Введение. На сегодняшний день прогноз течения рака простаты определяют степень дифференцировки клеток опухоли, стадия заболевания, уровень ПСА сыворотки крови. Тем не менее до сих пор повсеместно наблюдается как гипердиагностика и лечение клинически незначимого рака простаты [1], так и несвоевременное выявление агрессивных и прогностически неблагоприятных форм заболевания [2].
Одним из признаков, характерных для любого типа злокачественных клеток, является нарушение клеточного метаболизма [3], и рак простаты также не является исключением. Однако фенотип, характерный для классического эффекта Варбурга – активное поглощение глюкозы и выделение массы лактата в ходе гликолиза при достаточном снабжении клеток кислородом, проявляется лишь на поздних стадиях заболевания и является прогностически неблагоприятным фактором [4].
Семейство переносчиков монокарбоксилатов представлено 14 типами, однако экспериментально доказано, что лишь типы MCT1-MCT4 участвуют в транспорте лактата, пирувата, кетоновых тел и других метаболически важных веществ через клеточную мембрану. Также было указано, что переносчики монокарбоксилатов 1-го и 4-го типов принимают активное участие в метаболизме лактата в клетках рака простаты и стромы опухоли [5].
Задачей исследования стало измерение уровня экспрессии переносчиков монокарбоксилатов 1-го и 4-го типов в опухоли аденокарциномы простаты различной степени злокачественности и определении роли полученных данных в прогнозировании течения и эффективности радикального лечения заболевания.
Материалы и методы
Материал исследования. Клинико-морфологическое исследование архивного операционного материала проводили на базе Централизованного патологоанатомического отделения ФГАОУ ВО «Первый МГМУ им. И. М. Сеченова» МЗ России (Сеченовский Университет) (Москва) в период с июня 2015 по март 2017 г. Анализ собственной базы данных позволил идентифицировать 100 лиц, перенесших операцию радикальной простатэктомии в клинике НИИ урологии и репродуктивного здоровья человека ФГАОУ ВО «Первый МГМУ им. И. М. Сеченова» МЗ России (Сеченовский Университет) по поводу рака простаты. В исследование были включены пациенты с гистологически подтвержденной аденокарциномой простаты. Оценен ряд клинических параметров (возраст, уровень ПСА, объем простаты, балл ISUP [International Society of Urological Pathology]), а также факт наличия биохимического рецидива после операции (повышение ПСА>0,2 нг/мл). При стандартном гистологическом исследовании с окрашиванием гематоксилином и эозином во всех наблюдениях проводился подсчет баллов согласно шкале Глисона в модификации J. Epstein et al. (2016), а также оценивалось наличие положительных хирургических краев и экстрапростатическое распространение. Положительными хирургические края резекции считали в случаях, при которых комплексы аденокарциномы контактировали с краем простаты, при этом измеряли число положительных блоков, линейный размер края в миллиметрах. Экстрапростатическое распространение включало наличие опухолевых клеток в перипростатической жировой клетчатке, периневральных пространствах сосудисто-нервного пучка, регионарных лимфатических узлах. Медиана наблюдения составила от 12 до 60 мес.
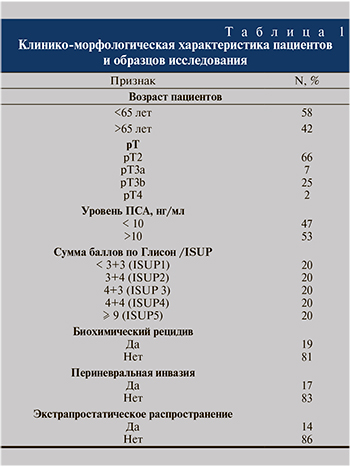
Подробная клинико-морфологическая характеристика отражена в табл. 1.
Иммуногистохимическое исследование
Иммуногистохимическое исследование материала проводили на парафиновых срезах согласно стандартному протоколу. В работе использованы следующие антитела к антигенам человека: МСТ1 (монокарбоксилатный транспортер 1) (разведение 1:400, ANTI-SLC16A1, Sigma-AldrichCo. LLC, США); МСТ4 (монокарбоксилатный транспортер 4) (разведение 1:200, ANTI-SLC16A3, Sigma-AldrichCo. LLC, США).
