Введение. Доброкачественная гиперплазия предстательной железы (ДГПЖ) – это гистологический диагноз, подразумевающий пролиферацию гладкомышечных и эпителиальных клеток в переходной зоне предстательной железы [1]. У мужчин гистологическая распространенность ДГПЖ увеличивается в возрасте 40 лет, достигая 60% в 60 лет и 80% в 80 лет [2]. ДГПЖ макроскопически характеризуется увеличением объема предстательной железы, что в конечном итоге может вызывать инфравезикальную обструкцию. Именно в этом возрастном периоде повышается распространенность СД2 у мужчин. Так, по данным регистра больных СД в РФ, наличие СД2 (по состоянию на 01.01.2021) составило 60,5% (2 681 908 человек) именно у мужчин старше 65 лет от всех пациентов с СД [3]. Наблюдаемые при СД2 гиперинсулинемия и инсулинорезистентность могут являться триггером гиперактивации симпатических волокон урогенитального тракта у мужчин, способствуют гиперпролиферации клеток простаты вплоть до развития выраженных симптомов нижних мочевыводящих путей (СНМП) [4]. Кроме того, СНМП оказывают отрицательное комплексное влияние на качество жизни с точки зрения повседневной жизни, производительности труда и даже психологического благополучия [5].
Традиционно «золотым» стандартом оперативного лечения ДГПЖ является трансуретральная резекция простаты (ТУРП), применяющаяся с 1940–1950-х гг. [6]. Появление и активное внедрение лазер-опосредованных методик (в частности, HoLEP) в 1990-х гг. привело к тому, что стандарт ТУРП неоднократно подвергался сомнению из-за появления множества новых оперативных методов. В настоящее время применение трансуретральной резекции сократилось, и все больше получает распространение лазерная энуклеация [7]. Применение лазерных методик в лечении ДГПЖ подразумевает деструкцию и коагуляцию тканей или их вапоризацию (фотоселективная лазерная вапоризация аденоматозной ткани), что позволяет в анатомических слоях выполнить энуклеацию транзиторной зоны с надежным гемостазом и сохранением функциональных структур [8].
Другим не менее признанным методом лечения ДГПЖ, позволяющим добиваться значимого уменьшения объема предстательной железы и ускоренной госпитальной реабилитации («fast track surgery») и топографо-анатомически щадящей техники исполнения, с 2000-х гг. является лапароскопическая позадилонная аденомэктомия (по Миллину) [9]. В рамках научно-технических изысканий по поиску способов, позволяющих избегать массивной кровопотери вследствие особенностей анатомии операционной зоны и методики операции и уменьшения послеоперационных контрактур шейки мочевого пузыря и стриктур уретры, авторы настоящей статьи предлагают дополнять стандартную технику проведением временного пережатия внутренних подвздошных артерий и наложением уретроцистоанастомоза. Во многом схожая методика без наложения уретроцистоанастомоза в роботизированной модификации ранее применялась F Sergi et al. (2014) с последующим улучшением показателей кровопотери, IPSS, урофлоуметрии и без сосудистых осложнений [10].
Отсутствие высококачественных достоверных доказательств, сравнивающих современные методики лечения ДГПЖ – лапароскопическую позадилонную аденомэктомию с временным пережатием внутренних подвздошных артерий и наложением уретроцистоанастомоза (ЛПА+ ВПА+УЦА) и гольмиевую лазерную энуклеацию предстательной железы (HoLEP) – является актуальным вопросом в урологии.
Цель исследования: сравнить показатели эффективности двух оперативных методов лечения – гольмиевой лазерной энуклеации предстательной железы (HoLEP) и лапароскопической позадилонной аденомэктомии с временным пережатием внутренних подвздошных артерий и наложением уретроцистоанастомоза (ЛПА+ВПА+УЦА) – больных доброкачественной гиперплазии предстательной железы (ДГПЖ) и СД2.
Материалы и методы. Нами проведено открытое одноцентровое рандомизированное сравнительное исследование в параллельных группах методом «случайной выборки», утвержденное этическом комитетом ГНЦ РФ ФГБУ «НМИЦ эндокринологии» Минздрава России. Проанализировано 56 пациентов с СД2, перенесших оперативное лечение ДГПЖ (28 методом HoLEP, 28 – ЛПА+ВПА+УЦА) в период с 2021 по 2022 г. на базе одноименного учреждения. По данным диабетологического анамнеза: обе группы были идентичными, длительность СД2 у пациентов составила в среднем 10,6 года, доверительный интервал – ДИ 95%: 5,4–15,8); уровень гликированного гемоглобина (HbA1c, %) 8,4±1,7% (6,7–10,1%). Каждая из представленных групп была разделена на подгруппы по принципу получаемой (в соответствии с национальными клиническими рекомендациями) сахароснижающей терапии: базис-болюсной инсулинотерапии в режиме множественных инъекций аналогами инсулина и монотерапией пероральными сахароснижающими препаратами (метформин – 1000 мг/сут.). Подбор сахароснижающей терапии выполнялся в зависимости от разницы между фактическим и целевым уровнем гликированного гемоглобина (HbA1c, %).
