В соответствии с классификацией, предложенной Международным обществом по удержанию мочи (International Continence Society, ICS), выделяют следующие группы симптомов нарушения функции нижних мочевыводящих путей (СНМП): накопления, опорожнения и после опорожнения [1]. С возрастом значительно увеличивается число больных с различными расстройствами функции НМП, особенно с гиперактивным мочевым пузырем (ГМП) [2, 3]. По данным [4], у 49% мужчин с СНМП выявляются симптомы как опорожнения, так и накопления. До 80% пациентов с выраженной формой инфравезикальной обструкции (ИВО) имеют гиперактивность детрузора, которая отмечается в 2 раза чаще, чем у пациентов без ИВО. У большинства мужчин с СНМП наблюдается комбинация симптомов различных типов. Результаты опроса EpiLUTS в США, Великобритании и Швеции [5] показали, что СНМП, связанные с накоплением мочи, опорожнением мочевого пузыря и возникающие после мочеиспускания, у пациентов часто наблюдаются одновременно. Хотя ИВО вследствие доброкачественной гиперплазии предстательной железы (ДГПЖ) – наиболее частая причина расстройств мочеиспускания у пожилых мужчин, СНМП возможны и при других заболеваниях. Причиной развития симптомов наполнения и/или опорожнения могут стать нейрогенные нарушения, ятрогенные факторы и вмешательства на предстательной железе.
Обструктивное мочеиспускание может быть обусловлено органическими и функциональными причинами. Такое нарушение мочеиспускания наблюдается при наличии препятствия оттоку мочи из мочевого пузыря у мужчин, чаще обусловленного ДГПЖ, раком простаты, стриктурой уретры, воспалительными процессами в задней и передней уретре мужчин. Помимо органических причин, приведших к затрудненному мочеиспусканию, его могут определять и функциональные нарушения мочевого пузыря и/или уретры. Всевозрастающий интерес клиницистов к этим вопросам, с одной стороны, связан с отсутствием единого мнения о критериях диагностики ИВО. С другой – изучение расстройств мочеиспускания и правильная интерпретация полученных данных позволяют определить тяжесть заболевания, уточнить его прогноз, влияют на сроки и методы терапии. Мощным стимулом к изучению функциональных особенностей расстройств мочеиспускания послужило широкое внедрение в практику новых высокоэффективных методов терапии заболеваний простаты и уретры.
Общеизвестно, что ДГПЖ является одним из самых распространенных доброкачественных новообразований у мужчин старшего возраста. Социальная значимость и актуальность этой проблемы подчеркиваются демографическими исследованиями ВОЗ, указывающими на тенденцию роста населения в возрасте более 60 лет. Эта закономерность характерна и для нашей страны.
В основе механизмов нарушения акта мочеиспускания у этой категории больных лежат ИВО и ухудшение функции детрузора. Причиной обструкции служит увеличение простаты в размерах с постепенным сужением просвета мочеиспускательного канала (механический компонент) и повышением тонуса гладкомышечных волокон простаты и задней уретры (функциональный компонент). Новое понимание сущности происходящих при ДГПЖ процессов связано с пересмотром природы обструкции. Ее перестали отождествлять исключительно с механическим фактором.
Нарушение нормального функционирования мочевого пузыря может приводить к таким осложнениям, как мочевая инфекция, вторичный пузырно-мочеточниковый рефлюкс, гидродинамическая обструкция с развитием уретрогидронефроза и хроническая почечная недостаточность [6–9].
Устранение ИВО на ранней стадии заболевания может способствовать быстрому и полному восстановлению нормальной, или практически нормальной, функции мочевого пузыря. Однако, в случае если происходит декомпенсация и она достигла критической точки (уже появились необратимые изменения), устранение ИВО не приводит к улучшению функции мочевого пузыря [10].
