Гиперактивный мочевой пузырь – симптомокомплекс, включающий ургентные позывы к мочеиспусканию, учащенное дневное и ночное мочеиспускание, в ряде случаев – и ургентное недержание мочи.
Так, недержание мочи, по разным данным, встречается у 10–50% пациентов [1–3]. Большая часть из них страдают именно ургентным типом инконтиненции. Современные эпидемиологические исследования свидетельствуют о большой социальной значимости данного состояния. Так, в американском исследовании NOBLE [The National Overactive Bladder [Evaluation (n=5204)] признаки гиперактивного мочевого пузыря определялись у 16% мужчин и у 16,9% женщин [4].
Одно из крупнейших международных исследований, EPIC (n=19165), проведенное в четырех странах Европы и Канаде, позволило выявить, что симптомы гиперактивного мочевого пузыря отмечали 10,8% мужчин и 12,8% женщин [5]. В России встречаемость гиперактивного мочевого пузыря составляет у мужчин 18%, у женщин – 28% популяции [6]. И лишь треть обратившихся пациентов получают адекватную терапию.
В настоящее время первой линией терапии данного состояния служат м-холиноблокаторы. В Российской Федерации для лечения таких больных доступны неселективные (оксибутинин, толтеродин, фезотеродин, троспиум) и селективный (солифенацин) антимускариновые препараты. Все перечисленные лекарственные средства имеют самый высокий уровень доказательности (1) и степень рекомендаций А. Однако данные статистики показывают, что ряд больных отказывается от долгосрочного приема м-холиноблокаторов либо в связи с побочными эффектами, либо из-за недостаточной эффективности [7]. Это обстоятельство побудило мировое научное сообщество к поиску альтернативных методов терапии.
Мирабегрон – селективный агонист β3-адренорецепторов (см. рисунок), новое слово в лечении пациентов с гиперактивным мочевым пузырем.
Адренорецепторы – это трансмембранные рецепторы, сопряженные с G-белком, реагирующие на адреналин и норадреналин. В 1948 г. фармаколог R. P. Ahlquist впервые опубликовал теорию о существовании в симпатической нервной системе млекопитающих двух классов адренергических рецепторов – α и β [9]. Только в 1967 г. A. M. Lands et al. [10] показали существование двух типов β-адренорецепторов. В работе описано, что оба рецептора располагаются во всех тканях, однако обычно в том или ином органе один из этих двух типов преобладает. Именно этот труд лег в основу концепции селективности β-адреноблокады. Однако только спустя 10 лет стало понятно, что основным β-адренорецептором мочевого пузыря является не β1 и не β2. A. Nergårdh et al. [11] изучали β-адренорецепторы мочевых пузырей кошки и человека. В обеих моделях катехоламиновая стимуляция вызывала расслабление детрузора. Однако в человеческом мочевом пузыре рецепторы не подходили под характеристики ни β1-, ни β2-типов адренорецепторов. Авторы предположили, что β-адренергические рецепторы пузыря человека относятся к третьему типу [11]. Данное наблюдение в то время не нашло должного применения. Однако изучение β3-рецепторов было продолжено. Появились работы, описывающие наличие данного рецептора в белом, и преимущественно, в буром жире грызунов, его участие в метаболических процессах и терморегуляции [12, 13]. Во многом благодаря этим трудам изучение β3-адренорецепторов стало перспективным направлением для ряда фармацевтических компаний.
Так, в начале 2000-х гг. была создана первая молекула мирабегрона под кодовым названием YM178. Начались клинические исследования данного вещества сразу по трем направлениям: ожирение при сахарном диабете 2 типа, гиперактивный мочевой пузырь и симптомы нижних мочевых путей на фоне инфравезикальной обструкции. Сегодня с уверенностью можно сказать, что мирабегрон – хорошо изученный препарат. Всего было проведено 29 клинических фармакологических и 3 исследования (фаза 2) при изучении диабета и инфравезикальной обструкции, а также 3 (фаза 2) и 6 (фаза 3) – при гиперактивном мочевом пузыре.
 Так, мероприятиями одними из первых линий лечения сахарного диабета 2 типа считаются соблюдение диеты и увеличение физической нагрузки, что направлено на снижение веса. Соответственно, повышение затрат энергии за счет активации эндогенной бурой жировой ткани является потенциальным подходом к лечению ожирения и диабета. Как уже было описано выше, агонисты β3-адренергических рецепторов стимулируют метаболические процессы у грызунов [12, 13]. Однако подобное действие не было подтверждено в человеческой популяции. Видимо, это связано с разницей в строении рецепторов грызунов и человека.
