отражения сосудов (табл. 3).
Обсуждение. Амбулаторно-поликлинические условия наблюдения за пациентами МКБ с высоким риском развития почечной недостаточности включают раздел, посвященный тактике регулярной оценки функции почек и стратификации сердечно-сосудистого риска. Результаты исследований последних лет свидетельствуют: изменения в СКФ возможны даже при неосложненном течении МКБ [11]. Установлено, что пациенты со скрытыми формами течения хронической болезни почек (ХБП) имеют высокий риск смертности от сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний (ССЗ) и терминальной стадии почечной недостаточности [12]. Однако эти пациенты могут быть выявлены лишь в том случае, если рассчитывать СКФ с помощью цистатина, а не креатинина крови. Исходя из этого, многие исследователи рекомендуют при начальных стадиях ХБП (диапазоны снижения СКФ менее 40–70 мл/мин/1,73 м2, что ниже порога чувствительности для креатинина) использовать показатель цистатина С [13, 14]. В ранее проведенном исследовании [14] отмечено, что как маркер клубочковой фильтрации креатинин имеет некоторые ограничения. Во-первых, содержание креатинина в организме человека варьируется в зависимости от пола, возраста, мышечной массы, характера питания и лекарственной терапии [15]. Во-вторых, уровень креатинина может не изменяться в случаях, когда большая часть почечной паренхимы не функционирует, и при замедлении клубочковой фильтрации происходит компенсаторное усиление канальцевой секреции креатинина, в результате чего оценка функции почек может быть завышена [16]. В нашем исследовании также продемонстрировано (табл.1), что у пациентов с МКБ медиана СКФ, рассчитанная по методике F. J. Hoek, была достоверно ниже, чем по формулам CKD-EPI и MDRD с использованием креатинина крови. Кроме того, число пациентов с оптимальным уровнем СКФ по цистатину С крови было существенно меньше (рис. 2). Полученные нами данные подтверждает гипотезу, согласно которой на ранней стадии ХБП цистатин как маркер СКФ превосходит креатинин крови.
Биомаркеры снижения функции почек могут иметь дополнительное клиническое значение. Так, повышенный уровень цистатина С считается предиктором ССЗ при ХБП и служит неблагоприятным фактором [17, 18]. У пациентов с МКБ нарушения пуринового и минерального обменов могут повышать общий сердечно-сосудистый риск [19]. Гиперфосфатемия, гиперкальциемия и гиперхолестеринемия не только служат фактором, ассоциированным с формированием уролитиаза, но и увеличивают риск сердечно-сосудистых событий. Мета-анализ W. Luo et аl. (2020), поставивший целью оценить взаимосвязи между МКБ и риском атеросклероза, включил 8 наблюдательных исследований [19]. Так, по результатам исследования установлено, что МКБ связана с повышенным риском развития коронарного и каротидного атеросклероза, причем независимо от уровня сывороточной мочевой кислоты [19]. При ХБП отмечается ускоренное старение сосудов, а повышение ее жесткости может провоцировать нарушение барорецепторной регуляции кровообращения и развитие экстраренальных осложнений [20, 21]. В нашей работе показатели жесткости сосудов, такие как индекс жесткости и индекс отражения, были достоверно выше в подгруппе лиц с легким и умеренным снижением СКФ, вычисленной на основе цистатина С крови (табл. 2). Примечательно, что нами была установлена тесная взаимосвязь между снижением СКФ по методике F. J. Hoek и повышением жесткости сосудов (табл. 3). Вместе с тем показатель аугментационного индекса также был связан с величиной СКФ независимо от способа ее расчета. Структурно-функциональная перестройка сосудов при МКБ получена и в работе A. Fabris et al. [21]. В другом исследовании R. S. Hsi et al. (2016) отмечено наличие связи между числом атеросклеротических бляшек в коронарных артериях и рецидивным течением МКБ [22]. Рецидивирующее течение МКБ способствует кальцификации крупных сосудов и возникновению ССЗ. Объясняется это тем, что нарушение демпфирующей функции магистральных артерий уменьшает кардиальный, церебральный и ренальный кровотоки. Как отмечают исследователи, индекс жесткости (SI, м/с) оценивает скорость пульсовой волны крупных артерий и служит показателем ригидности крупных артерий.
Заключение. Таким образом, полученные данные свидетельствуют о преимуществе определения цистатина С в сыворотке крови для оценки функционального состояния почек и сердечно-сосудистого риска при МКБ. Использование СКФ по методике F. J. Hoek на основе цистатина С у лиц с уролитиазом дает представление о суммарной азотовыделительной функции почек, а также о величине сердечно-сосудистого риска.



