Симптомы нижних мочевыводящих путей (СНМП) часто встречаются в мужской популяции, особенно в пожилом возрасте [1, 2]. При этом доброкачественная гиперплазия предстательной железы (ДГПЖ) является частой причиной развития СНМП у данной категории пациентов [3, 4]. Важно отметить, что степень выраженности СНМП не всегда связана только с ДГПЖ и не всегда коррелирует с объемом предстательной железы [5–7].
На основе современных эпидемиологических данных известно, что примерно у 25% мужчин в популяции развивается ДГПЖ/СНМП [8]. По данным О. И. Аполихина и соавт., в России более 13 млн мужчин могут страдать данным заболеванием [9]. Распространенность СНМП зависит от возраста мужчин: от 14% в 40–49 лет до 40–60% и более в 60–69 лет и позднее [10]. Актуальность данной проблемы подчеркивается значительными темпами старения населения, что характерно как для стран Европы и Америки, так и для России [11]. Следовательно, в ближайшем будущем ожидается увеличение количества пациентов в популяции, страдающих ДГПЖ/СНМП, что делает эту тему еще более важной.
Актуальные научные данные об изучении ДГПЖ основываются на всесторонних фундаментальных исследованиях. В результате ряда проведенных исследований была сформирована концепция Isaacs и Coffey, согласно которой по мере взросления мужчины ДГПЖ в своем развитии проходит последовательные стадии микро- и макроскопических изменений, которые впоследствии переходят в стадию клинических проявлений [11, 12]. Данные многочисленных исследований показывают, что патофизиологический процесс формирования ДГПЖ является многофакторным, при этом одна из главных причин заболевания – изменения гормонального фона у мужчин в процессе старения [13, 14].
Возможности современной медикаментозной терапии СНМП включают альфа-адреноблокаторы, ингибиторы 5-альфа-редуктазы, ингибиторы фосфодиэстеразы 5-го типа, значительно реже – агонисты бета-3-адренорецепторов, антагонисты мускариновых рецепторов [15, 16]. Согласно данным канадского эпидемиологического исследования [17], препараты группы альфа-адреноблокаторов назначаются чаще всего (70%), ингибиторы 5 альфа-редуктазы – в 27% случаев, фитотерапия – в 2%, а М-холиноблокаторы только в 3% случаев медикаментозной терапии. При этом монотерапия используется намного чаще, чем терапия препаратами из нескольких фармакологических групп (88 и 12% соответственно, р<0,001).
В европейских странах монотерапия альфа-адреноблокаторами, по данным различных исследований, применяется у 60–90% больных, а ингибиторы 5 альфа-редуктазы – у 10–15% пациентов [18].
Как уже было отмечено, относительный риск появления СНМП при ДГПЖ возрастает прямо пропорционально возрасту мужчины, что также связано с угасанием эндокринной функции и развитием состояния дефицита эндогенного тестостерона (возрастного гипогонадизма) в процессе старения, что в свою очередь требует соответствующей и своевременной медикаментозной коррекции.
В результате проведения ряда пилотных исследований было показано, что тестостерон-заместительная терапия положительно влияет на выраженность и течение СНМП у пациентов с возрастным андрогенным дефицитом [19–23]. Данные демонстрировали сильную отрицательную корреляционную связь между уровнями сывороточного тестостерона (свободного и биодоступного) и выраженностью простатических симптомов, оцененных по международной шкале IPSS (International Prostate Symptom Score). На этой основе и была выдвинута гипотеза о влиянии сывороточного уровня тестостерона на развитие и выраженность СНМП. Данное влияние тестостерона и его метаболитов патофизиологически можно объяснить их действием на альфа-адренорецепторы, фосфодиэстеразу-5 (ФДЭ-5), си-стему Rho-киназы и эндотелин, а также синтазу оксида азота (NO-синтазу), эффекты которых, в свою очередь, являются андроген-зависимыми [24].