Так, мероприятиями одними из первых линий лечения сахарного диабета 2 типа считаются соблюдение диеты и увеличение физической нагрузки, что направлено на снижение веса. Соответственно, повышение затрат энергии за счет активации эндогенной бурой жировой ткани является потенциальным подходом к лечению ожирения и диабета. Как уже было описано выше, агонисты β3-адренергических рецепторов стимулируют метаболические процессы у грызунов [12, 13]. Однако подобное действие не было подтверждено в человеческой популяции. Видимо, это связано с разницей в строении рецепторов грызунов и человека.
В общественном отчете Astellas Австралийскому департаменту здравоохранения сообщалось, что эффекты не воспроизводятся на собаках, обезьянах и людях [14].
На сегодняшний день агонист β3-адренорецепторов не прошел дальше второй фазы клинических испытаний для лечения метаболических нарушений. Однако ранее считалось, что существует только два типа жировых клеток: под действием симпатических нервов белая жировая ткань накапливает и хранит химическую энергию, в то время как бурая потребляет энергию и выделяет тепло. С возрастом количество бурой ткани в организме человека уменьшается. Недавнее открытие у взрослых людей термогенных бежевых, или брайт- (brite – аббревиатура от «brown–in-white»), адипоцитов может радикально изменить ситуацию. Эти клетки являются некой промежуточной формой между белыми и бурыми. Уникальность брайт-адипоцитов в том, что 10–30% от всего из митохондриального белка составляет протеин UCP1 – главный элемент термогенного механизма [15]. Дискутируется вопрос о путях появления этих жировых клеток. В работе Y. H. Lee et al. [16] показано, что пищевые или фармакологические стимулы могут значительно изменить клеточный фенотип белой жировой ткани в сторону бурой. Авторы доказали, что введение мышам β3-агониста CL316,243 провоцировало усиленную пролиферацию и дифференцировку клеток, экспресcирующих фактор роста тромбоцитов, в сторону брайт-адипоцитов [16]. Освобожденный из симпатических окончаний норадреналин через β3-адренорецепторы и протеинкиназу А запускает липолиз. Последующая активация β3-рецепторов бежевой жировой ткани будет стимулировать повышение потребления энергии и термогенез [17].
В плацебо-контролируемом проекте [17] здоровые мужчины получали 200 мг мирабегрона в сутки. Посредством позитрон-эмиссионной томографии было выявлено усиление термогенной активности жировой ткани. Скорость метаболизма увеличилась в среднем на 203±40 ккал/сут (+13%, p=0,001) в активной группе по сравнению с когортой плацебо [18]. Стоит отметить, что использовалась доза, в 4 раза превышающая рекомендованную.
В настоящее время проходит исследование 1-й фазы NCT02919176, цель которого изучить возможности активации бурой и бежевой жировой ткани в лечении метаболических нарушений при сахарном диабете 2 типа. Результаты данной работы должны быть опубликованы в 2020 г. [19].
Эффекты β3-адренорецепторов в детрузоре человека изучались сразу в нескольких научных группах [20–24]. Так, в гладкой мускулатуре данного органа присутствуют все типы рецепторов, однако плотность β3 составляет 97% общей мРНК транскрипции. А в работах [21, 22] доказано, что именно они ответственны за β-опосредованное расслабление детрузора. Таким образом, исследования японских ученых стали фундаментом для клинической разработки и изучения принципиально новых лекарственных средств для контроля симптомов гиперактивного мочевого пузыря.
Известно, что функция мочеиспускания контролируется как симпатической, так и парасимпатической нервной системой. Мочевой пузырь – орган, богатый различными рецепторами. Основными рецепторами, способными оказывать влияние на функцию нижних мочевых путей, считаются α1, β3, м3 и м2. С одной стороны, сокращение детрузора здорового человека опосредовано выделением ацетилхолина и его влиянием на м-холинорецепторы. М3-холинорецепторы отвечают за непосредственное сокращение мочевого пузыря, в то время как М2 участвуют в этом процессе косвенно – через аденилатциклазу посылают импульсы в симпатическую нервную систему к β3-рецепторам, ответственным за состояние покоя (фазу накопления мочевого пузыря). Получая сигнал от м2-адренорецепторов, β3-адренорецепторы прекращают свое действие и создаются предпосылки для сокращения детрузора. С другой стороны, в работах [25, 26] было доказано, что при патологических состояниях у людей нехолинергические стимулы, такие как АТФ или брадикинин, также могут существенно способствовать сокращению мочевого пузыря.
