Введение. Анализ специализированной литературы, связанной с классификацией хирургических осложнений, показал в целом отсутствие систематизации по данному вопросу и последовательности в объяснении проблемы [1]. Как правило, для объективного анализа хирургических осложнений авторы статей пользуются критериями клинического материала на основе ретроспективных и проспективных рандомизированных исследований за 1975−2001 гг. [1]. На наш взгляд, одним из наиболее важных аспектов является оценка степени тяжести осложнений.
Поскольку после различных видов хирургических вмешательств наблюдаются осложнения как общего характера, так и присущие только данной категории операций, их систематизация была крайне затруднительна. Созданная в 1992 г. группой ученых под руководством Пьера-Алена Клавьена (Pierre-Alain Clavien) из Университетского госпиталя Цюриха и усовершенствованная в 2004 г. их коллегой, доктором медицины Даниэлем Диндо (Daniel Dindo), классификация осложнений хирургических вмешательств была успешно протестирована на базе 10 хирургических центров разных стран [2, 3]. На основании полученных результатов данная классификация была признана специалистами хирургических подразделений важным инструментом качественной оценки послеоперационных осложнений. Впервые в урологии классификацию Clavien–Dindo применили для оценки осложнений, возникших после лапароскопической радикальной простатэктомии, лапароскопической или ретроперитонеоскопической нефрэктомии [4–10].
Таким образом, ретроспективный анализ частоты и характера интра- и послеоперационных осложнений илеоцистопластики (ИЦП) при помощи классификации Clavien–Dindo позволит на современном этапе оценить и улучшить результаты реконструктивно-пластической хирургии [11].
Цель – совершенствование реконструктивно-восстановительных операций за счет систематизации осложнений на основе классификации Clavien−Dindo.
Материал и методы. С целью улучшения результатов заместительной илеопластики выполнено исследование с участием 95 пациентов с рубцово-сморщенным мочевым пузырем туберкулезной и иной этиологий. Группу 1 составили 50 (50/95; 52,6%) пациентов с длиной использованного сегмента подвздошной кишки 30−35 см; в группе прео-бладали пациенты мужского пола (32/50; 64,0%); возраст больных составил от 20 до 72 (53,3±4,1) лет. В группе 2 во всех (45/95; 47,4%) наблюдениях протяженность кишечного аутотрансплантата варьировалась в пределах 45−60 см; преобладали лица мужского пола (29; 64,4%); возрастные характеристики были сопоставимыми с группой 1 – от 22 до 73 (49,2±3,9) лет.
Техника илецистопластики. При замещении мочевого пузыря у больных группы 1 использовали изолированный сегмент подвздошной кишки длиной не более 30–35 см с отступом 20–25 см от илеоцекального угла. Проходимость кишечника восстанавливали однорядным непрерывным викриловым швом «конец в конец». Дефект брыжейки ушивали. Дистальную часть аутотрансплантата детубуляризировали на протяжении 25–30 см и укладывали в виде буквы U. Ее медиальные края сшивали между собой непрерывным серозно-мышечным швом. Нижняя часть получившейся площадки заворачивалась кверху и становилась передней стенкой неоцистиса, который за счет этого приема приобретал сферическую форму. В проксимальный недетубуляризированный сегмент кишки, выполняющий роль антирефлюксного механизма, имплантировали мочеточники «конец в бок», при этом левый мочеточник проводили через брыжейку сигмовидной кишки. В самой нижней точке резервуара вырезали отверстие 8–10 мм в диаметре снаружи от линии шва. Анастомоз уретры или шейки мочевого пузыря с резервуаром осуществляли узловыми швами, перед затягиванием швов в резервуар вводили катетер Фолея размером 18 Ch.
В группе 2 применялась аналогичная техника ИЦП, но с более протяженным трансплантатом – 45–60 см.
Перечень обследований включал клинико-лабораторные, рентгенологические и ультразвуковые методы. Комплексное уродинамическое обследование неоцистиса, данные суточного ритма спонтанных мочеиспусканий, анализ показателей кислотно-основного состояния и электролитного баланса крови у наблюдаемых больных выполнялись в сроки через 15−20 дней и 12 мес. после заместительной ИЦП. Интерпретация результатов проводилась в соответствии с терминологией и стандартами Международного общества по проблемам удержания мочи (International continence society, ICS).
