«Нельзя рассматривать больного сквозь узкое окно своей специальности. Необходимо помнить, что организм - единое целое...» Д. Д. Яблоков
Введение. Подавляющее большинство травм почек — это закрытые тупые изолированные и непроникающие повреждения, соответствующие I—III степеням тяжести [1], чаще полученные в бытовых конфликтных и криминальных ситуациях. Ударные сотрясения почки вызывают повреждения анатомической структуры и внутриорганной ангиоархитектоники. Замкнутость системы кровообращения обусловливает тесную взаимосвязь между отдельными ее элементами [2].
В соответствии с общей теорией систем она представляет собой «упорядоченное целостное множество взаимосвязанных элементов, обладающих собственной организацией и структурой» [3]. Поскольку организм — это гомеостатическая, саморегулирующаяся система, его физиологические функции неизбежно должны быть скоррелированы по их количественным характеристикам. Любая часть организма испытывает влияние со стороны других частей и оказывает влияние на них. Результирующая многостороннего постоянного взаимодействия и является непосредственной причиной корреляции биологических структур (компонента организма) разной степени сложности. Другими словами, корреляция функций рассматривается как выражение постоянной составляющей многостороннего взаимодействия [4].
В. П. Казначеевым [5] отмечено, что «процесс самосохранения и саморазвития саморегулирующейся системы в неадекватных условиях среды — это выбор функциональной стратегии, обеспечивающий оптимальное выполнение главной конечной цели поведения биосистем: адаптации». Результаты экспериментов [6], полученные на различных биологических объектах, подтвердили существование следующего эффекта: наибольшую информацию о степени адаптации несут корреляции между физиологическими параметрами. По мнению авторов, корреляционные характеристики намного чувствительнее к адаптационному напряжению, чем абсолютные величины параметров организма. Сами физиологические параметры могут варьироваться в широких пределах, а приспособительный эффект наблюдается в системе взаимосвязей между ними. Основанный на этом подход к изучению адаптации и его практическое применение названы корреляционной адаптометрией — методом косвенной оценки состояния исследуемой группы пациентов по средней величине коэффициентов корреляций между разными числовыми показателями, характеризующими состояние организма [7]. При увеличении адаптационной нагрузки уровень корреляций повышается, а в результате успешной адаптации снижается.
Цель исследования: оценка взаимодействия ренальных функций и гемодинамического гомеостаза методом корреляционной адаптометрии в группах, пострадавших от закрытой травмы почки с разной площадью повреждения органа.
Материалы и методы. Обследованы 114 пострадавших в возрасте от 18 до 40 лет, проходивших консервативное лечение с изолированными комоционными повреждениями почек Grade-I—III [1] с вовлечением одного сегмента органа - 30 (26,0%), двух сегментов - 26 (22,8%), 3 сегментов - 58 (51,2%), в течение 10 сут. с момента получения травмы.
Для разделения пострадавших на группы проводили ультрасонографическое полипозиционное исследование на аппарате GE Healthcare Vivid-7 (США) экспертного класса с использованием высокочастотного (частота до 5МГц) конвексного датчика. Эхографическую оценку ведущих очаговых изменений при травме почки осуществляли на основании морфодинамических стереотипов, прямых и косвенных признаков травм, «гиперэхогенного паттерна» [8].
Выполняли радионуклидное исследование - статическую и динамическую нефросцинтиграфию на гамма-камере NB-9100 (Венгрия) с компьютерной системой обработки информации СЦИНТИРО© по стандартной методике [9]. При статической сцинтиграфии использовали тубулотропный радиофармпрепарат (РФП), 99мТс технемек в дозе 80-100 МБк, вводимый внутривенно. По сцинтиграммам оценивали положение, форму, размер, контуры почек, интенсивность и равномерность включения РФП в их паренхиму. Количественный анализ данных проводили на основании включения РФП в почки (референтные значения 50±5%).