Выборка данных проведена на основании катамнестических (электронные базы) данных пациентов, находившихся на базис-болюсной инсулинотерапии в режиме множественных инъекций аналогами инсулина (n=14 в каждой изучаемой группе) и получавших пероральную сахароснижающую терапию (n=14 в каждой изучаемой группе). Перед проведением оперативного пособия определялся средний возраст (в годах), объем предстательной железы (см³), индекс Международной шкалы симптомов предстательной железы (IPSS, баллы), индекс качества жизни (QoL), оценка эректильной функции (IIEF-5/МИЭФ-5, баллы), максимальная скорость потока мочи (Qmax), объем остаточной мочи (мл), уровень простатоспецифического антигена (ПСА) в сыворотке крови (нг/мл), наличие/отсутствие цистостомического дренажа. Из исследования были исключены пациенты с диагнозом «рак предстательной железы» или с оперативным лечением ДГПЖ в анамнезе с объемом (V) предстательной железы менее 80 см3.
В ходе определения интраоперационных показателей оценивались такие показатели, как средняя длительность операции (мин), средняя масса удаленной ткани (г), средняя длительность катетеризации (дни), средняя продолжительность госпитализации (дни), общее снижение уровня гемоглобина (г/л), среднее количество дней работы промывной системы.
Оценка интра- и ближайших послеоперационных осложнений производилась с использованием шкалы Clavien–Dindo и распределением по группам (I–IV). В качестве послеоперационной контрольной точки через год после операции оценивались такие показатели, как индекс Международной шкалы симптомов предстательной железы (IPSS, баллы), индекс качества жизни (QoL), оценка эректильной функции (IIEF-5/МИЭФ-5, баллы), максимальная скорость потока мочи (Qmax), объем остаточной мочи (мл), количество пациентов, имеющих стриктуры уретры и рубцовую деформацию шейки мочевого пузыря.
Эффективность проведенных оперативных вмешательств оценивалась между двумя группами (HoLEP, ЛПА+ВПА+УЦА) по истечению 1 года послеоперационного периода в соответствии с критериями «trifecta»: отсутствие послеоперационных осложнений через год (стриктура уретры, рубцовая деформация шейки мочевого пузыря), недержания мочи, достижения максимальной скорости потока мочи (Qmax) >15 мл/с.
Статистический анализ
Статистическая обработка данных осуществлялась при помощи пакета статистических программ IBM SPSS Statistics 26 (SPSS. Inc, Chicago, IL, USA).
Количественные показатели оценивались на предмет соответствия нормальному распределению с помощью критерия Шапиро–Уилка. Категориальные данные описывались с указанием абсолютных значений и процентных долей. Сравнение процентных долей при анализе многопольных таблиц сопряженности выполнялось с помощью критерия хи-квадрат Пирсона. Количественные показатели, имеющие нормальное распределение, описывались с помощью средних арифметических величин (M) и стандартных отклонений (SD), границ 95% доверительного интервала (95% ДИ). Для непрерывных переменных использовали t-критерий Стьюдента или однофакторный дисперсионный анализ, а для категориальных переменных использовали критерий хи-квадрат. Все значения P были двусторонними и P<0,05 считалось статистически значимым.
Оперативная техника гольмиевой лазерной энуклеации предстательной железы (HoLEP)
HoLEP выполняли по модифицированной методике Гиллинга. После разделения предстательной железы на анатомические доли энуклеацию каждой доли проводили ретроградным способом с помощью гольмиевого лазера (50 Вт), доставляемого по оптоволокну SlimLine 550 мм (Boston Scientific Auriga ХL) через систему резектоскопов с непрерывным потоком 26F. Для морцелляции и извлечения тканей мы использовали нефроскоп 26F с тканевым морцеллятором Karl Storz UNIDRIVE S III.