Все наблюдаемые после хирургического вмешательства осложнения проанализированы с помощью классификации Clavien–Dindo.
Для статистической обработки данных использована программа IBM SPSS Statistics 26, Microsoft Excel. Приемы статистического анализа: 95% доверительный интервал, стандартное отклонение, стандартная ошибка; приемы корреляционного анализа: коэффициенты Пирсона и Спирмена.
Результаты. Оперативное лечение микроцистиса позволило значимо снизить патологические симптомы рубцово-сморщенного мочевого пузыря, такие как частые (каждый час) непреодолимые позывы к мочеиспусканию; боли в промежности, паху, над лоном, поясничной области, в том числе при появлении позыва к мочеиспусканию (боль наполнения); ургентное или тотальное недержание мочи. Динамика жалоб пациентов после операции представлена в табл. 1.

Как видно из табл. 1, частота каждого из симптомов после заместительной илеоцистопластики снизилась в 5−10 раз: хороший результат в купировании дизурии достигнут в 88 (92,6%) случаях, удовлетворительный – в 12 (12,6%); неудовлетворительных показателей не отмечено.
Структура и частота интра- и послеоперационных осложнений заместительной цистопластики зависят от состояния больного (ранее оперированный кишечник, коморбидные заболевания, возраст и др.), объема и длительности выполненного оперативного вмешательств, опыта оперирующего хирурга. Послеоперационные осложнения бывают типичными для больших хирургических вмешательств и специфичными для заместительной ИЦП. К первой группе осложнений относят потерю крови, осложнения после ее переливания, легочную и сердечную недостаточность в результате пролонгированной анестезии, инфицирование раны, несостоятельность послеоперационной раны, сепсис, пневмонию, тромбоз, эмболию и др. Специфические осложнения кишечной пластики мочевого пузыря делят на ранние и поздние. К раннему послеоперационному периоду относятся первые 90 дней после оперативного вмешательства (табл. 2).
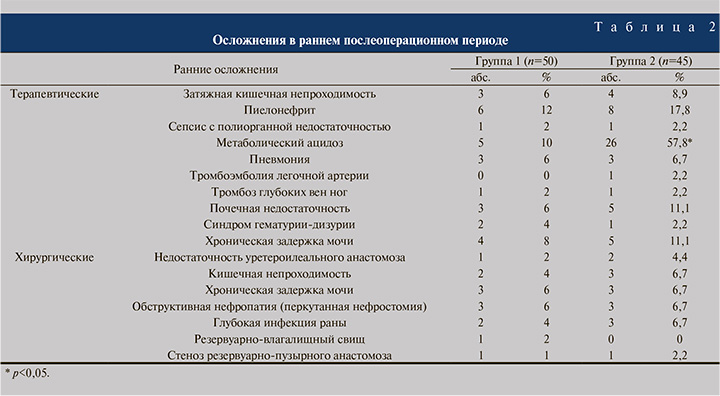
Ранние осложнения нами были разделены на терапевтические и хирургические. Наиболее распространенными терапевтическими осложнениями были метаболический ацидоз, пиелонефрит и почечная недостаточность, которые статистически значимо (p<0,05) чаще встречались в группе 2.
Остальные терапевтические осложнения отмечались в обеих группах с сопоставимой частотой (p>0,05). В отношении хирургических осложнений статистически значимой разницы в частоте их выявления не установлено: 13 и 15 пациентов в группах 1 и 2 соответственно.
Наиболее частыми причинами ранних ревизий (16/95; 16,8%) являлись глубокая инфекция раны, кишечная непроходимость, стеноз резервуарно-пузырного анастомоза и уретероилеальная недостаточность. Перкутанная нефростомия и трансуретральные методы коррекции хронической задержки мочи в обеих группах были выполнены с одинаковой частотой. В группе 2 в раннем послеоперационном периоде вследствие тромбоэмболии легочной артерии умер 1 (2,2%) пациент.