Ткани простаты фиксировали в 10%-ном забуференном формалине (рН 7,4) и заливали в парафин. Использован парафин с температурой плавления +540°С. Нарезали серийные срезы толщиной 5 мкм и наклеивали на полиL-лизиновые стекла. Депарафинизация выполнена в термостате при температуре +600С в течение 1 ч. После погружения в ксилол срезы регидрировались проводкой по спиртам в убывающей концентрации в течение 15 мин. Блокирование эндогенной пероксидазной активности выполнено с помощью 3%-ной перекиси водорода в течение 10 мин. Для проведения иммуногистохимической реакции на срезы наносили 50 мкл разведенной первичной сыворотки. Срезы инкубировались при 37°С в течение 30 мин. Интенсивность иммуногистохимической реакции в каждом препарате контролировалась под микроскопом: после достижения необходимой интенсивности окрашивания срезы отмывали в дистиллированной воде, затем в течение 3 мин докрашивали гематоксилином Майера.
Для МСТ 1 оценивалась только плотность экспрессии эпителия:
- 0 – отрицательная реакция – экспрессия отсутствует.
- 1 – слабоположительная реакция – экспрессия в <20% клеток.
- 2 – умеренная реакция – экспрессия положительная от 20–40% клеток.
- 3 – выраженная реакция – экспрессия положительная в более чем 40% клеток.
Паттерны окрашивания эпителия и стромы с помощью МСТ4 изучались количественно и оценивались независимо друг от друга. При определении процента иммуноположительных участков карциномы и стромальных компонентов в образце учитывался весь объем опухоли на предметном стекле.
Окончательный результат окрашивания эпителия определяли по следующим критериям:
- 0 – отрицательная реакция – экспрессия отсутствует.
- 1– слабоположительная реакция – экспрессия в <20% клеток.
- 2 – умеренная реакция – экспрессия положительная от 20–40% клеток.
- 3 – выраженная реакция – экспрессия положительная в более чем 40% клеток.
Окончательный результат окрашивания стромы определяли по следующим критериям:
- 0 – отрицательная реакция – экспрессия отсутствует.
- 1 – слабоположительная реакция – экспрессия в <20% клеток.
- 2 – умеренная реакция – экспрессия положительная от 20–40% клеток.
- 3 – выраженная реакция – экспрессия положительная в более чем 40% клеток.
Статистический анализ
Статистическая обработка производилась в программе IBM IPSS Statistics 20. Достоверным считался уровень p<0,05. В связи с тем что операции проводились с 2015 по 2017 г., с целью возможности сравнения оценивалось наличие биохимического рецидива в течение года после оперативного вмешательства. Выполнен подсчет чувствительности и специфичности уровня экспрессии каждого диагностического ИГХ маркера для прогнозирования биохимического рецидива рака простаты и периода безрецидивной выживаемости во всех группах злокачественности по ISUP.
Этическое соглашение
Данное исследование одобрено Локальным этическим комитетом Сеченовского Университета (Протокол № 34–20 от 09.12.2020).
Результаты. При иммуногистохимическом исследовании маркер МСТ1 выявляли в виде окрашивания цитоплазматической мембраны опухолевых клеток. Иммуноэкспрессия МСТ1 в опухолевых клетках варьировалась от отрицательной до выраженной (рис. 1, табл. 2). В 14% случаев отмечена отрицательная реакция. В ряде наблюдений помимо положительной экспрессии опухолевыми клетками также характерна положительная реакция сохранных желез – 21%. Статистически значимой корреляции между уровнем экспрессии MCT1, вероятностью биохимического рецидива и степенью злокачественности опухоли по ISUP не получено. Также отсутствует корреляция между экспрессией MCT1 и наличием экстракапсулярного распространения опухоли.