Согласно классической физиологической концепции, функция мочевого пузыря обеспечивается антагонистическим взаимодействием симпатического и парасимпатического отделов нервной системы. Рецепторы в области окончаний симпатических нервов мочевого пузыря и мочеиспускательного канала в зависимости от физиологических эффектов, возникающих при их стимуляции, разделяются на α- и β-адренорецепторы (АР). Парасимпатическая нервная система представлена м-холинорецепторами. Гладкая мускулатура мочевого пузыря человека содержит смешанные популяции м2- и м3-подтипов холинорецепторов. Адренергические рецепторы находятся в ЦНС и на мембранах эффекторных клеток, иннервируемых постганглионарными симпатическими нервами. Антагонисты α1-АР (α1-адреноблокаторы [АБ]) являются одними из самых эффективных препаратов для лечения пациентов с СНМП, вызванными ДГПЖ (СНМП/ДГПЖ). На основании анализа результатов лечения эти препараты были признаны Американской урологической ассоциацией препаратами выбора для терапии ДГПЖ [11].
Теория о существовании в симпатической автономной нервной системе двух классов АР, α и β впервые была выдвинута в 1948 г. [12, 13]. С конца XIX в. известно, что мочевой пузырь иннервируется как парасимпатической, так и симпатической автономной нервной системой [14]. В конце 1980-х гг. β3-АР были открыты и впервые обнаружены в жировой ткани, где, как было показано на моделях у животных, они участвовали в липолизе и терморегуляции [15]. Функциональная роль β3-АР в мочевом пузыре человека была подтверждена спустя 20 лет [16, 17]. Все три типа β-АР экспрессируются в мочевом пузыре человека, но 97% всех мРНК β-АР в мочевом пузыре относятся к подтипу β3-АР [17].
В мочевом пузыре фаза наполнения цикла мочеиспускания регулируется прежде всего симпатической нервной системой [18]. Опорожнение мочевого пузыря, напротив, стимулируется высвобождением ацетилхолина в парасимпатических нервных окончаниях [19].
По данным [20], мускариновые рецепторы играют неменьшую роль в патогенезе СНМП/ДГПЖ, чем α1-АР. В той же работе показано, что мускариновые рецепторы концентрируются в передней капсуле и простатической уретре.
Достоверное уменьшение числа холинергических рецепторов при гиперактивном детрузоре показано [21]. Уменьшение количества адренергических нервов также представляется возможным. По-видимому, гиперактивность детрузора при обструкции связана с изменениями как β-, так и α1-АР [22, 23]. Причина гиперактивности детрузора служит типичным примером постсинаптической денервационной гиперчувствительности.
Отмечена корреляция между дисфункцией детрузора и степенью выраженности препятствия к оттоку мочи. Появление неконтролируемых сокращений при цистометрии свидетельствует о гиперактивности детрузора. Последняя наблюдается примерно у 70% мужчин с ДГПЖ и симптомами обструкции [24].
По данным [25], у обследованных 162 больных СНМП/ДГПЖ в 45% наблюдений ИВО сочеталась с гиперактивностью детрузора. Авторы не выявили различий в объеме предстательной железы, максимальной скорости потока мочи (Qmax) и в объеме остаточной мочи между пациентами с наличием и отсутствием при ДГПЖ гиперактивности детрузора. Однако пациенты с гиперактивностью детрузора были более старшего возраста. В работе [26] гиперактивность детрузора диагностирована у 78% больных ИВО.
Согласно данным [27, 28], среди пациентов с ИВО на фоне ДГПЖ, перенесших простатэктомию, при уродинамическом исследовании у 50% мужчин выявляется гиперактивность детрузора. Необходимо отметить, что гиперактивность детрузора также нередко встречается у больных ДГПЖ без признаков обструкции как при наличии, так и при отсутствии неврологических нарушений.
Механизм возникновения гиперактивности детрузора у больного ДГПЖ, по-видимому, обусловлен изменением активности детрузора по отношению к адренергическим влияниям на фоне ослабления его сократительных свойств в результате гипертрофии. Перерастяжение мочевого пузыря, особенно в области мочепузырного треугольника, а также рост гиперплазированной ткани предстательной железы приводят к локальному повышению активности α-АР, относящихся к симпатической нервной системе. Исследования последних лет доказали, что ДГПЖ обусловливает увеличение активности симпатических нервных волокон, что вызывает повышение тонуса гладкомышечных структур основания мочевого пузыря, задней уретры и предстательной железы.