Послеоперационные осложнения анализировали по пяти степеням в соответствии с усовершенствованной классификацией Clavien−Dindo (табл. 3).
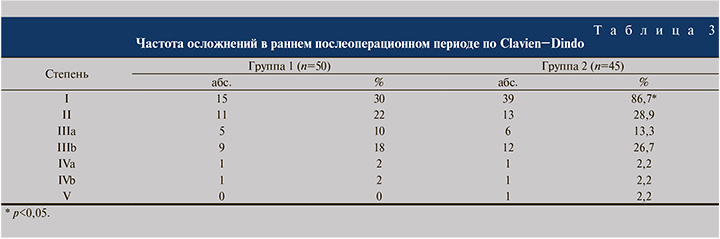
Поскольку осложнения I степени не требовали расширенной консервативной терапии, хирургических и радиологических методов коррекции и не пролонгировали сроков лечения, в нашем исследовании они подробно не анализировались. Осложнения II степени развились у 11 (22,0%) пациентов группы 1 и у 13 (28,9%) – группы 2, IIIа- степени – у 5 (10,0%) и 6 (13,3%), IIIb-степени – у 9 (18,0%) и 12 (26,7%) соответственно. Серьезные осложнения IVa- и IVb-степеней регистрировали в обеих группах с одинаковой частотой (по 1 наблюдению). Осложнение V степени с летальным исходом зафиксировано только в группе 2.
Развитие осложнений I−II степеней, обусловленных в основном метаболическим ацидозом и острым пиелонефритом, приводило к пролонгированию сроков антибактериальной терапии, замене антибиотика на препараты резервного ряда (карбапенемы, линезолид), ощелачивающей терапии гидрокарбонатом натрия. Зарегистрированные случаи анемии тяжелой степени служили основанием для трансфузии компонентов крови, восполнения объема циркулирующей крови с последующим включением в схему лечения препаратов железа. Эвентрация и уретерогидронефроз, расцененные как осложнения IIIa-степени, требовали повторного наложения швов и перкутанной нефростомии под спинальной и местной анестезией. С осложнениями IIIb-степени пациентов переводили в палату интенсивной терапии и проводили повторное оперативное вмешательство под эндотрахеальным наркозом, что в целом увеличивало сроки их пребывания в стационаре. При возникновении осложнений IVa- и IVb-степеней больных переводили в отделение реанимации, при острой почечной недостаточности проводили заместительную почечную терапию. В случае развития сепсиса и полиорганной недостаточности пациент длительно находился на искусственной вентиляции легких с пролонгацией периода пребывания в отделении реанимации и интенсивной терапии с последующим переводом в профильное отделение. Тромбоэмболия легочной артерии, возникшая у 1 пациента на 7-е сутки после операции, расценена как V степень осложнений по классификации Clavien−Dindo.
К позднему послеоперационному периоду относили осложнения, повлекшие за собой госпитализацию больного в стационар спустя 90 дней от момента оперативного вмешательства (табл. 4).

Поздние осложнения зарегистрированы у 63/94 (67,0%) пациентов, из них 26 в группе 1 (16 терапевтических и 10 хирургических) и 37 в группе 2 (24 терапевтических и 13 хирургических), что свидетельствует о статистически значимом увеличении их частоты в группе 2 (p<0,05). Рецидивирующая инфекция мочевыводящих путей в обеих группах связана с обструктивным воспалением почек или резервуарно-мочеточниковым рефлюксом, при этом осложнения во всех случаях купированы при помощи перкутанной нефростомии с назначением парентеральных антибиотиков. Хроническая почечная недостаточность, а также метаболический ацидоз нивелированы после восстановления пассажа мочи. В табл. 5 приведены случаи поздних осложнений, потребовавших хирургической коррекции.