Синтаза оксида азота (NO-синтаза) подробно изучена у мужчин, и доказано ее наличие в нижних отделах мочевыводящих путей. Кроме того, ряд исследований показал, что ее активность является наибольшей в простатическом сегменте уретры, в шейке мочевого пузыря и меньшей – в детрузоре [19, 20]. Вероятно, что оксид азота может являться одним из важнейших триггеров в расширении шейки мочевого пузыря при акте мочеиспускания [11]. Половая и мочевыделительная системы мужчины взаимосвязаны эмбрионально и анатомически. Тестостерон координирует активность синтазы оксида азота в кавернозной ткани, регулируя механизм эрекции путем влияния на синтазу оксида азота и фосфодиэстеразу-5, а его действие на ткани нижних мочевыводящих путей можно объяснить подобным образом в связи с наличием таких же ферментов и рецепторов к андрогенам в данных структурах [19, 20, 24].
В случае же эндогенного дефицита тестостерона необходимо проведение заместительной гормональной терапии для его восполнения до средненормальных значений, что в настоящее время считается обоснованной формой терапии возрастного гипогонадизма и, следовательно, лечением и профилактикой связанных с этим состояний и заболеваний [11, 23, 25, 26]. Таким образом, применение препаратов экзогенного тестостерона является обоснованным в случае недостаточности эндогенного тестостерона у пациентов с СНМП при доброкачественной гиперплазии предстательной железы.
Настоящее наблюдательное исследование было проведено для получения дополнительных данных об эффективности и безопасности применения препарата Андрогель®, геля для наружного применения (Безен Хелскеа СА, Бельгия), у мужчин с недостаточностью эндогенного тестостерона и СНМП при доброкачественной гиперплазии предстательной железы.
Материалы и методы. Проведено многоцентровое проспективное сравнительное неинтервенционное исследование «ПОТОК», посвященное анализу данных наблюдений за пациентами старше 50 лет с лабораторно подтвержденной недостаточностью эндогенного тестостерона (утренняя концентрация общего тестостерона <12,1 нмоль/л) и СНМП (8–19 баллов по шкале IPSS) при доброкачественной гиперплазии предстательной железы в рутинной клинической практике. Условием для проведения данного исследования являлось одобрение Межвузовского комитета по этике (выписка из протокола № 2 от 17.02.2022). Все процедуры в рамках исследования выполнялись в точном соответствии с протоколом и являлись рутинными, т.е. выполняемыми в ежедневной рутинной клинической практике лечебных учреждений, принимавших участие в исследовании, что определило наблюдательный (неинтервенционный) характер исследования.
С февраля по июнь 2022 г. в 40 профильных клиниках России в исследование были включены 500 пациентов в возрасте старше 50 лет. В зависимости от получаемой терапии все пациенты были распределены на две группы. Решение врача о назначении пациенту того или иного препарата (согласно утвержденным инструкциям по медицинскому применению), а также о тактике дальнейшего наблюдения и лечения принималось до включения пациента в исследование и независимо от него. Пациенты первой группы (250 мужчин) получали терапию альфа-адреноблокаторами и препаратом Андрогель®, пациенты второй группы (250 мужчин) – альфа-адреноблокаторами без тестостерон-заместительной терапии (ТЗТ). Набор пациентов в исследование велся в медицинских центрах в соответствии с утвержденными протоколом критериями включения и невключения.
Критерии включения пациентов в исследование:
- Мужчины старше 50 лет с лабораторно подтвержденной недостаточностью эндогенного тестостерона (утренняя концентрация общего тестостерона <12,1 нмоль/л);
- Наличие симптомов нижних мочевыводящих путей (8–19 баллов по шкале IPSS) при доброкачественной гиперплазии предстательной железы (объем предстательной железы > 25 см3);
- Сохранение сексуальной активности или желание ее восстановления;
- Решение врача о назначении препаратов α-адреноблокатора или α-адреноблокатора+Андрогель® до момента включения пациента в исследование;
- Желание и способность пациента подписать и датировать письменное информированное согласие об участии в исследовании до включения в исследование.
Критерии исключения пациентов:
- Рак простаты, оперативные вмешательства в период проведения исследования;
- Появление в ходе исследования любых заболеваний или состояний, которые ухудшают прогноз пациента, а также делают невозможным дальнейшее участие пациента в исследовании;
- Нарушение протокола исследования, ошибочное включение пациента, не соответствующего критериям включения и/или соответствующего критериям невключения;
- Отказ пациента от участия в исследовании;
- Нежелательное явление (НЯ), требующее отмены исследуемого препарата.