При этом события развиваются в определенной последовательности [29]:
- повышение активности симпатической нервной системы;
- спазм сосудов;
- циркуляторная гипоксия детрузора;
- нарушение биоэнергетики гладких мышц детрузора;
- перегрузка гладкомышечных клеток кальцием;
- нарушение расслабления детрузора;
- уменьшение резервуарной функции мочевого пузыря;
- появление ирритативных симптомов – поллакиурии днем и ночью, ургентных позывов, ургентного недержания мочи.
С другой стороны, одновременное наличие ИВО и гиперактивности детрузора не всегда служит доказательством наличия причинно-следственной связи между ними. Так, показано, что частота гиперактивности детрузора увеличивается с возрастом и может достигать 50% у мужчин старше 70 лет вне зависимости от наличия ИВО [30].
По данным G. N. Sibley [31], ИВО может вызывать гиперактивность детрузора вследствие холинергической денервации детрузора и последовательной гиперчувствительности мускариновых рецепторов к ацетилхолину. Некоторые данные указывают на увеличение роли м2-холинорецепторов с возрастом [32].
В работе [33] 206 пациентам с различными обструктивными заболеваниями НМП были проведены комбинированные уродинамические исследования с целью оценки функционального состояния НМП. Среди обследованных были 128 пациентов с ДГПЖ, 26 – с раком простаты, 41 – со стриктурой уретры, 11 – с деформацией шейки мочевого пузыря. В 120 (58,25%) наблюдениях при комбинированном уродинамическом исследовании выявлена гиперактивность детрузора, средняя длительность жалоб таких пациентов составила 5,34 года. Максимальный цистометрический объем мочевого пузыря пациентов с ГМП составил 183,59 мл, среднее колебание детрузорного давления – 73,44 см водн.ст. Показано, что с увеличением длительности ИВО, снижением комплаенса детрузора, появлением его гиперактивности, увеличением амплитуды сокращений детрузора в момент некоординированного сокращения усугубляется и состояние верхних мочевыводящих путей – от пузырно-мочеточникового рефлюкса до уретерогидронефроза и ХПН [33]. Наиболее часто при уродинамическом исследовании выявлялась гиперактивность детрузора (58,25% больных), которая, возможно, была следствием ИВО и последующей ишемии мочевого пузыря. Эта дисфункция мочевого пузыря могла быть основным ведущим звеном в развитии осложнений ИВО со стороны верхних мочевыводящих путей. Полученные данные [33] соответствуют функциональной классификации ИВО, отражающей степень не только нарушения функции мочевого пузыря, но и изменения уродинамики верхних мочевыводящих путей, а также функциональной способности почек [34].
Таким образом, имеет место высокая распространенность СНМП, особенно комбинированных, среди мужчин, причем симптомы опорожнения встречаются чаще, чем таковые наполнения. Гиперактивность детрузора может быть и обусловлена ИВО, и существовать без ИВО. Несмотря на противоречивость данных, следует признать, что как возраст, так и ИВО могут приводить к постсинаптической денервации мочевого пузыря. Это обстоятельство еще раз подчеркивает важную роль нервной системы в контроле за накопительной функцией мочевого пузыря.
Благодаря появлению новых фармакологических препаратов сегодня стало возможно осуществлять консервативное лечение урологической патологии в тех случаях, которые еще 10 лет назад неизменно ассоциировались с хирургическим вмешательством. С другой стороны, это обстоятельство потребовало более глубоких знаний физиологии и патофизиологии мочевыводящих путей.
Наиболее часто применяемыми в урологической практике α-АБ – препаратами первой линии в лечении НМП у мужчин – являются тамсулозин, теразозин, доксазозин, альфузозин и силодозин. α1-Адреноблокаторы отличаются уроселективностью и, соответственно, переносимостью: селективный α1-АБ тамсулозин пациенты переносят лучше, чем другие α1-АБ без подтиповой селективности, например доксазозин или теразозин [35], что особенно важно в отношении нежелательных явлений со стороны сердечно-сосудистой системы [36].
