Введение. Доброкачественная гиперплазия предстательной железы (ДГПЖ) и хронический простатит (ХП) входят в число наиболее значимых урологических заболеваний [1–5]. В возрасте до 60 лет ДГПЖ диагностируют более чем у 42% мужчин. К 90 годам заболевание выявляют практически у 90% мужчин. При этом более 30% из них не менее 1 раза в течение жизни подвергаются хирургическому лечению [6–9].
Некоторые анатомические особенности, бесконтрольная и/или нерегулярная половая жизнь, сидячий пассивный образ жизни, хроническая интоксикация, а также уретрогенные инфекции могут приводить к застойным процессам в малом тазу и стать причиной развития воспалительных изменений в ткани предстательной железы [3–5].
Хроническое воспаление предстательной железы относится к числу часто рецидивирующих урологических заболеваний и, как правило, плохо поддается лечению. Согласно сведениям Национального института здоровья, около 25% мужчин, страдающих заболеваниями органов мочевыделительной системы, имеют симптомы простатита, что составляет более 9% мужской популяции [3].
Гиперплазия простаты часто протекает на фоне воспалительных изменений, которые обычно носят очаговый характер и ограничены парауретральной зоной. Данные морфологических исследований мужчин с ДГПЖ в 96,7% случаев свидетельствуют о наличии в тканях предстательной железы признаков хронического воспаления различной степени выраженности [10]. Согласно результатам [6–9, 11], у 57,2% мужчин с ХП имелась ДГПЖ, а у 38,7% пациентов с ДГПЖ был выявлен ХП.
Значимость ДГПЖ и ХП определяется не только их распространенностью, но и существенным снижением качества жизни пациентов данной категории. Кроме того, следует помнить о высокой частоте развития осложнений, таких как острая задержка мочи, поражение верхних мочевыводящих путей, эректильная дисфункция [12, 13].
К причинам коморбидности ДГПЖ и ХП можно отнести нарушения микроциркуляции и венозный стаз, застойные явления в простате и сдавление протоков ацинусов [14, 15].
Сопутствующий ХП негативно сказывается и на клиническом течении ДГПЖ. Воспалительные изменения в простате могут влиять и на ирритативную, и на обструктивную симптоматику. Недооценка симптомов простатита может стать причиной низкой эффективности консервативного лечения и увеличения числа осложнений после трансуретральной резекции простаты или чреспузырной аденомэктомии [16–18].
В настоящее время имеется широкий выбор методов лечения, начиная с медикаментозной терапии, заканчивая хирургическими вмешательствами. Препаратами первой линии в лечении больных ДГПЖ являются α-адреноблокаторы и ингибиторы 5α-редуктазы. Терапия ХП преимущественно проводится с использованием антибактериальных и противовоспалительных средств. Кроме того, активно применяются фитопрепараты и физиотерапия [1, 2]. Тем не менее выбор правильной тактики лечения ДГПЖ в сочетании с ХП вызывает много вопросов. Преобладание ирритативной симптоматики, отсутствие стойкого эффекта от приема α-адреноблокаторов, частые обострения ХП требуют использования дополнительных методов в лечении таких пациентов [13, 19–21].
В последнее время все шире применяется новая группа энтомологических препаратов, представляющих собой биологически активные субстанции с противовоспалительными и антиоксидантными свойствами, полученные из биомассы определенных насекомых [22, 23].
Аденопросин – новый энтомологический препарат, полученный из личинок Lymantria dispar с использованием современных биотехнологий. В доклинических исследованиях было доказано, что лекарство обладает противовоспалительным, антиоксидантным, ангиопротективным, иммуномодулирующим свойствами, что позволяет использовать его как вспомогательное средство в лечении пациентов с ДГПЖ и ХП [24, 25].
Цель исследования: изучить эффективность применения энтомологического препарата Аденопросин в составе комплексной терапии пациентов с ДГПЖ и ХП.
Материалы и методы. В исследование были включены 60 пациентов с ДГПЖ в сочетании с хроническим бактериальным простатитом категории II (NIH,1995) в стадии обострения. Диагноз устанавливался на основании анамнеза, результатов пальцевого ректального исследования ПЖ (ПРИ), ТРУЗИ, урофлоуметрии, анализа крови на ПСА, микроскопии и бактериологического исследования секрета ПЖ.
Пациенты соответствовали следующим критериям включения в исследование: суммарный балл по шкале IPSS от 8 до 19, объем остаточной мочи (Vом) от 30 до 100 мл, объем предстательной железы (Vпж) более 30 см3, уровень ПСА в крови не более 4 нг/мл, бактериальный характер воспаления (микробное число >104 КОЕ/мл), отсутствие сопутствующей медикаментозной терапии, продолжительность хронического простатита и аденомы простаты от 5 до 10 лет, подписанное информированное согласие на участие в исследовании.
