Введение. Одной из наиболее сложных проблем в современной урологии остается инфекция нижних мочевыводящих путей (ИНМП). Каждый год более 7 млн женщин обращаются за медицинской помощью по поводу цистита. Не менее 30% из них страдают от хронической рецидивирующей формы заболевания. В 40% случаев данное заболевание встречается у женщин в работоспособном возрасте 20–40 лет и приводит к утрате трудоспособности [1–5]. Оно приводит к резкому снижению физической и психической активности, ограничению свободы передвижений, нарушению привычного образа жизни и психоэмоциональным расстройствам, что, в свою очередь, отражается и на состоянии всего организма [6–8].
В основе лечения ИНМП чаще всего лежит антибактериальная терапия. Однако существует четкая тенденция к снижению ее эффективности, прослеживающаяся в последние годы [9–11]. С одной стороны, причиной этому служит нерациональное использование данных препаратов как врачами, так и пациентами, которое приводит к снижению чувствительности микроорганизмов и селекции антибиотикорезистентных штаммов. При этом важное значение имеет тот факт, что в ближайшие 10–15 лет не ожидается появления антибактериальных препаратов с принципиально новым механизмом действия, что обусловливает необходимость разработки новых альтернативных схем терапии и методов более эффективного использования уже имеющихся препаратов [12, 13].
С другой стороны, это связано со свойствами самих микроорганизмов. Возбудители ИНМП имеют способность к адгезии – прикреплению при помощи ворсинок к клеткам эпителия, что позволяет бактериям противостоять току мочи и обеспечивает их способность к колонизации. Кроме того, патогенные микроорганизмы обладают свойствами репликации, репродукции в зонтичных клетках эпителия мочевыводящих путей, инвазии в глубокие слои уротелия и образования биопленок. Микробная биопленка – специализированная экосистема, обеспечивающая жизнеспособность и сохранение составляющих ее видов микроорганизмов, а также увеличение их общей популяции. В ее состав входят отдельные микроколонии бактерий одного или разных родов и видов, внеклеточный матрикс внутри микроколоний и между ними с сетью каналов для движения жидкости и поверхностная оболочка матрикса, содержащая мембранно-подобную структуру. Поверхностная оболочка уменьшает доступ антибактериальных препаратов, а компоненты межклеточного матрикса их связывают и инактивируют. Внутри биопленки устойчивые бактерии защищают чувствительные, выделяя ферменты в матрикс, и происходит распространение генов антибиотикоустойчивости [14, 15].
Чем больше нарушены местные и общие защитные механизмы организма человека, тем большим патогенным потенциалом могут обладать бактериальные агенты. Таким образом, выраженность воспалительного процесса зависит от состояния местного и общего иммунитета, как специфического, так и неспецифического. Патологические изменения иммунной системы являются одной из вероятных причин, приводящих к хроническому течению и рецидивированию воспалительного процесса. Стандартная терапия инфекций НМП обычно включает антибактериальные препараты [1, 2]. Но ни один из антибиотиков не обеспечивает защиты от рецидивов инфекции при нарушении защитных механизмов мочевыводящих путей [15, 16].
Важнейшим звеном патогенетической терапии хронического цистита, способным предотвратить хронизацию воспаления, признается иммуномодулирующая терапия. В ее задачи входят стимуляция фагоцитарной активности, нормализация баланса Т-клеточного звена иммунитета, стимуляция интерферонообразования и синтеза неспецифических факторов защиты. Поэтому в последние годы появился ряд публикаций, доказывающих преимущества иммуноакивной терапии [17, 18]. Включение интерферона в комплексное лечение инфекций мочевой системы обусловлено тем, что бактериальная инфекция повреждает клетки уроэпителия и препятствует синтезу собственных интерферонов. Из трех идентифицированных видов интерферона человека – интерферон альфа, бета и гамма – в терапии латентных форм инфекций НМП используются препараты интерферона альфа. Среди них наиболее известен ВИФЕРОН®, комплексный препарат, содержащий интерферон альфа-2b, токоферола ацетат и аскорбиновую кислоту [19].