При динамической нефросцинтиграфии использовали технеций-99т (Tc-99m) - диэтилтриаминопентоацетат (Пентатех, Диамед) объемной активности 370 МБк. Методика позволяет получать количественные данные в относительных цифрах: кровенаполнения сосудистого русла почки (физиологические референтные значения - 50±5%) - непрямая ангиография; клубочковой фильтрации (СКФ) для корректного сопоставления с гемоперфузией почки в % - динамическая нефросцинтиграфия. Для выявления реноваскулярных нарушений на основании оценки скорости перемещения индикатора по нефрону [10, 11] использовали РФП меркаптоацетилглицерин (МАГ-3), меченный Tc-99m, в дозе 74-148 МБк. Устанавливали индекс времени перемещения радиоиндикатора в паренхиме (Parenchymal transit time index, PTTI, физиологический норматив <156 с) и среднее время перемещения в паренхиме (Mean parenchymal transit time, MPTT, физиологический норматив 270 с).
Изучение гемодинамического гомеостаза по характеру интегральных показателей центрального кровотока, которые отражают состояние системы в целом, выполнено методом тетраполярной реографии на комплексе функциональной диагностики «Рео-Валента» с оценкой артериального давления (АД): систолического, диастолического, среднединамического; сердечного (СИ) и ударного (УИ) индексов, характеризующих сердечную составляющую; общего периферического сопротивления (ОПС) - сосудистой составляющей.
Адаптационный потенциал определяли на основании данных, полученных при тетраполярной реографии. Расчет индекса функционального напряжения (ИФН, в абс. значениях) выполнялся созданной компьютерной программой [12], где ИФН соизмеряет волновые характеристики сердечно-сосудистой системы по интегративному показателю сопряженного сдвига систолического АД и ЧСС в системе координат. Полученные результаты анализировали с учетом градаций: ИФН=0,0-2,1 - удовлетворительная адаптация (имеются достаточные функциональные возможности [ФВ] организма, гомеостаз поддерживается при минимальном напряжении регуляторных систем); ИФН=2,2-3,3 - напряжение механизмов адаптации (ФВ не снижены, гомеостаз поддерживается напряжением регуляторных систем); ИФН=3,3-4,3 - неудовлетворительная адаптация (ФВ снижены, гомеостаз сохранен при значительном напряжении регуляторных систем); ИФН >4,3 - срыв адаптации (резкое снижение ФВ, гомеостаз нарушен) [13].
В работе использовано 1254 результата физиологических показателей гомеостаза, объединенных в 11 групп.
Оценка сопряженности анализируемых параметров проведена на основе корреляционного анализа созданной компьютерной программой [14]. Устанавливали количество достоверных корреляционных связей в общем числе рассмотренных коэффициентов корреляции и степень выраженности этих связей. Степень связанности параметров оценивали с помощью корреляционного графа, рассчитываемого как сумму весов его ребер (сумма соответствовавших коэффициентов парной корреляции):

где rj — коэффициенты корреляции между i-м и j-м. Принимались во внимание только достоверные коэффициенты корреляции, значения которых больше или равны 0,5 [15].
Результаты. Оценку полученных результатов обследования пострадавших проводили в несколько этапов. На первом этапе устанавливали динамику ренальных и гемодинамических показателей.
Данные радиоизотопных исследований представлены в табл. 1.
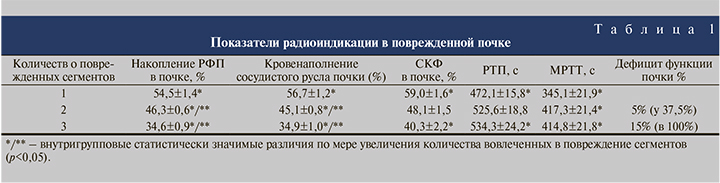
Как свидетельствуют данные табл. 1, с увеличением количества поврежденных сегментов почки совокупно регрессируют основные физиологические параметры органа с нарастанием функционального дефицита.
Результаты изучения гемодинамических показателей приведены в табл. 2.
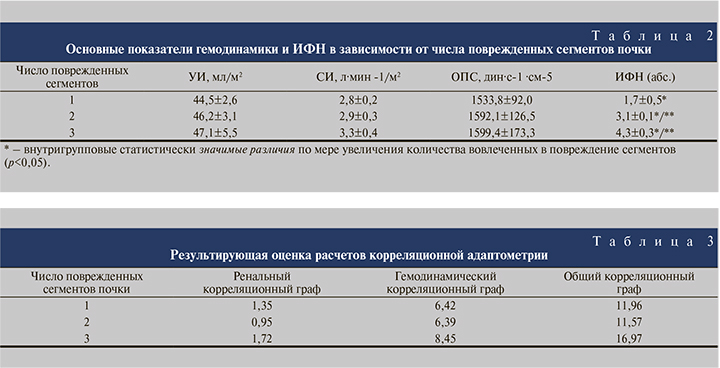
Представленные в таблице данные демонстрируют снижение функциональных возможностей организма по результирующей величине гемодинамических показателей (ИФН): с удовлетворительной адаптации (при травмировании одного сегмента почки); напряжением механизмов адаптации (два сегмента); до неудовлетворительной адаптации (три сегмента), когда гомеостаз сохранен при значительном напряжении регуляторных систем.