Селективная блокада α1A-АР может обеспечить эффективное лечение СНМП/ДГПЖ [37]. При наличии селективности в отношении α1A-АР препарат будет вызывать меньше побочных эффектов со стороны сердечно-сосудистой системы по сравнению с неселективным препаратом.
Детрузорная гиперактивность исчезает у 60% больных ДГПЖ после хирургической ликвидации препятствия оттоку мочи. Гиперактивный мочевой пузырь отмечается у 52–80% мужчин с ИВО вследствие ДГПЖ, у 38% мужчин с ИВО вследствие ДГПЖ симптомы ГМП сохраняются после оперативного устранения обструкции [38, 39]. В то же время у 15–20% больных ДГПЖ после операции сохраняются ирритативные симптомы: учащенное мочеиспускание, ноктурия, повелительные (ургентные) позывы, ургентное недержание мочи. В первую очередь это относится к случаям, когда отсутствует корреляция между выраженностью гиперактивности детрузора и ИВО. По данным [40], из 100 больных ИВО только у 63% наблюдается нивелирование гиперактивного детрузора в стабильный после простатэктомии.
В настоящий момент наиболее часто в лечении ГМП применяются препараты, воздействующие на мускариновые рецепторы мочевого пузыря. Доказано, что опосредованная ацетилхолином стимуляция м-холинорецепторов детрузора играет ведущую роль как при нормальных, так и при «нестабильных» сокращениях детрузора [41].
На сегодняшний день в России используются следующие м-холиноблокаторы (м-ХБ): солифенацин, оксибутинин, троспия хлорид, толтеродин. Наиболее селективным в отношении мочевого пузыря является солифенацин [42, 43]. Хорошая его переносимость пациентами старшей возрастной группы служит значимым моментом в пользу выбора данного препарата в лечении ургентных расстройств мочеиспускания, так как подобные пациенты и без того отягощены сопутствующими заболеваниями, что осложняет прием препаратов с большим количеством побочных эффектов [44].
У больных ДГПЖ с симптомами ГМП после проведения оперативного лечения симптомы наполнения сохраняются достоверно реже при предоперационной терапии м-ХБ, чем при лечении α1-АБ, – 12,5 против 27,5% [45]. В работе [46] при сопоставлении двух групп больных по степени снижения выраженности симптомов на основании данных дневника мочеиспусканий выявлено, что на фоне приема м-ХБ наблюдается уменьшение проявлений симптомов ГМП в большей степени, чем при терапии α-АБ. При этом статистически значимый характер носили различия по показателям частоты недержания мочи и объема мочи при ургентных позывах (р<0,05). Что касается такого осложнения, как острая задержка мочи, то ни в той, ни в другой группе не было отмечено ни одного подобного случая.
До 50% пациентов после трансуретральной резекции (ТУР) назначается медикаментозная терапия СНМП, в основном м-ХБ, что связано с выраженными симптомами ГМП [47]. Согласно данным [48], 30,4% пациентов, перенесших ТУР, получали медикаментозную терапию СНМП, при этом антихолинергические препараты были наиболее часто назначаемыми. Адекватный отбор пациентов на дооперационном этапе позволит снизить частоту развития осложнений и риск дополнительного лечения после операции [48].
Результатом исследования [20] стала разработка новой схемы терапии СНМП/ДГПЖ комбинацией антагонистов α1-АР и антимуcкариновых препаратов. В руководстве Европейской ассоциации урологов (EAU) содержатся рекомендации, согласно которым вышеуказанная комбинированная терапия может быть использована в лечении пациентов с умеренными или выраженными СНМП, если при монотерапии любым из указанных препаратов выраженность терапевтического эффекта была недостаточной [49].
Комбинированная терапия α1-АБ и м-ХБ демонстрирует высокую терапевтическую эффективность для пациентов с ДГПЖ в сочетании с ГМП [50]. На фоне подобного лечения не выявлено существенного увеличения объема остаточной мочи, равно как и развития эпизодов острой задержки мочи [51–56]. В нескольких исследованиях показано, что добавление антимускаринового препарата к α1-АБ уменьшает выраженность симптомов, связанных с накоплением мочи, которые сохранялись после монотерапии α1-АБ [56–64].