Критерии невключения: камни мочевого пузыря и мочеточников, гематурия, подозрение на рак простаты или мочевого пузыря, аллергические реакции на используемые препараты, оперативные пособия на органах малого таза, инфекции мочевыводящих путей, нейрогенная дисфункция мочевого пузыря, врожденные аномалии развития мочеполовой системы, онкологические и тяжелые сердечно-сосудистые заболевания, сахарный диабет, гипогонадизм.
Методом случайной выборки пациенты были распределены в две группы по 30 человек.
В группу сравнения (ГС) включены больные, которым проводилась традиционная терапия препаратами группы α-адреноблокаторов (тамсулозин 0,4 мг 1 раз в день) и фторхинолонов (левофлоксацин 500 мг 1 раз в день в течение 4 нед.). В основной группе (ОГ) проводилась аналогичная традиционная терапия, но в сочетании с Аденопросином по 1 свече 1 раз в день в течение 3 мес.
Оценку состояния пациентов проводили при обращении (визит 1), через 4 нед. (визит 2) и через 3 мес. (визит 3). Оценивали частоту микций, количество ночных мочеиспусканий (ноктурия), средний балл по шкалам IPSS, QoL, NIH-CPSI, максимальную скорость потока мочи (Qmax), Vпж и Vом, результаты бактериоскопического и бактериологического исследований секрета простаты.
Статистическую обработку результатов проводили с помощью программы MS Exсel 11.0 из стандартного пакета MS Office 2013, а также программного обеспечения IBM SPSS Statistics 21.0. При проверке статистических гипотез применяли методы параметрической (t-test Cтьюдента) статистики. При оценке достоверности выявленных различий между средними значениями выборок рассчитывали параметр р, вероятность справедливости нулевой гипотезы была принята равной 5% (р<0,05).
Результаты. При бактериологическом исследовании секрета предстательной железы на визите 1 получены следующие результаты: из 30 (100%) пациентов в ГС наиболее часто была выявлена E. coli – у 17 (56,7%) человек, Ent.faecalis был обнаружен у 13 (43,3%) человек. В ОГ результаты были сопоставимыми: E. coli выявлена у 18 (60%) человек, Ent. faecalis обнаружен у 11 (36,7%), St. epidermidis – у 1 (3,3%) человека. Выделенные возбудители были чувствительными к левофлоксацину.
К визиту 2 у пациентов обеих групп отмечено снижение выраженности дизурии, увеличение показателя Qmax, что в свою очередь выразилось в повышении среднего балла по шкалам IPSS и QoL. Кроме того, по данным УЗИ, в обеих группах выявлено уменьшение объема остаточной мочи. Несмотря на отсутствие статистически значимых различий (р>0,05), в ОГ отмечена более выраженная положительная динамика большинства исследуемых показателей, в особенности Vпж.
По результатам бактериологического исследования в ГС рост микроорганизмов обнаружен в 10 (33,3%) посевах: E. coli выявлена в 6 (20%) случаях, Ent. faecalis – в 4 (13,3%). В ОГ микроорганизмы были выделены в посевах 4 (13,3%) пациентов: E. coli обнаружена у 3 (10%) из них, Ent. faecalis – у 1 (3,3%).
Через 3 мес. терапии значения исследуемых показателей в группе сравнения со времени предыдущего визита значимо не изменились. Полученные в ОГ результаты статистически значимо (p<0,05) отличались от показателей в ГС.
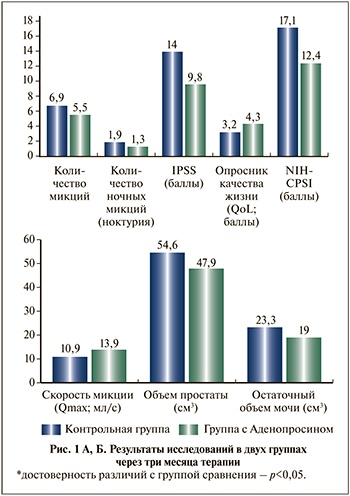
В ОГ к этому визиту количество дневных и ночных мочеиспусканий было меньше на 20,3 и 31,6% соответственно, результат по шкале NICH-CPSI – в среднем на 4,7 балла, по шкале IPSS – на 4,2, а качество жизни, по данным шкалы QoL, улучшилось на 1,1 балла (см. таблицу). Указанные субъективные изменения в состоянии пациентов подтверждались объективными данными: максимальная скорость потока мочи в основной группе была выше на 21,6%, объем простаты был меньше на 12,3%, объем остаточной мочи – на 18,5% (см. таблицу).