В настоящее время существует несколько схем применения препарата: ВИФЕРОН® в виде суппозиториев по 1 000 000 МЕ ректально в течение 10 дней и по 3 000 000 МЕ ректально в течение 10 дней [20].
Целью настоящего исследования явился сравнительный анализ эффективности различных дозировок препарата ВИФЕРОН® в комплексном лечении хронического рецидивирующего бактериального цистита.
Материалы и методы. Нами проведено обследование 90 женщин в возрасте от 18 до 45 лет с диагнозом «хронический рецидивирующий бактериальный цистит в стадии обострения».
Критериями постановки диагноза служили клиническая картина заболевания, данные микроскопического и бактериологического исследований мочи.
Критериями невключения в исследование явились признаки острого пиелонефрита и осложненной инфекции мочевыводящих путей (лихорадка, боль в пояснице, нарушение оттока мочи, аномалии развития мочеполовой системы, травмы и операции на органах малого таза, пролапс тазовых органов), сахарный диабет и тяжелые сопутствующие соматические заболевания, неоткорригированная гипоэстрогения, постменопауза, прием антибиотиков в течение последних 12 месяцев.
Пациенты были разделены методом случайной выборки на 3 группы по 30 человек. Группы были сравнимы по демографическим и клиническим характеристикам.
В группу 1 входили женщины, получавшие стандартную антибактериальную терапию препаратами нитрофуранового ряда в соответствии с клиническими рекомендациями «Цистит у женщин – 2021» [1]. При необходимости производилась ее коррекция по результатам бактериального посева мочи с учетом чувствительности микроорганизмов.
В группу 2 входили пациентки, которые в сочетании со стандартной антибактериальной терапией получали препарат ВИФЕРОН® в виде суппозиториев по 1 000 000 МЕ ректально 2 раза в сутки в течение 10 дней.
В группу 3 входили пациентки, которые в сочетании со стандартной антибактериальной терапией получали препарат ВИФЕРОН® в виде суппозиториев по 3 000 000 МЕ ректально 2 раза в сутки в течение 10 дней.
Всем больным было проведено обследование: сбор анамнеза заболевания и жизни, физикальное обследование, консультация гинекологом. Каждой женщине было предложено ежедневное заполнение дневников мочеиспусканий, по данным которых оценивались частота мочеиспусканий, наличие ургентных позывов, ноктурия на 1-е, 5-е и 10-е сутки. Произведена оценка интенсивности рези при мочеиспускании по визуально-аналоговой шкале (ВАШ) боли на 1-е, 5-е и 10-е сутки.
Лабораторный мониторинг включал общий анализ крови (ОАК); общий анализ мочи (ОАМ), трехкратное бактериологическое исследование проб мочи с посевом урокультуры на твердые питательные среды, установление вида возбудителей, чувствительность к антибиотикам и степень бактериурии на 1-е, 5-е и 10-е сутки.
Статистическую обработку результатов проводили с помощью программы MS Excel 11.0 из стандартного пакета MS Office 2013, а также программного обеспечения IBM SPSS Statistics 21.0. При проверке статистических гипотез применяли методы параметрической (t-test Cтьюдента) статистики. При оценке достоверности выявленных различий между средними значениями выборок рассчитывали параметр р, вероятность справедливости нулевой гипотезы была принята равной 5% (р<0,05).
Протокол исследования был одобрен локальным этическим комитетом. Все пациентки подписали форму добровольного информированного согласия на участие в исследовании.
Результаты. Исходно у всех пациенток в трех группах были зафиксированы признаки, характерные для обострения хронического цистита, такие как поллакиурия, боль и резь при мочеиспускании, ургентные позывы, ноктурия, лейкоцитурия (см. таблицу). Достоверных различий в указанных показателях перед началом терапии не выявлено (p≥0,05).
