Введение. Бесплодием страдают около 15% пар во всем мире и почти половина случаев связана с мужским фактором [1–4]. Несмотря на развитие методов лечения, многие вопросы, особенно связанные с лечением мужского бесплодия, остаются без ответа. Мужское бесплодие считается сложным заболеванием и имеет множество причин, начиная от генетических мутаций и заканчивая образом жизни, сопутствующими заболеваниями или приемом лекарств. Некоторые причины мужского бесплодия до сих пор неизвестны, и бесплодие неясного генеза было классифицировано как идиопатическое мужское бесплодие [3–5]. Применение новых генетических, протеомных и метаболомных технологий и выявление новых биологических маркеров открывают перспективы для диагностики и лечения мужского бесплодия [6–9].
Биомаркер определяется как типичный биологический маркер процесса или состояния, который может быть независимо рассчитан, оценен и изучен [10]. Соответствующий биомаркер должен быть легко выявляем на ранней стадии, а методика его получения неинвазивной [4, 11]. В нашем исследовании изучается метаболом, в частности липидом, семенной плазмы с целью классификации специфических биомаркеров для более точной диагностики мужского бесплодия. Метаболомика – это исследование клеток, тканей или биологических жидкостей путем оценки их метаболитов [12, 13]. Метаболиты являются конечным результатом клеточных регуляторных процессов; ряд метаболитов, созданных системой клеток, составляtт ее «метаболом» [14–16]. Было показано, что оценка уровней метаболитов очень важна из-за регулирующего действия метаболитов как частей биохимических путей, особенно с точки зрения их применения в качестве диагностических маркеров некоторых заболеваний [17]. Липидомика – это исследование липидного профиля (липидома) в клетке, ткани или организме. Липидомику также можно рассматривать как ветвь метаболомики, которая представляет собой качественную и количественную оценку основных классов метаболитов в данном образце [18].
Цель исследования: оценка возможности метаболомного, в частности липидомного, анализа семенной плазмы для выявления пациентов с остаточным очаговым сперматогенезом в яичках, которые могут иметь разумные шансы на извлечение сперматозоидов при процедуре microTESE.
Материалы и методы. В работе использованы образцы семенной плазмы 64 мужчин с азооспермией и 24 фертильных мужчин, составивших контрольную группу. Пациенты с азооспермией были обследованы в отделении андрологии и урологии Национального медицинского исследовательского центра акушерства, гинекологии и перинатологии им. В. Кулакова (Москва, Россия) с января 2019 по февраль 2021 г. Исследование одобрено этическим комитетом Первого МГМУ им. И. М. Сеченова. Все пациенты дали письменное согласие на участие в исследовании.
Критерии включения в исследование: азооспермия (подтвержденная не менее 2 раз с помощью микроскопического анализа), подписанная форма информированного согласия на участие. Критерии невключения: обострения хронических заболеваний, активная гормональная терапия, инфекции, передающиеся половым путем, декомпенсированные воспалительные состояния, анэякуляция, ретроградная эякуляция, лейкоцитоспермия. Клиническое обследование включило подробный сбор анамнеза пациента, оценку уровня сывороточных гормонов (ФСГ, ЛГ, пролактин, тестостерон, эстрадиол, ингибин В), генетический скрининг (кариотип, AZF, CFTR) и ультразвуковое исследование мошонки. Всем пациентам была проведена микродиссекционная биопсия яичек. В данном исследовании оценивали липидомный состав семенной плазмы при азооспермии.
Из эякулята были выделены липиды модифицированным методом экстракции Фолча. Липидные экстракты и образцы контроля качества анализировали на жидкостном хроматографе Dionex UltiMate 3000 по описанной ранее методике [19].
Липиды идентифицировали с использованием R-скрипта Lipid Match [20] по точной массе с помощью базы данных Lipid Maps [21] и по характерным тандемным масс-спектрам (МС/МС).