Критерии невключения пациентов в исследование:
- Противопоказания к применению препаратов α-адреноблокаторов и/или Андрогель® в соответствии с инструкцией по применению препарата;
- Наличие показаний к оперативному лечению доброкачественной гиперплазии предстательной железы;
- Инфекции нижних мочевыводящих путей;
- Неврологические заболевания, сопровождающиеся СНМП;
- Пациенты, ранее включенные в данное исследование, но выбывшие по какой-либо причине;
- Прием α-адреноблокаторов менее чем за 1 мес. и/или андрогенных препаратов менее чем за 6 мес. до включения в исследование;
- Любые клинические состояния, которые, по мнению врача-исследователя, противоречат критериям включения, могут стать причиной досрочного прекращения участия пациента в исследовании или затруднят трактовку результатов последнего.
Медицинское наблюдение за пациентами в рамках исследования проводили в течение 6 мес. Визит включения пациента в исследование осуществлялся в любой день, который в соответствии с рутинной клинической практикой центра был оптимален для оценки состояния пациента и последующего назначения соответствующей терапии. После принятия решения о назначении препаратов альфа-адреноблокаторов и препарата Андрогель® или альфа-адреноблокаторов без тестостерон-заместительной терапии врач предлагал пациенту принять участие в исследовании, подписав информированное согласие. После оценки соответствия критериям включения и невключения пациенту проводили все необходимые процедуры в соответствии с протоколом исследования и пациент начинал принимать назначенную терапию. Доза назначенных альфа-адреноблокаторов и их выбор определялись врачом в индивидуальном порядке в соответствии с рутинной клинической практикой, медицинскими стандартами и утвержденными инструкциями по медицинскому применению препаратов. Визиты последующего наблюдения – визит 2 и визит 3 – проводили через 3 и 6 мес. терапии. После прохождения визита 3 пациент завершал участие в исследовании и далее наблюдался врачом в соответствии с принятыми медицинскими стандартами.
В рамках включения больного в исследование и проводимых визитов выполняли следующие процедуры: сбор демографических и антропометрических данных, значимого медицинского анамнеза; физикальное обследование; оценка утренней концентрации общего тестостерона и общего простатического специфического антигена (ПСА) в сыворотке крови, уровня СНМП по шкале IPSS, симптомов андрогенного дефицита по шкалам AMS и симптомов дисфункции по шкале IIEF; ультразвуковое исследование предстательной железы; урофлоуметрия (оценка максимальной скорости потока мочи, суммарного объема мочеиспускания); УЗИ мочевого пузыря через <15 мин после окончания урофлоуметрии (с целью определения объема остаточной мочи); оценка сопутствующей терапии и нежелательных явлений.
Главным критерием оценки эффективности (первичная конечная точка) проводимой терапии являлась выраженность СНМП по международной шкале оценки простатических симптомов (IPSS) через 3 и 6 мес. лечения. Вторичные критерии оценки эффективности (в динамике лечения через 3 и 6 мес.): изменение симптомов по шкалам AMS и IIEF, показатели урофлоуметрии, объем предстательной железы и остаточной мочи по данным УЗИ. Безопасность оценивалась по общему количеству у пациентов нежелательных явлений, стратифицированных по тяжести и частоте.
Анализ полученных данных имел исследовательский и описательный характер, проводился с использованием релевантных методов статистики (параметрических или непараметрических критериев для тестирования статистических гипотез с учетом типа и характера изучаемых переменных) в программе IBM SPSS Statistics 26.0. При тестировании гипотез (оценке имеющихся различий между группами) применялся двусторонний 5%-ный уровень значимости.
Результаты и обсуждение. Исследуемые группы пациентов изначально оказались неоднородными по ряду антропометрических, демографических и анамнестических данных (табл. 1). На момент включения в исследование средние показатели массы тела, индекса массы тела (ИМТ), окружности талии и бедер значимо преобладали в группе 1 по сравнению с группой 2 (p<0,05). Однако в процессе проводимого лечения была выявлена динамика в уменьшении этих показателей в группе 1 через 3 и 6 мес. терапии, что фактически привело к выравниванию средних значений переменных между группами пациентов на визитах 2 и 3 до отсутствия статистических различий между ними (p>0,05). Анализ анамнеза ДГПЖ у пациентов показал преобладание длительности ДГПЖ/СНМП у пациентов, распределенных в группу 1 – 19 [4–47] мес. – по сравнению с 11 [2–35,5] мес. в группе 2; p<0,05. По показателям возраста, роста, СНМП, применяемым препаратам альфа-адреноблокаторов и ряду сопутствовавших заболеваний исследуемые группы пациентов значимо не различались между собой (p>0,05).