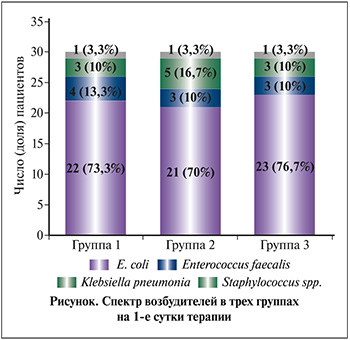
На 1-е сутки по результатам микробиологического исследования мочи у всех пациенток был подтвержден бактериальный характер воспаления. Спектр возбудителей в трех группах на 1-е сутки представлен на рисунке. Все выявленные микроорганизмы были чувствительны к фосфомицину, нитрофуранам и цефалоспоринам.
Результаты клинико-лабораторных исследований, полученные на 5-е сутки терапии в группах 2 и 3, статистически значимо (p<0,05) отличались от показателей в группе 1 (см. таблицу). Наиболее выраженная положительная динамика числа ночных мочеиспусканий, количества ургентных позывов в сутки и интенсивности болевых ощущений была отмечена в группе 3. Данные различия были также статистически значимыми (p<0,05).

К 5-м суткам эрадикация возбудителя отмечена в 100% наблюдений во всех трех группах.
К 10-м суткам терапии средние значения исследуемых клинико-лабораторных показателей снизились до нормального уровня во всех трех группах. Статистически значимых различий выявлено не было (p<0,05).
На 10-е сутки посевы мочи в трех группах также были стерильны.
Обсуждение. Ведущую роль в патогенезе любых хронических воспалительных заболеваний играет гипоксия тканей и транзиторная дисфункция иммунной системы. При возникновении цистита в организме человека первоначально происходит активация местного и гуморального иммунитета в виде выработки антител. Несостоятельность врожденного иммунитета слизистых оболочек мочевыводящих путей приводит к активации инфекции и развитию острого воспаления [17, 18].
Следовательно, оправданным является применение для лечения или профилактики ИНМП альтернативных подходов к лечению, среди которых более обоснованной и доказанной на сегодняшний день является иммунотерапия. Способность интерферона увеличивать продукцию иммуноглобулинов, фагоцитарную активность макрофагов, подавлять размножение бактерий обусловливает целесообразность его применения в лечении данной категории больных.
ВИФЕРОН® оказывает противовирусное, антибактериальное и антипролиферативное действия [20]. Его непосредственное влияние на иммунную систему проявляется активацией естественных киллеров, Т-хелперов, увеличением числа цитотоксических Т-лимфоцитов и усилением дифференцировки В-лимфоцитов. Токоферол и аскорбиновая кислота в составе препарата ВИФЕРОН®, как известно, являются компонентами антиоксидантной системы и оказывают мембраностабилизирующее действие, способствуют регенерации тканей, улучшают тканевое дыхание. Данные обстоятельства позволяют использовать интерфероны, когда при нарушении проницаемости мукополисахаридной субстанции мочевого пузыря необходима антиоксидантная и регенеративная активность для снижения процессов воспаления в стенке мочевого пузыря. Показано, что ректальное введение интерферона альфа-2b обеспечивает более длительную циркуляцию его в крови, чем при внутримышечном и внутривенном введении.
Препарат ВИФЕРОН® уже длительное время успешно применяется при инфекционных заболеваниях и имеет широкую доказательную базу. Однако существует небольшое количество исследований, посвященных его применению при ИНМП [17, 18].
В исследовании профессора Х.С. Ибишева [17], опубликованном в 2012 г., были приведены результаты применения препарата ВИФЕРОН® в комплексной терапии женщин с подтвержденным хроническим бактериальным циститом без анатомо-физиологических нарушений мочевыводящих путей. В исследование были включены 64 женщины, которые были распределены на 2 группы.