Каковы же основные показания к такой комбинированной терапии? Основными претендентами для подобной схемы лечения считаются мужчины с сочетанием ИВО и персистирующими симптомами ГМП, а также с низким риском возникновения острой задержки мочи, имеющие следующие показатели:
- 5 мл/с< Qmax <15 мл/с;
- частота мочеиспусканий ≥8 за 24 ч;
- ургентные позывы ≥1 за 24 ч, с ургентным недержанием мочи или без;
- ноктурия;
- суммарный балл IPSS ≥12;
- балл QоL ≥3;
- объем остаточной мочи <150 мл;
- отсутствие острой задержки мочи в анамнезе.
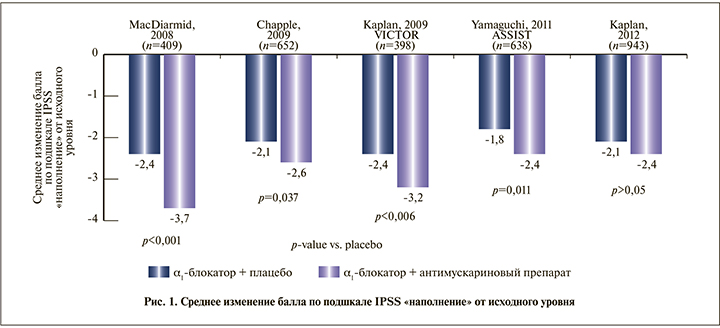
На рис. 1 представлены результаты, полученные в пяти 12-недельных двойных слепых рандомизированных контролируемых исследованиях (РКИ) с участием мужчин в возрасте 40–50 лет и старше, у которых симптомы, связанные с накоплением мочи, сохранялись после 4 и более недель терапии α1-АБ [56–60].
Для оценки динамики СНМП, связанных с накоплением мочи, использовали соответствующую подшкалу IPSS (Международная шкала оценки симптомов со стороны предстательной железы). В 4 из 5 исследований симптомы, связанные с накоплением мочи, которые сохранялись после первичной терапии α1-АБ, статистически значимо улучшились после добавления антимускаринового препарата (рис. 1).
В другом исследовании показано, что терапия первой линии с применением комбинации α1-АБ с антимускариновым препаратом может обеспечить быстрое облегчение симптомов у мужчин с причиняющими беспокойство симптомами наполнения и опорожнения [61]. В 12-недельном двойном слепом плацебо-контролируемом РКИ с участием 176 пациентов в возрасте 50 лет и старше с СНМП, связанными с мочеиспусканием, и умеренными или выраженными СНМП, связанными с накоплением мочи, были рандомизированы для терапии первой линии с применением α1-АБ и плацебо или α1-АБ в комбинации с антимускариновым препаратом. Как симптомы наполнения, так и качество жизни статистически значимо улучшились у мужчин, получавших комбинацию антимускаринового препарата с α1-АБ по сравнению с мужчинами, получавшими плацебо и α1-АБ. В отношении улучшения симптомов опорожнения статистически значимых различий между группами выявлено не было [61].
Руководствуясь положительными результатами применения комбинированной терапии α1-АБ и м-ХБ, был разработан новый препарат Везомни для лечения комплекса симптомов наполнения (ургентные позывы и учащенное мочеиспускание) и опорожнения у мужчин с ДГПЖ. Везомни 6 мг/0,4 мг является комбинацией антимускаринового препарата солифенацина и α1-АБ тамсулозина в лекарственной форме ОКАС. Каждая двухслойная таблетка содержит один слой солифенацина сукцината (6 мг), что соответствует 4,5 мг солифенацина, и один слой тамсулозина гидрохлорида (0,4 мг), что соответствует 0,37 мг тамсулозина.