Важно понимать, что агонисты β-адренорецепторов могут влиять на функцию детрузора на нескольких уровнях [27]. На клеточном уровне они способствуют формированию цАМФ [28, 29], активации K+- и ингибированию Са2+-каналов, что способствует релаксации гладкой мускулатуры [30]. На уровне ткани агонисты β-адренорецепторов могут не только вызывать прямое расслабление, но и противодействовать сокращению через мускариновые рецепторы [31–33]. Таким образом, доказанным фактом является то, что β-адренорецепторы ингибируют выделение ацетилхолина и АТФ и способствуют высвобождению NO, который в свою очередь может воздействовать на C- и Aδ-афферентные нервы, приводя к расслаблению детрузора. По определению, антагонисты мускариновых рецепторов влияют только на холинергические раздражители, в то время как агонисты β-адренорецепторов работают против всех известных сократительных медиаторов [34].
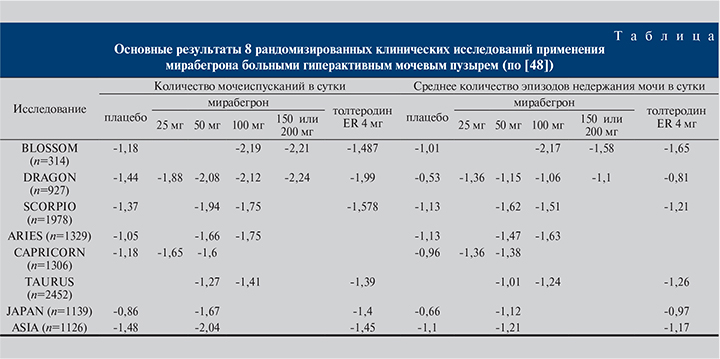
Эффективность и безопасность мирабегрона изучены в нескольких двойных слепых рандомизированных клинических испытаниях мужчин и женщин с гиперактивным мочевым пузырем: BLOSSOM [35, 36], DRAGON [37, 38], ARIES [39, 40] CAPRICORN [41] TAURUS [42, 43], SCORPIO [44, 45], ASIA [46], JAPAN [47]. Семь из них были плацебо-контролируемые. Во все проекты набирали как мужчин, так и женщин в возрасте старше 18 лет, страдавших симптомами гиперактивного мочевого пузыря в течение как минимум 3 мес. до начала исследования. Критериями включения были число мочеиспусканий ≥8 раз в сутки с эпизодами ургентности ≥3 за 72 ч. Императивность оценивали с использованием шкалы восприятия пациентом интенсивности ургентности (The patient perception of intensity of urgency scale – PPIUS). Участвовали больные как с «сухим», так и с «мокрым» гиперактивным мочевым пузырем. Общее число участников составило более 10,5 тыс. человек.
Как видно из таблицы, в ходе испытаний доказана результативность исследуемого препарата в снижении частоты мочеиспусканий и эпизодов ургентности. Эффекты мирабегрона и толтеродина медленного высвобождения были сравнимыми, а различия между ними не достигли статистической значимости.
Отдельного внимания заслуживает исследование TAURUS [42, 43], так как его целью была оценка как эффективности, так и безопасности мирабегрона при длительном применении. Пациенты, включенные в проект, получали лечение на протяжении 52 нед. На 8-й неделе участия протокол исследования позволял титровать дозу препарата до 100 мг в сутки больным с недостаточной эффективностью. Исследователи отметили тенденцию к дальнейшему улучшению симптоматики. Однако при окончательной оценке изменения по сравнению с исходным уровнем были сопоставимыми с таковыми у пациентов, получавших мирабегрон в дозе 50 мг. На протяжении 52 нед. отмечено стойкое улучшение симптоматики без нивелирования эффекта. Существенных различий по частоте нежелательных явлений лекарственных средств между группами 50 и 100 мг не было отмечено. Побочными реакциями были подъем артериального давления, сухость во рту, запоры и головная боль. Эти состояния одинаково часто наблюдались у больных, принимавших как мирабегрон, так и толтеродин медленного высвобождения. Исключением стало возникновение чувства сухости во рту, которое чаще регистрировали в группе холиноблокаторов. Большинство нежелательных явлений имели слабую или умеренную степень выраженности, что не потребовало отмены назначенного лечения.