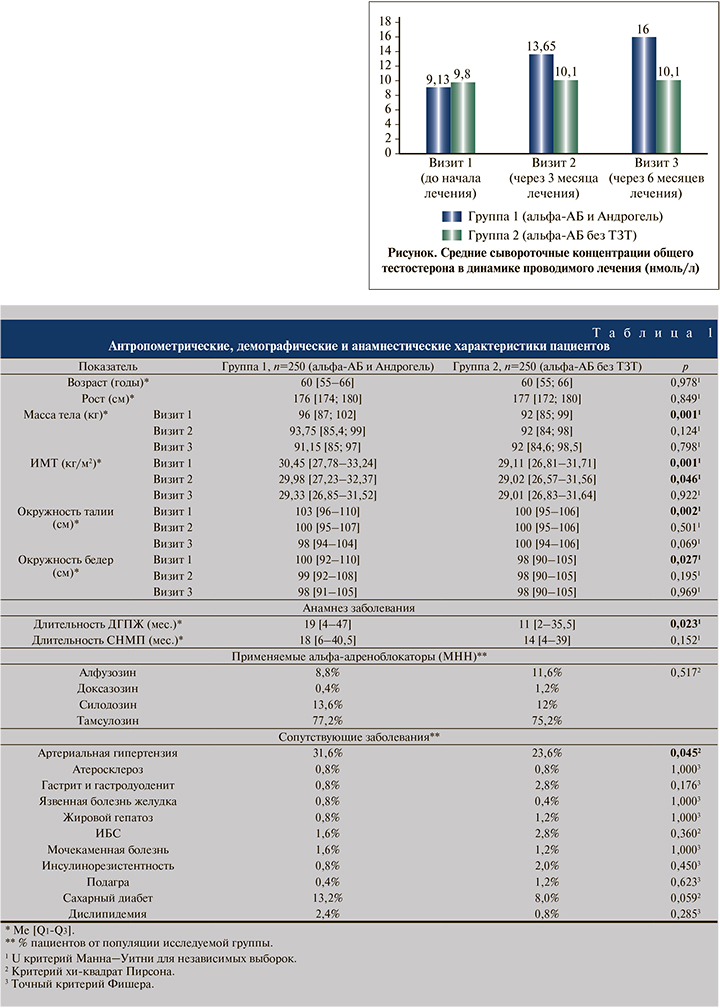
На момент начала исследования средние сывороточные концентрации общего тестостерона были значимо меньшими в группе 1 по сравнению с группой 2: 9,13 и 9,80 нмоль/л соответственно; p<0,001 (см. рисунок). Однако в динамике проводимой терапии данный показатель продемонстрировал значительный рост в группе 1 и превзошел аналогичный показатель в группе 2 через 3 мес. (13,6 и 10,10 нмоль/л; p<0,001) и 6 мес. (16,0 и 10,10 нмоль/л; p<0,001) проводимого лечения, что безусловно связано с действием препарата Андрогель® в терапии пациентов группы 1. Концентрация тестостерона в группе 2 в динамике наблюдения достоверно не изменялась.
Анализ показателя простатспецифического антигена (ПСА) выявил отсутствие значимых различий между группами 1 и 2 как на момент начала исследования 1,90 [1,26–2,80] и 1,96 [1,20–2,80] нг/мл (p=0,373), так и в динамике проводимой терапии: через 3 мес. – 1,90 [1,40–2,50] и 1,90 [1,21–2,55] нг/мл (p=0,968), через 6 мес. – 1,85 [1,40–2,40] и 1,90 [1,40–2,70] нг/мл (p=0,363) в исследуемых группах соответственно. Следовательно, на основании полученных данных можно сделать вывод об отсутствии влияния (высоком профиле безопасности) краткосрочной тестостерон-заместительной терапии препаратом Андрогель® на показатель ПСА у пациентов с СНМП и ДГПЖ, что также согласуется с выводами ранее опубликованного мета-анализа [27].