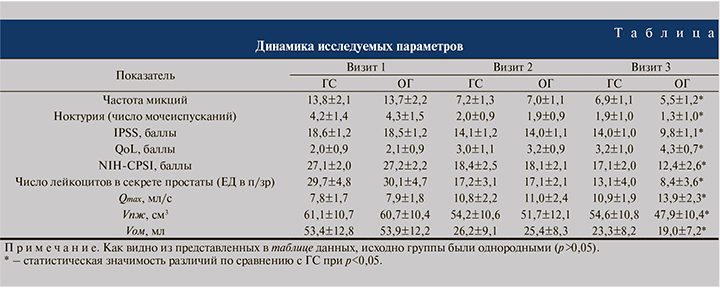
На визите 3 по результатам бактериологического исследования секрета простаты в обеих группах роста микроорганизмов выявлено не было. В основной группе к этому визиту количество дневных и ночных мочеиспусканий было меньше на 20,3% и 31,6% соответственно, результат по шкале NICH-CPSI был меньше в среднем на 4,7 балла, по шкале IPSS – на 4,2 балла, а качество жизни по данным шкалы QоL улучшилось на 1,1 балл (рис. 1А). Данные субъективные изменения в состоянии пациентов подтверждаются объективными данными: максимальная скорость потока мочи в основной группе была выше на 21,6%, объем простаты был меньше на 12,3%, а объем остаточной мочи – на 18,5% (рис. 1Б).
 Обсуждение. Насекомые давно известны как источник лекарственных субстанций. Изучение биохимии насекомых показало, что вырабатываемые ими многочисленные пептиды, гормоны, феромоны и другие биологически активные вещества в малых количествах оказывают ряд благоприятных эффектов на организм человека. Одним из представителей группы препаратов, содержащих указанные вещества, является Аденопросин.
Обсуждение. Насекомые давно известны как источник лекарственных субстанций. Изучение биохимии насекомых показало, что вырабатываемые ими многочисленные пептиды, гормоны, феромоны и другие биологически активные вещества в малых количествах оказывают ряд благоприятных эффектов на организм человека. Одним из представителей группы препаратов, содержащих указанные вещества, является Аденопросин.
L. Olariu et al. [22] выявили антиоксидантный эффект энтомологических комплексов, связанный с уменьшением внутриклеточного пероксида водорода в клетках гиперплазии предстательной железы, а также значительное уменьшение активности внеклеточного интерлейкина-6 и интерлейкина-8, что подтверждает наличие также и противовоспалительного эффекта.
V. Ghicavii et al. [24] по результатам своего исследования заключили, что Аденопросин может уменьшать фиброзные изменения и объем простаты при ее доброкачественной гиперплазии. Данное средство может быстро и эффективно способствовать устранению симптомов заболевания и улучшать уродинамические показатели уже в первые 3–4 нед. лечения. По мнению авторов, уменьшение объема предстательной железы происходит за счет как уменьшения парапростатического отека и венозной задержки в ткани предстательной железы, так и влияния на сосудистую фазу проницаемости капилляров при воспалении.
В исследовании I. Dumbraveanu et al. Аденопросин назначали мужчинам с ХП и возникшей на его фоне эректильной дисфункцией. По результатам исследования, у пациентов отмечено значительное уменьшение выраженности симптомов ХП и эректильной дисфункции [23, 25].
Результаты проведенного нами исследования согласуются с данными, представленными в литературе. На фоне применения Аденопросина отмечено уменьшение выраженности симптомов нижних мочевыводящих путей и симптомов хронического простатита, повышение показателя Qmax, уменьшение Vпж и Vом уже через 4 нед. приема препарата. Однако статистически значимые (p<0,05) различия с ГС по всем исследуемым показателям отмечены через 3 мес. терапии.
Полученные результаты могут быть обусловлены не только противовоспалительным эффектом, способствующим уменьшению парапростатического отека и венозного стаза в ткани предстательной железы, но и влиянием на сосудистую фазу проницаемости капилляров при воспалении. Аденопросин также может защищать от апоптоза клетки в условиях воспалительного процесса, при этом вызывая совершенно противоположный эффект в гиперпластических клетках в отсутствие воспаления, индуцируя апоптоз клеток простаты. Об антипролиферативном эффекте свидетельствует и выявленный в исследовании [22] факт уменьшения образования колоний клеток гиперплазии простаты. Тем не менее указанные патогенетические механизмы требуют дальнейшего изучения и подтверждения.
Заключение. Энтомологические препараты, в частности Аденопросин, могут стать новым направлением в комплексной терапии пациентов с ДГПЖ и ХП с учетом их противовоспалительной, антиоксидантной активности и антипролиферативного эффекта в отношении клеток гиперплазии предстательной железы. Однако для подтверждения полученных на данном этапе результатов и более детального изучения механизмов терапевтического действия данной группы препаратов необходимо провести более обширные плацебо-контролируемые клинические исследования.