В настоящее время Европейская ассоциация урологов рекомендует антихолинергические препараты на первой ступени терапии, а мирабегрон – пациентам, которые неадекватно реагируют на другие методы лечения. В то же время Американская урологическая ассоциация уже поставила β3-агонисты в один ряд с м-холиноблокаторами в качестве препаратов первой линии терапии симптомов гиперактивного мочевого пузыря.
Одним из интересных и перспективных направлений будущих исследований является изучение взаимодействия мирабегрона с α-адренорецепторами. Так, одной из первых стала работа E. C. Alexandre [49]. В экспериментальной модели использовались гладкие миоциты мышей и крыс, взятые из уретры, простаты, семевыносящих протоков, аорты и селезенки. Предварительно мышечную ткань приводили в спастическое состояние посредством фенилэфрина (агониста α-адренорецепторов). Мирабегронопосредованная релаксация отмечена в миоцитах уретры мышей, семявыносящих протоков, предстательной железы и аорты крыс. Авторы сделали вывод, что эффекты мирабегрона в гладких миоцитах уретры служат результатом агонизма β3-адренорецепторов вместе с антагонизмом α1A и α1D [49]. Подобные эффекты в гладких мышечных элементах предстательной железы человека были также отмечены в работе [50]. Теория E. C. Alexandre вызвала диссонанс в научном мире [51]. На сегодняшний день консенсуса не достигнуто. Надо отметить, что V. W. Nitti et al. [52] провели рандомизированное двойное слепое плацебо-контролируемое клиническое исследование, в котором оценивали уродинамические изменения у мужчин с инфравезикальной обструкцией на фоне приема 50 или 100 мг мирабегрона. Работа показала, что лекарственное средство не оказывает негативного влияния на максимальную скорость мочеиспускания, давление детрузора в этот момент или индекс сокращений мочевого пузыря [52]. При этом авторы не описали статистически значимых улучшений параметров оттока мочи ни при использовании 50 мг, ни на фоне приема 100 мг. Видимо, вопрос о влиянии мирабегрона на α-адренорецепторы предстоит решить в будущих исследованиях.
Еще одним перспективным направлением использования мирабегрона служит назначение при хронической сердечной недостаточности.
Сила, скорость сокращения миокарда и его расслабление контролируются β1-адренорецепторами. В условиях сердечной недостаточности под действием катехоламинов симпатической нервной системы происходит постоянная активация β1- и β2-адренорецепторов. Данное воздействие приводит к их десенсибилизации (снижению чувствительности) и интернализации (погружению внутрь клетки). Следствиями становятся снижение сократимости, изменение формы сердца и потеря кардиомиоцитов. В экспериментальной работе [53] показано, что при длительной стимуляции кардиальной ткани норадреналином повышается функционал β3-адренорецепторов, активация которых может уменьшать перегрузку кардиомиоцитов и окислительный стресс при сердечной недостаточности [53].
В исследовании [54] пациенты принимали либо мирабегрон по 150 мг 2 раза в день, либо плацебо в течение 6 мес.
У больных, где изначально фракция выброса левого желудочка не превышала 40% от нормы, мирабегрон значительно увеличивал этот показатель по сравнению с пациентами, не получавшими активный препарат. Хотя статистически значимых различий получено не было, авторы предположили, что мирабегрон может быть полезным при лечении сердечной недостаточности у пациентов с уменьшенной фракцией выброса левого желудочка.
В данный момент кардиологи проводят многоцентровое исследование по оценке эффективности мирабегрона в профилактике сердечной недостаточности Beta3_LVH. В 2020 г. научное сообщество получит исчерпывающую информацию в этой сфере [55].
Таким образом, на сегодняшний день очевидно, что мирабегрон – эффективный препарат для лечения пациентов с гиперактивным мочевым пузырем с минимальным количеством побочных явлений. Данный факт увеличивает приверженность больных к назначенной терапии. Лекарственное средство может использоваться как пациентами, имеющими противопоказания к применению антимускариновых препаратов, так и коморбидными больными. Возможно, в Российских рекомендациях мирабегрон встанет в один ряд с м-холиноблокаторами как препарат первой линии терапии ургентного недержания мочи. Вполне вероятно, в ближайшем будущем откроются новые возможности применения данного β3-агониста для коррекции ожирения и терапии сердечной недостаточности.