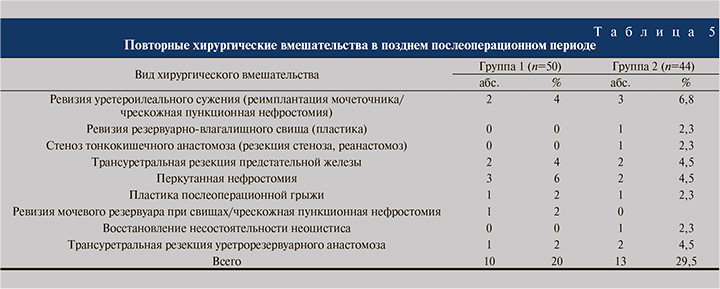
В позднем послеоперационном периоде выполнено 23 оперативных вмешательства, из них 10 в группе 1 и 13 в группе 2. В группе 1 трансуретральную резекцию уретрорезервуарного анастомоза и реимплантацию мочеточника выполняли реже, чем в группе 2, при этом с одинаковой частотой осуществляли трансуретральную резекцию предстательной железы. В то же время чрескожная пункционная нефростомия в группе 1 применялась чаще – в 6% случаев против 4,5% в группе 2.
Таким образом, не обнаружено статистически значимой разницы между группами по показаниям к оперативным вмешательствам в позднем послеоперационном периоде. Летальные исходы в позднем послеоперационном периоде отсутствовали.
Далее было проведено сравнительное изучение функцио-нальных результатов ИЦП в двух группах больных: у 65 пациентов в ближайшем послеоперационном периоде, у 57 – в отдаленном.
Объективная оценка показателей кислотно-основного состояния в ближайшем периоде после ИЦП показала наличие клинически значимого гиперхлоремического ацидоза у 18 больных. Это осложнение проявлялось повышенной утомляемостью, тошнотой и рвотой у 15 (83,3%) больных, анорексией – у 3 (16,6%), спутанностью сознания вплоть до ступора – у 1 (5,5%). Нарушения сердечно-сосудистой деятельности (снижение сократительной способности миокарда, расширение сосудов), связанные с ацидозом, привели 2 (11,1%) пациентов к сердечной недостаточности и/или гипотензии. Во всех случаях проведена ощелачивающая терапия с выраженным клиническим эффектом.
У одного больного с единственной почкой и прогрессирующей хронической почечной недостаточностью наблюдали метаболический ацидоз, потребовавший дренирования артифициального мочевого пузыря уретральным катетером Фолея и назначения ощелачивающих растворов. Установлено, что метаболический ацидоз всегда развивался на фоне хронической почечной недостаточности.
Таким образом, анализ полученных данных показал, что развившийся у 18 (27,7%) больных после ИЦП метаболический гиперхлоремический ацидоз связан с нарушением как функции почек, так и опорожнения кишечного мочевого резервуара.
Показатели кислотно-основного состояния и электролитного баланса крови у наблюдаемых больных в сроки через 15−20 дней и 12 мес. после заместительной ИЦП приведены в табл. 6.
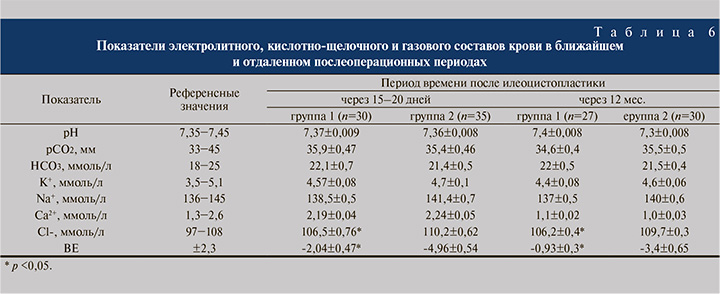
В ранние сроки после операции у пациентов, которым выполнялась ИЦП с использованием укороченного фрагмента кишки, гиперхлоремического ацидоза не наблюдали, а имеющийся незначительный дефицит оснований оказался в 2,4 раза ниже, чем у больных, прооперированных по классической методике (р<0,05), у которых также существенно повышался уровень ионов хлора крови (до 110,2±0,62 ммоль/л; р<0,05). Остальные показатели электролитного и газового состава крови не выходили за пределы допустимых значений в обеих группах и существенно не различались между собой.