Солифенацин подавляет гиперактивность детрузора и уменьшает выраженность симптомов, связанных с накоплением мочи. Тамсулозин ОКАС расслабляет гладкую мускулатуру предстательной железы, капсулы, простатической части мочеиспускательного канала и шейки мочевого пузыря и уменьшает в основном выраженность симптомов опорожнения, в меньшей степени – симптомов наполнения.
Использование комбинации солифенацина с тамсулозином в качестве двух отдельных препаратов также изучали в исследованиях фазы IV, в ходе которых оценивали динамику умеренных или выраженных симптомов наполнения (ургентные позывы, учащенное мочеиспускание) и опорожнения при СНМП/ДГПЖ у мужчин. К ним относятся американское исследование VICTOR и японское исследование ASSIST [56, 59]. Исследование VICTOR представляло собой многоцентровое двойное слепое рандомизированное плацебо-контролируемое исследование с участием 398 мужчин с СНМП, включая симптомы, связанные с накоплением мочи, которые сохранялись после 4 и более недель монотерапии тамсулозином 0,4 мг [56]. Сравнивали эффективность 12-недельной монотерапии тамсулозином 0,4 мг и комбинации солифенацина 5 мг и тамсулозина 0,4 мг (в качестве однокомпонентных препаратов). В исследовании ASSIST аналогичного дизайна, в котором приняли участие 638 пациентов с СНМП, включая симптомы, связанные с накоплением мочи, которые сохранялись после 6 и более недель монотерапии тамсулозином 0,2 мг [59]. В данной работе сравнивали эффективность 12-недельной монотерапии тамсулозином 0,2 мг и комбинации солифенацина (2,5 и 5 мг) и тамсулозина 0,2 мг в качестве однокомпонентных препаратов. Результаты обоих исследований показали, что при использовании солифенацина с тамсулозином наблюдалось статистически значимо более выраженное улучшение симптомов, связанных с накоплением мочи, по сравнению с монотерапией тамсулозином. Несмотря на то что в этих исследованиях не применяли препарат Везомни в таблетках и их дизайн отличался от такового исследований с применением указанного препарата, их результаты вносят вклад в доказательную базу эффективности комбинации солифенацина с тамсулозином в отношении улучшения умеренных и выраженных симптомов наполнения (ургентные позывы, учащенное мочеиспускание) и опорожнения на фоне ДГПЖ.
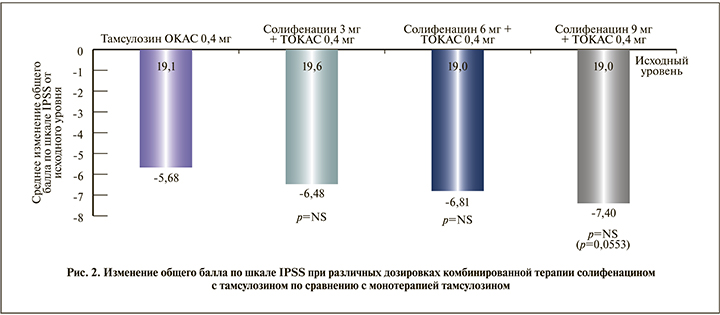
В исследовании фазы II с целью определения оптимальной дозы (SATURN) были оценены эффективность и безопасность применения комбинации солифенацина с тамсулозином ОКАС [62]. Данная комбинация обеспечивала большую эффективность по сравнению с монотерапией тамсулозином ОКАС и характеризовалась хорошей переносимостью в подгруппе мужчин с СНМП, связанными с накоплением мочи и опорожнением мочевого пузыря. В исследовании NEPTUNE определяли наличие дополнительной пользы при применении комбинированного препарата солифенацина и тамсулозина ОКАС по сравнению с монотерапией тамсулозином ОКАС и плацебо при лечении на протяжении 12 нед. мужчин с умеренными и тяжелыми симптомами, связанными с накоплением мочи и опорожнением [63]. Кроме того, эффективность и безопасность применения Везомни были оценены в подтверждающем исследовании фазы III (NEPTUNE) и в долгосрочном продолженном исследовании фазы III (NEPTUNE II) [64]. Исследование NEPTUNE II представляло