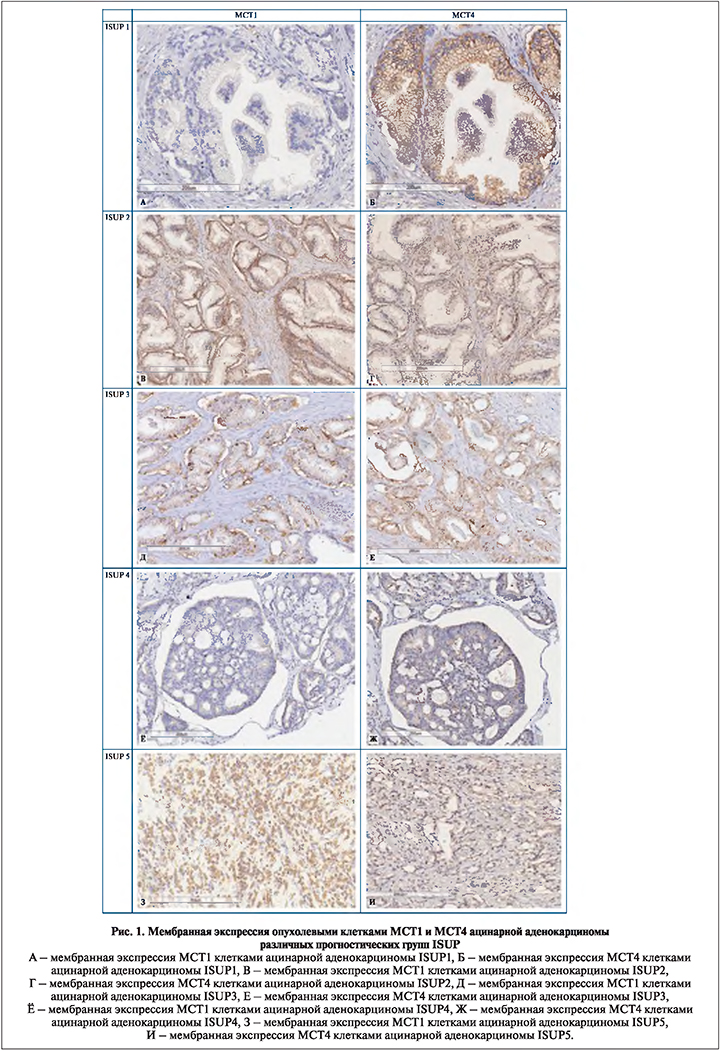
Экспрессия маркера МСТ4 наблюдается как опухолевыми клетками, так и стромальными элементами. Мембранная экспрессия опухолевыми клетками отмечена во всех наблюдениях, положительная экспрессия нормальными и гиперплазированными железами также присутствует в большей части наблюдений, однако достигает слабоположительной плотности окрашивания. Среди опухолевых клеток маркер определяется практически во всех наблюдениях, исключение составили 2 образца с массивными участками воспалительной инфильтрации, не показавших какой-либо реакции при иммуногистохимическом окрашивании с антителами к МСТ4. Для большей части образцов характерна умеренная или высокая экспрессия (рис. 1), при этом корреляции между оценкой степени мембранного окрашивания опухолевых клеток и прогностической группой не отмечено (p>0,05).
Уровень стромальной экспрессии МСТ4, как правило, был низким и определялся в 56% наблюдений. Значимая коррелятивная связь отмечена для комбинации высокой/ умеренной экспрессии МСТ1 и высокой степени окрашивания стромальными элементами МСТ4 (r=0,314, p<0,003). Кроме того, замечено, что по мере нарастания уровня атипии изменяется соотношение в преобладании мембранного окрашивания над стромальным. Так, в наблюдениях ISUP1 экспрессия опухолевыми клетками и стромой прослеживается в равном соотношении (50/50%), в образцах, относящихся к ISUP5, стромальная экспрессия отмечается лишь в 10% случаев (r=0,71, p<0,01) (рис. 2). В ходе подсчета непараметрической корреляции Спирмена определена статистически значимая прямая корреляция между преобладанием стромальной экспрессии MCT4 над мембранной и фактом биохимического рецидива (r=0,403, p<0,001), а также высокой степенью злокачественности по ISUP (4 и 5) (r=0,294, p=0,005).

Среди значимых клинико-морфологических параллелей мембранная экспрессия МСТ4 коррелировала с периневральной инвазией (p<0,001), объемом опухоли (p<0,001), Прямая зависимость экстрапростатического прогрессирвания опухоли прослеживалась с экспрессией МСТ4 в строме (p<0,001). Оценка объема опухоли не повлияла существенно на степень экспрессии MCT1 или MCT4 в строме (p>0,1).