Оперативная техника ЛПА+ВПА+УЦА
Лапароскопическая позадилонная аденомэктомия с временным пережатием внутренних подвздошных артерий и наложением уретроцистоанастомоза (ЛПА+ВПА+УЦА) выполнена с использованием следующего операционного пособия: под общим обезболиванием в параумбиликальной области с помощью иглы Вереша создавался карбоксиперитонеум и устанавливался оптический порт. Выполнялась лапароскопия. В правой и левой подвздошных областях параректально устанавливались четыре рабочих троакара. Рассекалась брюшина в проекции бифуркации наружной подвздошной артерии и внутренней подвздошной артерии справа, в области перекреста общей подвздошной артерии и мочеточника. С использованием энергетических инструментов выполнялась мобилизация внутренней подвздошной артерии. Внутренняя подвздошная артерия (ВПА) бралась силиконовой держалкой. Выполнялся гемостаз в зоне работы. Рассекалась брюшина в проекции бифуркации наружной подвздошной артерии и внутренней подвздошной артерии слева, в области перекреста общей подвздошной артерии и мочеточника. Выполнялся гемостаз в зоне работы. Выполнялась мобилизация передней и боковых поверхностей предстательной железы до внутритазовой фасции. Накладывались сосудистые зажимы типа «Бульдог» на внутренние подвздошные артерии в области бифуркации. Капсула предстательной железы рассекалась в поперечном направлении. Проводился контроль гемостаза. После идентификации слоя между капсулой предстательной железы и аденомотозным узлом последние выделялись единым блоком, шейка мочевого пузыря смещалась с преобладанием использования тупой диссекции. Аденоматозные узлы отсекались от уретры, помещались в контейнер. С ВПА снимались сосудистые зажимы. Проводился контроль гемостаза ложа аденоматозных узлов. После адекватной идентификации шейки мочевого пузыря выполнялось наложение анастомоза двумя нитями V-lock 3/0 между уретрой и шейкой мочевого пузыря. Наложение анастомоза проводилось непрерывным шагом, начиная с задней стенки (6 ч условного циферблата) в противоположные стороны, и заканчивая пересечением на передней поверхности анастомоза (12 ч условного циферблата). Устанавливался уретральный катетер Фолея № 20 Ch. В мочевой пузырь вводилось 150 мл физиологического раствора с целью проверки герметичности анастомоза. Капсула предстательной железы ушивалась непрерывным швом нитью V-lock 3/0. Ревизия раны, гемостаз. Контейнер с макропрепаратами удалялся через супраумбиликальный доступ.
В малый таз через контрапертуру установливался страховой дренаж. Производилось послойное ушивание ран. В завершение операции накладывалась асептическая наклейка.
Антибактериальная и противовоспалительная терапия
Всем пациентам в обеих группах проводилась антибиотикопрофилактика. Пациентам с признаками системной воспалительной реакции проводилась антибактериальная терапия. Нестероидный противовоспалительный препарат (диклофенак 75 мг 2 раза в день) вводили в течение 3 дней. Тромбоэмболическая профилактика проводилась согласно СОП «профилактика венозных тромбоэмболических осложнений от 15.09.2022»
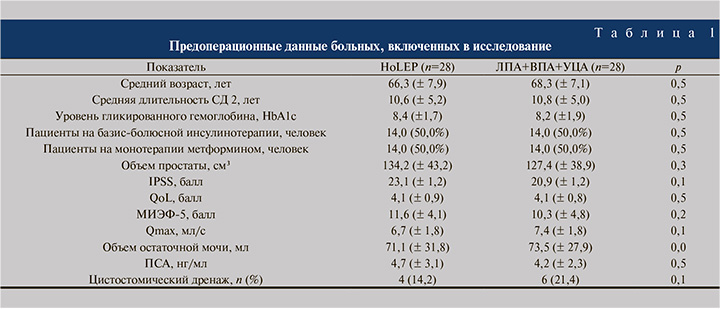
Результаты. По данным предоперационного обследования (табл. 1) пациенты из групп, которым планировалось оперативное лечение, были достоверно сопоставимы по таким параметрам, как средняя длительность СД2, уровень гликированного гемоглобина, доля больных, получающих базис-болюсную инсулинотерапию/монотерапию метформином, объем простаты, количество баллов по шкалам IPSS, QoL, МИЭФ-5, Qmax, объем остаточной мочи, уровень ПСА сыворотки крови, а также факт наличия цистостомического дренажа.
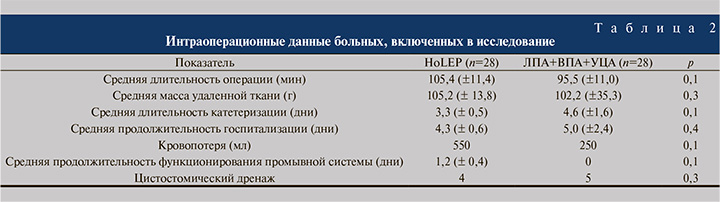
В группе пациентов, перенесших HoLEP, в отличие от группы ЛПА+ВПА+УЦА отмечалось статистически значимое преимущество в длительности катетеризации мочевого пузыря. HoLEP уступает ЛПА+ВПА+УЦА за счет более чем двукратного увеличения уровня потери гемоглобина, необходимости функционирования промывной системы. В обследуемых группах отмечается сопоставимость данных по средней продолжительности госпитализации, длительности пребывания в стационаре и средней массы удаленной ткани (табл. 2).