Сведения, отражающие состояние кислотно-основного состояния, электролитного и газового составов крови в отдаленном (через 12 мес.) послеоперационном периоде изучены у 27 (90,0%) больных группы 1 и у 30 (85,7%) – группы 2. Установлено, что в отдаленном после ИЦП периоде показатели кислотно-основного состояния претерпели существенные изменения: так, дефицит оснований снизился в 2 раза в группе 1, в 1,5 раза – в группе 2 (см. табл. 6). Для лечения использовали пероральный прием бикарбоната натрия по 1 столовой ложке 3 раза в день в течение 10 дней под контролем клинических и лабораторных данных. Внутригрупповые различия по показателям кислотно-основного состояния крови в ближайшем и отдаленном периодах оказались незначительными.
Таким образом, установлено, что в отношении больных с ретенционными изменениями верхних мочевыводящих путей и хронической почечной недостаточностью нецелесообразно использовать трансплантат длиной 45−60 см. При этом оптимальная протяженность трансплантата, препятствующая развитию метаболических и электролитных нарушений, не должна превышать 35 см.
В то же время представлялось важным изучить состояние уродинамики как нижних, так и верхних мочевыводящих путей у прооперированных пациентов. Частота жалоб, представленных поллакиурией, тазовыми и поясничными болями, а также недержанием мочи, в группе 1 снизилась с 56,6−90,0 до 10,0−13,3%, в группе 2 – с 45,7−85,5 до 8,6−11,4%. Хорошие результаты в отношении купирования дизурии достигнуты в 26 (86,7%) и 31 (88,7%) наблюдении, удовлетворительные – в 4 (13,3%) и 4 (11,4%) соответственно. Неудовлетворительные результаты операций не зарегистрированы. Данные суточного ритма спонтанных мочеиспусканий в ближайшем послеоперационном периоде после ИЦП приведены в табл. 7.
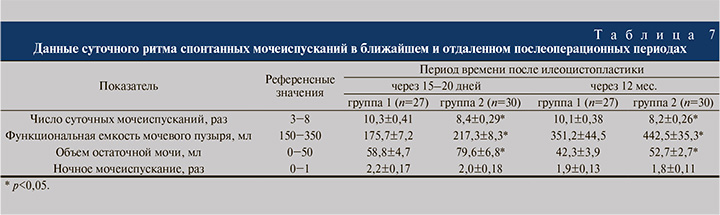
Из табл. 7 видно, что пациенты группы 1 мочились достоверно чаще, чем в группе 2. Частота ночных мочеиспусканий зарегистрирована на одинаковом уровне в обеих группах (дважды). Объем единовременно выпущенной мочи соответствовал физиологической норме, но при этом оказался существенно ниже в группе 1. В то же время обнаружены статистически значимые различия в объеме остаточной мочи: худший показатель отмечен в группе 2.
По прошествии 12 мес. после операции суточный ритм спонтанных мочеиспусканий остался на прежнем уровне. Прерывать ночной сон, чтобы помочиться, также приходилось дважды, однако отмечалось существенное увеличение объема единовременно выпущенной мочи, который в основной группе оказался статистически значимо ниже. Объем остаточной мочи в отдаленном послеоперационном периоде уменьшился в обеих группах, но при этом оказался существенно выше у пациентов, прооперированных по классической методике.
Количественная оценка симптомов нижних мочевыводящих путей по шкалам простатических симптомов (International Prostatic Symptom Score, I-PSS) и качества жизни (Quality of Life, QoL) проведена через 12 мес. после ИЦП. Установлено, что после операции сохранялась умеренная степень нарушений функции нижних мочевыводящих путей в обеих группах. Суммарный балл I-PSS в среднем составил 12,1±0,9 в группе 1 и 11,4±1,0 – в группе 2, что существенно отличалось от исходных показателей. После операции большинство пациентов отмечали удовлетворительное качество жизни, оценка которого не превышала 2 баллов из 6 возможных в обеих группах. В целом использование короткого отрезка кишечного трансплантата не приводило к ухудшению функции искусственного резервуара по сравнению с традиционной методикой.