собой открытое 40-недельное продолжение исследования NEPTUNE, разработанное для оценки долгосрочной безопасности и эффективности комбинации солифенацина 6 или 9 мг и тамсулозина ОКАС 0,4 мг для мужчин с СНМП/ДГПЖ, связанными с накоплением и опорожнением. В исследовании фазы III NEPTUNE обнаружено, что комбинация солифенацина и тамсулозина ОКАС приносит дополнительную пользу по сравнению с монотерапией тамсулозином ОКАС и применением плацебо при лечении на протяжении 12 нед. мужчин с умеренными и выраженными симптомами, связанными с накоплением мочи и опорожнением на фоне ДГПЖ. По данным исследования NEPTUNE, препарат Везомни значительно уменьшает ургентные позывы и частоту мочеиспусканий – на 84% по сравнению с плацебо, в то время как тамсулозин ОКАС менее эффективен в отношении данных симптомов (на 52% по сравнению с плацебо). На фоне приема Везомни и тамсулозина ОКАС значительно улучшается оценка по шкале IPSS по сравнению с плацебо – на 30 и 15% соответственно. По данным [64], положительная динамика общего балла по шкале IPSS и по шкале TUFS (Общая шкала оценки ургентных позывов и частоты мочеиспусканий) наблюдалась на протяжении 4 нед. применения комбинации и сохранялась до 52 нед. Аналогичное улучшение наблюдалось и в отношении числа баллов по подшкалам, связанным с накоплением мочи и опорожнением, и для переменных из дневника мочеиспусканий. Качество жизни и беспокойство, причиняемое симптомами, характеризовались положительной динамикой при применении комбинации после 4 нед., причем достигнутый результат сохранялся до 52 нед. Большинство пациентов были удовлетворены как эффективностью, так и безопасностью лечения. При комбинированной терапии наблюдалось количественное улучшение по сумме баллов по шкале IPSS по сравнению с монотерапией тамсулозином ОКАС 0,4 мг, однако различия не были статистически значимыми (рис. 2). Таким образом, у мужчин с умеренными или выраженными симптомами наполнения (ургентные позывы и учащенное мочеиспускание) и опорожнения на фоне ДГПЖ применение Везомни устраняет симптомы, связанные с накоплением мочи, более значимо, чем монотерапия тамсулозином ОКАС, с сопоставимой эффективностью в отношении уменьшения симптомов опорожнения [63].
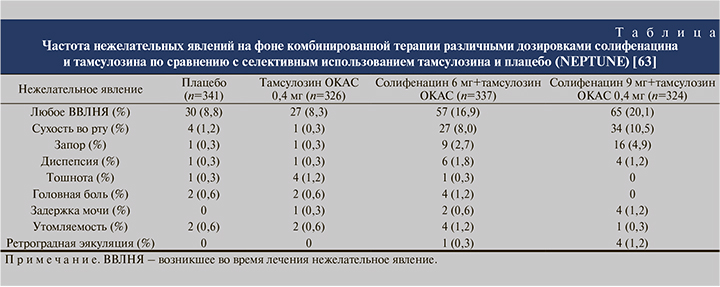
Комбинация солифенацина и тамсулозина показала себя положительно и в вопросах безопасности и переносимости (см. таблицу).
По данным проведенных исследований:
- комбинированная терапия фиксированной дозой тамсулозина 0,4 мг+солифенацин 6 мг показала значимо лучший результат лечения по сравнению с плацебо, была более эффективной по сравнению с селективным использованием тамсулозина 0,4 мг в отношении симптомов наполнения и качества жизни мужчин с СНМП (симптомы наполнения+симптомы опорожнения);
- комбинированная терапия с использованием высокой дозировки солифенацина (тамсулозин 0,4 мг+солифенацин 9 мг) не выявила дополнительных преимуществ по сравнению с более низкой дозировкой солифенацина;
- обе дозировки солифенацина (6 и 9 мг) при комбинированной терапии СНМП были хорошо переносимыми.
Таким образом, новый препарат Везомни – эффективное и безопасное средство для лечения комбинированных СНМП (затрагивающих как фазу наполнения мочевого пузыря, так и фазу его опорожнения) у мужчин.