Для статистической обработки результатов использовали скрипты, написанные на языке R [22], и программу RStudio [23]. Перед исследованием данные были нормированы на медианные значения соответствующих пиков в образцах контроля качества. При сравнении групп «контроль» и «азооспермия», «есть сперматозоиды»/«нет сперматозоидов» использовали тест Манна–Уитни. Для описания количественных данных использовали медиану (Me) и 1-й и 3-й квартили (Q1 и Q3). Величину порогового уровня значимости p принимали равной 0,05.
Выбор переменных для построения диагностических моделей на основе логистического регресса «контроль»/«азооспермия», «есть сперматозоиды»/«нет сперматозоидов» при азооспермии осуществляли двуступенчатым методом: с использованием дискриминантного анализа ортогональными проекциями проекций переменных на скрытые структуры (OPLS-DA) определяли значения проекций переменных (ПП) и выбирали те, которые удовлетворяли условию ПП>1. Из них переменные отбирались пошагово, опираясь на значение информационного критерия Акаике (ИКА). Когда рост ИКА останавливался, из выбранного набора соединений пошагово исключались те, чьи коэффициенты не отличались статистически значимо от 0 (порог значимости – 0,05). Перед построением итоговой модели значения площадей пиков нормировались на медианные значения сигнала от данного соединения по всему пулу образцов. Полученные модели валидировали с использованием кросс-валидации по отдельному объекту.
Результаты. Все пациенты имели азооспермию, но в 25 случаях сперматозоиды были обнаружены при исследовании ткани яичек. При сравнении контрольной группы и группы с азооспермией выбрано 23 липида в режиме положительных ионов и 37 липидов в режиме отрицательных ионов, содержание которых статистически значимо различалось между группами.
При оценке липидомного состава в режиме положительных ионов зафиксирована разница по концентрации липидов из таких групп, как церамиды, гексозилцерамиды, сфингомиелины, фосфотидилхолины, фосфотидилэтаноламины, а также по их простым эфирам.
В режиме отрицательных ионов б обнаружены еще более существенные различия по липидному составу в группах сравнения. В частности, разную концентрацию имели также липиды групп кардиолипинов, плазманилов и плазменилов. Отмечалась статистически значимая разница и по окисленным формам некоторых липидных соединений.
Мультивариантный регрессионный анализ среди выявленных выше соединений позволил выделить более узкую группу липидов, разница в концентрации которых не зависела от других соединений. Так, после проведения этого отбора значимыми в режиме положительных ионов остались лишь некоторые фосфатидилхолины и гексозилцерамиды (табл. 1).

Независимыми липидными факторами, различающими контрольную группу и группу с азооспермией, в режиме отрицательных ионов оказались по одному соединению из групп фосфатидилхолинов, церамидов, сфингомиелинов, фосфатидилглицеролов и окисленных кардиолипинов (табл. 2).
ROC-анализ продемонстрировал, что липидный состав семенной плазмы от пациентов с азооспермией и от фертильных пациентов имел яркие различия, позволившие построенным моделям иметь показатель площади под кривой, достигавший 0,94–0,95.
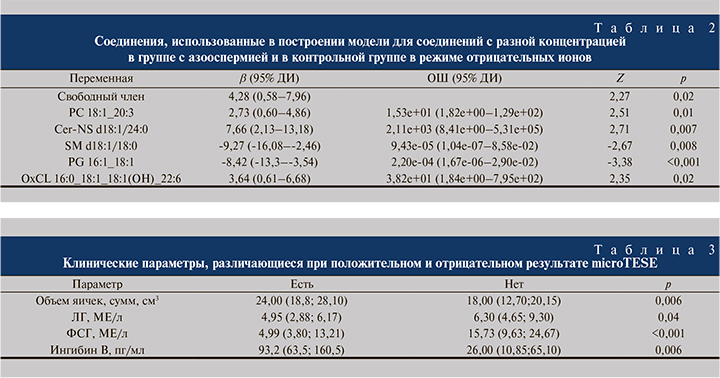
В табл. 3 представлены результаты унивариантного анализа характеристик, по которым отличались пациенты с положительным и отрицательным результатом microTESE. Перечислены клинические параметры, которые могут быть использованы для прогнозирования результатов этой процедуры.