В соответствии со шкалой послеоперационных осложнений по Clavien–Dindo (см. табл. 3) проведение HoLEP ассоциировалось с более высокой частотой развития осложнений в I (повреждение устьев мочеточников/слизистой оболочки мочевого пузыря, кратковременное недержание мочи, задержка мочи за счет кровяных сгустков), II (послеоперационная гипертермия, острая задержка мочи) и III (отложенная морцелляция, тампонада мочевого пузыря) группах. Проведение HoLEP и ЛПА+ВПА+УЦА сопоставимо и относительно редко ассоциировалось с развитием массивного кровотечения, мочевых затеков с необходимостью ревизионных (повторных) операций. Ни одно из вмешательств не ассоциировалось с осложнениями IV группы по Clavien–Dindo (тромбоэмболия легочной артерии [ТЭЛА]).

По результатам послеоперационного обследования через 12 мес. (см. табл. 4) в обеих группах отмечалось равноценное снижение баллов по шкалам IPSS, QoL и объема остаточной мочи до сопоставимых значений. По данным опросников оценки эректильной функции, у пациентов обеих групп отмечались стабильные показатели в баллах, аналогичных предоперационным. Обращает на себя внимание преимущество в восстановлении максимальной скорости потока мочи в группе пациентов после ЛПА+ВПА+УЦА (24,3 (± 2,4) v. 15,3 (± 3,6).

По результатам оценки послеоперационных осложнений ЛПА+ВПА+УЦА (см. табл. 5) частота развития стриктуры уретры, стрессового/ургентного недержания мочи, тампонады мочевого пузыря стремилась к нулевым значениям; в группе HoLEP отмечались случаи стрессового (10,7%) и ургентного (1 (3,5%) недержания мочи, стриктуры уретры (7,2%), рубцовой деформации шейки мочевого пузыря (10,6%).
Обсуждение. Среди пожилых пациентов ДГПЖ представляет собой наиболее распространенное доброкачественное заболевание мочеполовой системы, ассоциированное с обширным спектром коморбидных состояний [11]. Вопрос о необходимости подготовки пациентов с СД к оперативному лечению является актуальным, и данное исследование демонстрирует сопоставимые периоперационные результаты с литературными данными у пациентов, не осложненных сопутствующим СД.
Данная статья является попыткой перейти к изучению последствий проведения современных модификаций лапароскопических и лазеропосредованных методов лечения ДГПЖ на фоне такого состояния, как СД2.
Мы сравнили показатели успешности двух оперативных методов (HoLEP, ЛПА+ВПА+УЦА) у больных СД2 в соответствии с критериями «трифекта» и исследовали спектр показателей во временном континууме: начиная от пред- и интраоперационного обследования, включая интра- и ранние послеоперационные осложнения, заканчивая послеоперационными факторами (через 1 год).
С точки зрения авторов, качество проведенного исследования можно было бы повысить за счет увеличения выборки пациентов, стратификации пациентов по уровню компенсации углеводного обмена, по уровню гликированного гемоглобина (HbA1c, %), увеличения числа точек послеоперационного обследования (3, 6, 18, 24 мес. и т.д.), а также сравнением с другими видами оперативного лечения ДГПЖ, например, монополярной (ТУРП-М) и биполярной (ТУРП-Б) трансуретральной резекциями простаты. Другим способом расширения исследования было бы проведение работы в соответствии с критериями «пентафекта» и «октафекта».
При этом следует уточнить, что данное исследование имеет несколько ограничений, поскольку оно было выполнено на малой выборке больных (56 пациентов) с СД2 на фоне ожирения, что, возможно, привело к систематической ошибке при отборе: предоперационный объем предстательной железы был выше в группе HoLEP. Данное исследование продемонстрировало, что ЛПА+ВПА+УЦА и HoLEP являются эффективными методами для лечения ДГПЖ даже при таком сопутствующем заболевании как СД2.
Заключение. ЛПА+ВПА+УЦА обладает сравнительно выраженными и многообещающими преимуществами с точки зрения уретральных осложнений (стриктура уретры, рубцовая деформация шейки мочевого пузыря), недержания мочи, а также профилактики потери гемоглобина. Нельзя игнорировать необходимость инициации исследований в рамках доказательной медицины с целью изучения аспектов безопасности изучаемых методов (в т.ч. при других социально-значимых заболеваниях) и решения вопроса о целесообразности их внедрения в практическое здравоохранение.