Более точными и объективными методами оценки достигнутых результатов являются уродинамические. Сравнительные результаты цистометрии в фазе накопления у пациентов с малым мочевым пузырем после ИЦП укороченным и стандартным кишечным сегментом приведены в табл. 8.

Из табл. 8 следует, что показатели максимальной цистометрической емкости оказались статистически значимо выше в группе больных после ИЦП кишечным трансплантатом стандартной длины (р<0,05). Объем мочевого пузыря при первом позыве к мочеиспусканию в группе 1 составил 275,0±31,0 мл против 375,6±22,7 в группе 2 (р<0,05). Несколько более высокие значения внутрипросветного давления при первом позыве, максимальной цистометрической емкости и максимального сокращения неоцистиса наблюдали в группе 1.
Во всех случаях созданный кишечный резервуар отличался хорошей растяжимостью, количественное значение которой через 12 мес. достигало 38,9±4,3 мл/см водн.ст. в группе 1; несколько более высокие показатели достигнуты в группе 2 – 44,2±8,3 мл/см водн.ст. (p<0,05). Через 12 мес. после ИЦП укороченным кишечным трансплантатом наблюдали статистически значимо меньшие объемные параметры при увеличении показателей внутрирезервуарного давления. Внутрирезервуарное давление при первом позыве, максимальная цистометрическая емкость и максимальное сокращение кишечного пузыря в 1-й группе не имели существенных отличий от показателей 2-й группы. Сравнительный анализ данных урофлоуметрии выявил некоторые особенности (табл. 9).
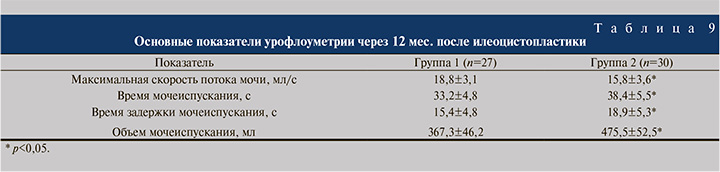
Установлено, что через 12 мес. после операции максимальная скорость потока мочи оказалась достоверно ниже у пациентов группы 2 и составила 15,8±3,6 мл/с против 18,8±3,1 в группе 1 (р<0,05). Время мочеиспускания было существенно больше после ИЦП с использованием стандартного отрезка подвздошной кишки – 38,4±5,5 против 33,2±4,8 с после применения укороченного сегмента. Аналогичные результаты зарегистрированы при изучении времени задержки мочеиспускания: в группе 2 оно оказалось достоверно бо́льшим. Статистически значимые межгрупповые различия отмечены и в отношении объема мочеиспускания, которое в группе 1 составило 367,3±46,2 мл против 475,5±52,5 в группе 2 (р<0,05). Остальные показатели между группами достоверно не различались.
Заключение. Таким образом, ранние серьезные осложнения послеоперационного периода по классификации Clavien−Dindo и необходимость их хирургической коррекции зарегистрированы примерно с одинаковой частотой в обеих группах. Один летальный случай вследствие тромбоэмболии легочной артерии отмечен только в контрольной группе, в которой также существенно чаще встречались поздние осложнения (p<0,05), при этом значимых различий в количестве повторных оперативных вмешательств в группах не выявлено.
Установлено, что функциональные показатели после ИЦП с использованием аутотрансплантатов различной длины в обеих группах во многом схожи. После кишечной пластики мочевого пузыря укороченным фрагментом подвздошной кишки объем единовременно выпущенной мочи оказался достоверно меньшим, но соответствовал физиологической норме (более 150 мл). Установлено, что созданный неоцистис характеризуется достаточной емкостью, минимальным количеством остаточной мочи, эффективным опорожнением, удовлетворительной функцией удержания мочи и низким внутрипросветным давлением, что способствует защите почек от резервуарно-мочеточниково-лоханочного рефлюкса.
В целом можно утверждать, что уродинамические параметры искусственного мочевого пузыря, сконструированного из подвздошной кишки длиной 30−35 см, являются удовлетворительными. Кроме того, уменьшение длины кишечного аутотрансплантата нивелирует развитие гиперхлоремического метаболического ацидоза.