По первичному критерию оценки эффективности (выраженность СНМП по шкале IPSS) изначально исследуемые группы пациентов достоверно не различались (по 15 [13–17] баллов в каждой группе, p=0,256), табл. 2. Однако в динамике проводимого лечения были выявлены значимые различия в группах 1 и 2 через 3 мес. – 11 [8–13] и 12 [9–15] баллов, p=0,009, и через 6 мес. терапии – 9 [7–11] и 11 [7–14] баллов соответственно, p<0,001.
Средние значения индекса качества жизни: на визите 1 и 2 – без значимых различий между группами (p>0,05), тогда как на визите 3 данный показатель определялся как значимо меньший в группе 1 по сравнению с группой 2: 2 [1–3] и 3 [2–3] балла соответственно (p<0,001). Данные анализа первичной конечной точки исследования свидетельствуют о значимо большей эффективности терапии СНМП при ДГПЖ альфа-адреноблокаторами и препаратом Андрогель® по сравнению с монотерапией альфа-адреноблокаторами. Эти данные согласуются с ранее обсуждаемыми гипотезами о возможностях ТЗТ способствовать облегчению СНМП у пациентов с гипогонадизмом и ДГПЖ [28–31].
По степени выраженности симптомов андрогенного дефицита, оцененной по шкале возрастных симптомов андрогенного дефицита мужчины (Aging Male Screening, AMS), на момент начала исследования пациенты 1 и 2 групп не различались: 41 [36–48] и 41 [33–48] балл соответственно (p>0,05), табл. 2. Однако данные показатели продемонстрировали более значимое снижение в группе 1 по сравнению с группой 2 в динамике проводимой терапии через 3 мес. (35 [28– 39] и 38 [31–46] баллов, p<0,001) и 6 мес. (28 [24–35] и 36 [30–45], p<0,001). Результаты говорят в пользу большей эффективности комплексной терапии СНМП при ДГПЖ с включением ТЗТ препаратом Андрогель®.
Анализ международного индекса эректильной функции (шкала МИЭФ, IIEF) показал, что на момент начала применения назначенное терапии группа 1 либо была сопоставимой с группой 2 (по доменам «оргазмическая функция», «удовлетворение половым актом»; p>0,05), либо показатели группы 1 демонстрировали значимо более низкие значения по сравнению с группой 2 (по доменам «эректильная функция», «сексуальное желание (либидо)», «общее удовлетворение»; p<0,05), табл. 2. Изучение данных показателей в динамике терапии выявило, что группа 1 превосходила группу 2 по всем изучаемым доменам международного индекса эректильной функции через 3 и 6 мес. лечения. Следовательно, полученные данные шкалы МИЭФ, группа пациентов, получавших препарат Андрогель® в комплексной терапии СНМП, показали преимущество перед монотерапией альфа-адреноблокаторами в плане улучшения сексуальной функции.
Изучение показателей урофлоуметрии и УЗИ (максимальная скорость потока мочи, объем выделенной и остаточной мочи) показали отсутствие значимых различий между исследуемыми группами на момент начала исследования (p>0,05), табл. 3. Через 6 мес. терапии в группе 1 было выявлено большее значение максимальной скорости потока мочи и меньший объем остаточной мочи по сравнению с аналогичными показателями группы 2: 16 [14,9–20] и 15,2 [13–18] мл/c (p=0,004), 10,0 [0,0–20,0] и 15,5 [5,0–30,0] мл (p=0,004).

Объем предстательной железы, оцененный при проведении УЗИ, составил 43,9 [35,0–54,5] и 44,4 [37,0–56,0] см3 в группах 1 и 2 на момент начала применения исследуемой терапии, p>0,05. Через 6 мес. лечения данный показатель значимо уменьшился в группе пациентов 1, получавшей ТЗТ в комплексе с альфа-адреноблокаторами, по сравнению с группой 2 – 39,5 [32,5–48,0] и 43,3 [36,1–54,0] см3 соответственно, p=0,002.
Вопрос о связи между уровнем тестостерона и объемом предстательной железы длительное время оставался контроверсионным. Однако результаты недавних исследований продемонстрировали обратную корреляцию между этими показателями – коррекция возрастного гипогонадизма препаратами ТЗТ и достижение адекватного уровня тестостерона могут способствовать уменьшению воспалительной реакции в простате и ее объема, а также снизить риск прогрессирования ДГПЖ [32]. Результаты, полученные в ходе текущего исследования, соотносятся с международными данными, что говорит о целесообразности применения препарата Андрогель® в популяции пациентов с недостаточностью эндогенного тестостерона и СНМП при доброкачественной гиперплазии предстательной железы.