Обсуждение. Метаболизм здоровых клеток простаты имеет ряд особенностей. Основным путем обмена глюкозы в этих клетках является аэробный гликолиз. Происходит данный процесс даже при условии достаточного снабжения кислородом, поскольку в простатических клетках цикл трикарбоновых кислот не происходит полностью вследствие ингибирования фермента м-аконитазы, взаимодействующего с цитратом, по причине десятикратного увеличения концентрации ионов цинка в цитоплазме клеток. Полученный в ходе реакции цитрат накапливается в клетке, выделяется в межклеточное пространство и покидает организм в составе сока предстательной железы [6, 7]. В ходе злокачественной трансформации клеток простаты на ранних стадиях доминирующим путем метаболизма глюкозы является окислительное фосфорилирование [8]. Злокачественные клетки становятся способными перейти на более эффективный метаболический путь вследствие снижения активности переносчиков цинка, что приводит к снижению его внутриклеточной концентрации [9, 10]. При этом на ранних стадиях заболевания потребление клетками глюкозы сравнительно невелико, что объясняет низкую чувствительность (18) F-FDG-PET в определении первичного рака предстательной железы на ранних стадиях. И с другой стороны, повышение чувствительности (18)F-FDG-PETCT для гормон-резистентных, имеющих высокий балл по Глисону форм рака, свидетельствует о повышенном поглощении клетками глюкозы [11]. Субстратом для метаболизма клеток рака простаты на начальных этапах могут быть такие монокарбоксилаты, как лактат или пируват [12]. С учетом вышеописанных метаболических путей в клетках рака простаты важно понимать роль переносчиков монокарбоксилатов (MCTs) в течении и прогнозе рака предстательной железы. Hao et al. в своей работе указывали на повышение экспрессии MCT4 совместно с маркерами инвазии опухоли CD147 и CD44v3-10 в клетках первичного рака простаты, при этом степень их экспрессии коррелировала с величиной ПСА и прогрессированием заболевания (стадия по Глисону, распространенность опухоли, вовлечение ЛУ) [13]. В исследовании Pértega-Gomes et al. наблюдался рост экспрессии MCT2 и MCT4 по направлению от нормальных клеток простаты до злокачественных. При этом экспрессия MCT1 падала по направлению от клеток ПИН до нормальных. Экспрессия MCT2 была выше в клетках ПИН по отношению к нормальным клеткам и при этом не отличалась от уровня экспрессии в злокачественных клетках. Повышение экспрессии MCT4 и CD147 было ассоциировано с увеличением возраста пациентов, повышением ПСА, более запущенной патоморфологической стадией заболевания, более высоким баллом по Глисону, наличием периневральной инвазии, биохимического рецидива [14]. Значительное влияние на метаболизм клеток рака простаты оказывает взаимодействие со специализированными клетками соединительнотканной стромы опухоли – канцер-ассоциированными фибробластами (CAFs). Определено, что CAFs, находясь под действием оксидативного стресса, изменяют свой метаболизм в сторону эффекта Варбурга: клетки начинают активно поглощать глюкозу и выделять массу лактата в межклеточный матрикс, в них наблюдается повышенная экспрессия GLUT1 (белок, отвечающий за транспорт глюкозы через клеточную мембрану) и MCT4. При этом клетки рака простаты начинают активно поглощать лактат. На это указывает снижение его концентрации в межклеточном матриксе в присутствии клеток рака простаты, а также повышение экспрессии клетками, находящимися в непосредственной близости от CAFs белка MCT1, отвечающего за транспорт монокарбоксилатов в клетку. Таким образом, стромальные клетки «скармливают» клеткам рака простаты большую часть субстрата для метаболизма. Данный эффект, названный лактатным шаттлом, или обратным эффектом Варбурга, активно влияет на рост и развитие опухолевых клеток [15, 16]. Анализ клинических данных указывал на связь между наличием лактатного шаттла и неблагоприятного прогноза среди пациентов с раком простаты: коэкспрессия MCT4 в CAFs и MCT1 в клетках рака простаты была ассоциирована с pT3-стадией заболевания, а повышенная экспрессия CAIX стромальными клетками ассоциирована с биохимическим рецидивом у пациентов [17].
Полученные в ходе нашего исследования данные соотносятся с результатами работ в мировой литературе по данной тематике. Наличии прямой коррелятивной связи между биохимическим рецидивом и соотношением в преобладании стромальной экспрессии над паренхиматозной при ацинарной аденокарциноме закономерно связано с повышенной экспрессией MCT1 в опухоли и MCT4 в строме, что подтверждает явление лактатного шаттла. Таким образом, возможно допустить использование данного метода как дополнительного инструмента стратификации риска заболевания. В дальнейшем планируется ИГХ-анализ материала с такими маркерами, как переносчик глюкозы 1-го типа (GLUT1), карбоническая ангидраза IX (CAIX).
Заключение. Определение уровня экспрессии переносчиков монокарбоксилатов (MCT) 1-го и 4-го типов в клетках аденокарциномы простаты и стромальных клетках опухоли может стать эффективным инструментом стратификации риска заболевания, а также позволить прогнозировать течение заболевания и эффективность радикального лечения.