На втором этапе проводили корреляционную адаптометрию. Степень скоррелированности параметров кровоснабжения и мочеобразования скомпрометированной почки указаны в табл. 3.
Приведенные в таблице данные свидетельствуют: закономерности изменения суммарной величины взаимосвязей между показателями зависят от количества вовлеченных в травматический процесс сегментов почки. Корреляционный граф — степень связанности («жесткости» соподчинения) анализируемых параметров, он может количественно оцениваться достаточно монотонно в случаях травмы одного и двух сегментов почки. При повреждении трех сегментов органа вес корреляционного графа резко увеличивается, что свидетельствует о выраженных структурных и функциональных дезадаптивных нарушениях в деятельности органа. Аналогичная тенденция прослеживается и в гемодинамической системе организма. Совокупную их взаимосвязь резюмирует общий корреляционный граф.
Обсуждение. В настоящее время вопросы кровоснабжения почки рассматриваются с позиций ее сегментарного строения. Понятие «почечный сегмент» впервые введено в 1956 г. F. T. Graves [16]. Под сегментом почки понимают ее участки с обособленной системой кровоснабжения и мочеотведения. Большинство авторов выделяют пять почечных сегментов: верхнеполюсной, верхний впередилоханочный, нижний впередилоханочный, позадилоханочный и нижнеполюсной. Аксиомой служит следующий факт: артерии почки между собой не анастомозируют и кровоснабжают самостоятельный сегмент органа. Понятие о биологической структуре невозможно рассматривать в отрыве от регуляторной сущности взаимодействующих элементов. В наших исследованиях установлено, что с увеличением количества вовлеченных в повреждение сегментов почки взаимообусловленность процессов микроциркуляции и мочеобразования увеличивается.
1. Selye [17] в универсальной концепции стресса указывал: «адаптационный синдром сам по себе не является патологической реакцией; наоборот, это необходимая физиологическая реакция на повреждение, имеющая защитный характер». Реакция на нарушение гомеостаза является системным процессом и обеспечивается, во-первых, системой (почка), специфически реагирующей на раздражитель (травма), и во-вторых, неспецифическими стресс-реализующими системами: симпатоадреналовой и гипоталамо-гипофизарно-адренокортикальной [18]. Степень напряжения регуляторных механизмов определяется вегетативным гомеостазом [16]. Согласно концепции системной регуляции, возможно определить «физиологическую цену» каждой целенаправленной реакции организма по характеру центрального кровотока. Замкнутость системы кровообращения обусловливает тесную взаимосвязь отдельных ее элементов [19].
Кардиоренальные взаимоотношения в условиях физиологической нормы впервые представлены A. С. Guyton в 1972 г. [20] в виде компьютерной гемодинамической модели, где расчет основан на регуляции артериального давления и сердечного выброса. Методы исследования этих центральных механизмов сердечно-сосудистой системы лежат в основе оценки степени напряжения регуляторных механизмов и функциональных резервов организма человека [21].
Заключение. По выражению K. J. Rothaman et al. [22]: «статистически значимые корреляции — это конечный этап доказательности». Установленные в ходе настоящего исследования корреляционные графы отражают общие структурные свойства систем почки и организма во взаимодействии их отдельных элементов при тупой травме. Организм подключает дополнительные ресурсы, обеспечивая восстановление морфофункциональных параметров почки. При этом наиболее чувствительны к изменению адаптационного напряжения не непоседственно показатели, а степень их взаимосвязи. С возрастанием напряженности адаптационных процессов возрастает величина веса корреляционных графов. Оценка сопряженности показателей ренального и организменного взаимодействия свидетельствуют о наибольшем напряжении резервов функционального потенциала при повреждении трех сегментов почки. Функциональные перестройки, приводящие к истощению адаптационных процессов, диктуют необходимость проведения реабилитационных и профилактических мероприятий в ближайшем посттравматическом периоде.