В данной небольшой выборке единственным значимым клиническим предиктором успеха microTESE в мультивариантной модели оказался объем яичек (табл. 4).
Единственным самостоятельным липидомным предиктором успеха microTESE, зафиксированным в режиме отрицательных ионов, был фосфатидилсерин PS 18:0_20:3. В группе с наличием сперматозоидов его содержание составило 4.12e+05(2.09e+05;1.15e+06), в группе без сперматозоидов – 2.41e+05(1.41e+05; 7.47e+05) (p=0,04).
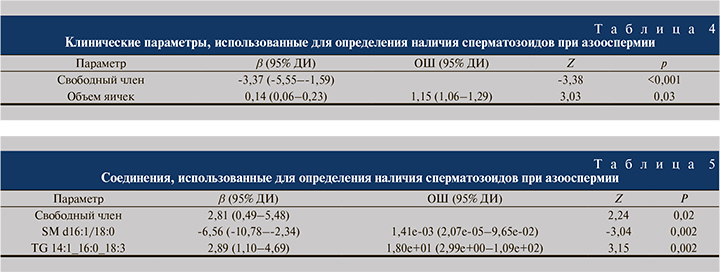
В регрессионной модели, построенной на основании липидомных характеристик, значимым предиктором успеха microTESE было содержание триацилглицерола TG 14:1_16:0_18:3, а предиктором неудачи – содержание сфингомиелина SM d16:1/18:0 (табл. 5).
Кроме того, мы попытались объединить клиническую и липидомную модели, чтобы повысить общую прогностическую ценность (табл. 6).
В результате ROC-анализа установлено, что данные модели оказались не столь эффективны, как модели, дифференцирующие азоо- и нормозооспермию, что было ожидаемо (табл. 7). Площадь под кривой для клинической и липидомной моделей составила 0,72, что, однако, позволяет оценивать их дискриминативную способность как удовлетворительную. Сочетание липидных факторов и единственного клинического параметра (объем яичек) позволило повысить показатель площади под кривой до 0,75.

Обсуждение. Целью настоящего исследования была оценка возможности липидомного анализа семенной плазмы для выявления пациентов с остаточным очаговым сперматогенезом в яичках, которые могут иметь разумные шансы на извлечение сперматозоидов при процедуре microTESE.
Нам удалось продемонстрировать существенные различия протеомного состава семенной плазмы у фертильных мужчин и у мужчин с азооспермией. Были выявлены липидомные предикторы успеха microTESE: фосфатидилсерин PS 18:0_20:3 и триацилглицерол TG 14:1_16:0_18:3 также предиктор неудачи – содержание сфингомиелина SM d16:1/18:0. Данных об этих конкретных липидах в мировой литературе крайне мало. В исследовании [24] сравнивался фосфолипидный и жирнокислотный составы эякулята 8 здоровых и 16 бесплодных мужчин с тератозооспермией. Установлено, что уровень фосфатидилсерина в семенной плазме бесплодных мужчин был увеличен более чем в 2 раза по сравнению со здоровыми мужчинами. Сфингомиелины являются компонентом простасом, при слиянии со сперматозоидами стабилизирующие их плазматическую мембрану, обогащая ее сфингомиелином, холестерином и глицерофосфолипидом. Это предотвращает преждевременное развитие акросомной реакции [25]. Хотя дискриминативная способность липидомной модели в плане прогнозирования успеха microTESE не так высока, как требуется для внедрения в клиническую практику, повышение показателя площади под кривой при ROC-анализе при объединении липидомной и клинической моделей вселяет надежду. Вероятно, внедрение в модель других омиксных маркеров позволит повысить эффективность прогностической модели.
Заключение. Семенная плазма служит богатым источником биологических маркеров для выявления пациентов с остаточным очаговым сперматогенезом в яичках. Липидомный профиль семенной плазмы пациентов контрольной группы с нормальным сперматогенезом имеет явные отличия от профиля пациентов с азооспермией, также выявлена разница липидов между пациентами с положительными и отрицательными исходами microTESE. Это предварительные результаты, и необходимы дальнейшие исследования, чтобы подтвердить информативность полученной панели липидов.