За время исследования было выявлено 18 НЯ легкой степени, 2 НЯ средней и 1 НЯ тяжелой степеней без значимых различий между группами (p>0,05), табл. 4. Все выявленные НЯ были ожидаемыми, описанными в действующих инструкциях по медицинскому применению лекарственных препаратов.
Гипогонадизм и ДГПЖ/СНМП считаются логичным и многоэтапным проявлением процесса старения у мужчин. Однако в связи с неблагоприятным влиянием данных состояний на качество жизни пациентов и их соматического здоровья изучению этого вопроса уделяется особое внимание. Этой теме посвящено множество отечественных и зарубежных работ, с которыми согласуются результаты нашего исследования «ПОТОК» [33–36]. Очевидным является тот факт, что ДГПЖ и связанные с ней СНМП представляют собой клинические состояния, часто наблюдаемые у пациентов с гипогонадизмом [33]. Хотя сильная корреляционная связь этих состояний на данный момент не вызывает сомнений, но патогенетические механизмы, лежащие в ее основе, по-прежнему являются не до конца понятными и изученными [34], что требует дальнейшего всестороннего исследования.
На данном этапе изучения проблемы гипогонадизма является очевидным, что восстановление сывороточных концентраций тестостерона препаратами ТЗТ до средне-нормальных значений у пациентов с ДГПЖ/СНМП демонстрирует значимую клиническую эффективность, оцениваемую по ряду валидированных шкал (IPSS, AMS, IIEF) и по показателям урофлоуметрии (максимальная объемная скорость и объем остаточной мочи) [33, 35, 36]. При этом влияние тестостерона на предстательную железу по-прежнему служит предметом дискуссий: в нашем исследовании было показано, что в динамике проводимой терапии с препаратом Андрогель наблюдется значимое уменьшение среднего объема предстательной железы, тогда как в ранее проведенном исследовании А. А. Камалова и др. [33] было показано увеличение этого параметра при одинаковой продолжительности проводимой терапии. Однако с учетом того, что достоверная связь интенсивности роста предстательной железы и концентрации тестостерона была не доказана большим числом ранее проведенных исследований, этот вопрос по-прежнему остается открытым. При этом уровень простатического специфического антигена (ПСА) не изменялся в динамике проводимой ТЗТ как в рамках нашего, так в ряде других ранее проведенных исследований [35, 36]. С учетом этих данных с уверенностью можно говорить о безопасности применяемой ТЗТ препаратом Андрогель у пациентов с гипогонадизмом и ДГПЖ/СНМП.
Актуальным остается вопрос относительно продолжительности ТЗТ: требуется ли ее курсовая или пожизненная схема применения? На основании результатов нашей работы является очевидным, что необходимо как минимум достаточно продолжительное время (не менее 6 мес.) до появления значимых результатов эффективности терапии, оцениваемых по параметрам качества мочеиспускания пациентов. Ряд ранее опубликованных работ сообщает, что последующая отмена ТЗТ приводит к откату (ухудшению) достигнутого состояния до первоначальных значений, при этом возобновление терапии вновь способствует улучшению [36]. Следовательно, есть основания считать о необходимости длительного или, вероятно, пожизненного применения тестостерон заместительной терапии в случае возрастного гипогонадизма и ДГПЖ/СНМП, что требует дельнейшего изучения этого вопроса в более масштабных и продолжительных эпидемиологических исследованиях.
Заключение. Результаты исследования «ПОТОК» показали большую эффективность и сопоставимую безопасность комплексной терапии СНМП при ДГПЖ у мужчин с недостаточностью эндогенного тестостерона альфа-адреноблокаторами и препаратом Андрогель® по сравнению с монотерапией альфа-адреноблокаторами в рутинной клинической практике. Восстановление сывороточных концентраций тестостерона до нормальных значений у пациентов с возрастным гипогонадизмом благоприятным образом отразилось как на динамике течения СНМП, так и на потенцировании эффекта от проводимого лечения в комплексной терапии данного заболевания. Сроки облегчения СНМП и симптомов андрогенного дефицита на фоне комбинированной терапии альфа-адреноблокаторами и гелем тестостерона убеждают в необходимости длительного лечения для достижения и поддержания благоприятного эффекта.