В первой группе проводилась терапия Фосфомицином, а во второй Фосфомицин назначался в сочетании с препаратом ВИФЕРОН® в дозировке 1 000 000 МЕ 2 раза в сутки. Согласно представленным результатам лишь у 53% пациенток первой группы к 5-м суткам было отмечено исчезновение симптомов цистита, тогда как во второй группе на фоне терапии препаратом ВИФЕРОН® симптомы отсутствовали у 90% пациенток. Терапия, сочетающая иммуномодуляторы и антибиотики, позволила достичь быстрого клинического и лабораторного эффекта у женщин с рецидивирующим циститом.
Полученные в ходе проведенного нами исследования результаты сопоставимы с данными, представленными в литературе. Сравнительный анализ динамики полученных показателей в каждой из изучаемых групп с 1-е по 10-е сутки показал, что в процессе лечения значения исследуемых показателей достигли нормальных значений. Динамика изменения показателей, которые достигли нормальных значений к 10-м суткам в обеих группах, свидетельствует об эффективности проведенной терапии. В группах пациенток, получавших препарат ВИФЕРОН®, была зафиксирована статистически более значимая (p<0,05) положительная динамика исследуемых клинических и лабораторных показателей к 5-м суткам терапии, которая позволяет говорить о более быстром купировании воспалительного процесса у больных, получавших иммунотерапию. Однако в нашем исследовании был также проведен анализ различных режимов терапии препаратом ВИФЕРОН®. Статистически более значимое снижение (p<0,05) частоты мочеиспусканий, ургентных позывов, а также выраженности лейкоцитурии к 5-м суткам в группе 3 позволяет говорить о более высокой эффективности препарата ВИФЕРОН® в дозе 3 000 000 МЕ 2 раза в день в комплексной терапии женщин с хроническим бактериальным циститом.
В исследовании 2012 г. [17] также была произведена оценка влияния антибактериальной терапии в сочетании с препаратом ВИФЕРОН® в дозе 1 000 000 ME на частоту развития рецидивов заболевания. Согласно представленным данным, рецидив инфекции отмечен через 3 мес. у 6% пациенток 1-й группы. Через 6 мес. повторное лечение назначалось 17,1% женщин 1-й группы против 6,6% пациенток 2-й группы соответственно. Рецидив заболевания через 12 мес. регистрировали в 35,3% наблюдений у пациенток 1-й группы, тогда как во 2-й группе данный показатель составил 10%, что указывает на достоверно более высокую эффективность сочетания антибактериальных препаратов с интерферонами, в частности с препаратом ВИФЕРОН® в отношении рецидивов заболевания.
Аналогичные результаты были получены в ходе следующего исследования в 2014 г., в которое были включены 43 женщины с длительно персистирующей ИНМП (средняя продолжительность заболевания – 6,5 лет) [18].
Учитывая полученные в ходе нашего исследования результаты, свидетельствующие о более высокой эффективности препарата ВИФЕРОН® в дозе 3 000 000 МЕ, целесообразно продолжить наблюдение за исследуемой когортой пациенток для оценки влияния данного режима иммунотерапии на частоту рецидивов цистита.
Заключение. Терапия, сочетающая иммуномодулятор и антибиотик, позволяет достичь быстрого статистически значимого эффекта у женщин с хроническим бактериальным циститом к 5-м суткам терапии. Применение препарата ВИФЕРОН® в дозе 3 000 000 МЕ в сочетании с антибактериальной терапией в данном исследовании продемонстрировало наибольшую эффективность при лечении данной категории больных в отношении клинических и лабораторных проявлений заболевания. Полученные данные, на наш взгляд, дают основание для дальнейшего изучения эффективности различных режимов иммунотерапии препаратом ВИФЕРОН®, в частности, с целью оценки влияния на частоту развития рецидивов заболевания у женщин с хроническим бактериальным циститом.



