Введение. Рак простаты (РП) является гетерогенным и многофакторным заболеванием, которое протекает в виде вялых или крайне агрессивных опухолей и является значимым источником заболеваемости и смертности среди мужского населения. В 2018 г., по оценкам, зарегистрировано 1,3 млн новых случаев и 359 тыс. связанных с ними смертей во всем мире [1, 2].
Простатспецифический антиген (ПСА) является наиболее часто используемым скрининговым биомаркером для диагностики РП и мониторинга развития злокачественного процесса. Однако использование тестирования на ПСА при скрининге РП вызывает споры из-за отсутствия окончательных данных рандомизированных исследований и отсутствия специфичности между доброкачественными и злокачественными новообразованиями. Стратификация на основе традиционных клинических параметров может определять риск развития у пациентов злокачественных новообразований, вероятность прогрессирования рака на ранней стадии заболевания [3].
Наиболее часто используемыми методами прогнозирования РП является классификация TNM, используемая с градацией по шкале Глисона, и определение уровня ПСА [4]. Однако клиническое применение этих показателей ограниченно. Американская урологическая ассоциация поощряет выявление новых генетических маркеров, которые помогут идентифицировать мужчин с повышенным риском развития и прогрессирования заболевания [5].
В исследованиях все чаще выявляется связь однонуклеотидных полиморфизмов (SNP) с развитием различных заболеваний, в результате чего SNP постепенно используются в качестве маркеров, связанных с раком, в том числе и с РП. Следовательно, SNP привлекают значительное внимание для использования их в качестве прогностических показателей до и после лечения пациентов с РП [6].
За последние десятилетия различные SNP связывают с развитием аденокарциномы простаты. SNP гена PTEN представляют значительный интерес в качестве генетического маркера риска развития злокачественных новообразований простаты.
Ген PTEN представляет собой супрессор опухоли с двойной специфичностью, основным субстратом которого является фосфатидилинозитол(3,4,5)-трисфосфат (PIP3). Белок PTEN действует как антагонист на пути PI3K/AKT, поддерживая низкий уровень PIP3: чем больше концентрация PIP3, тем сильнее сигнализация пути PI3K/AKT, которая провоцирует ингибирование клеточного цикла, миграцию, метастазирование и апоптоз. Вероятность потери функции гена PTEN выше при агрессивном метастатическом заболевании, что предполагает возможность его применения в качестве генетического маркера для прогнозирования течения заболевания и для отличия вялотекущих опухолей от агрессивных форм рака [7, 8, 19].
Среди прогностических биомаркеров ДНК, полученных в результате секвенирования тысяч случаев РП, потеря гена PTEN, возможно, остается одной из наиболее многообещающих [9]. Инактивация PTEN при опухолях простаты связана с неблагоприятными онкологическими исходами, такими как увеличение степени дифференцировки и распространенности онкологического процесса, более ранним биохимическим рецидивом после радикальной простатэктомии, метастазированием, смертью от РП и андроген-независимым прогрессированием заболевания [10–12]. В ранее проведенных исследованиях подтверждена корреляция делеции гена PTEN с увеличением балла Глисона и повышением вероятности экстрапростатического расширения у пациентов с локализованным РП, получивших хирургическое лечение [13]. В нескольких крупных исследованиях подтверждена связь потери PTEN с повышенным риском биохимического рецидива после простатэктомии [10, 14, 15]. Возможно, самое важное, что PTEN оказался независимым прогностическим показателем смерти от РП у пациентов, получавших консервативное или хирургическое лечение [16, 17]. В одном небольшом исследовании потеря PTEN в образце биопсии предсказала повышенный риск кастрационно-резистентного РП, метастазирования и смертности среди пациентов, получавших хирургическое лечение [18].
Принимая во внимание связь между потерей PTEN и увеличением балла Глисона, ген PTEN может быть полезным в качестве прогностического маркера при локализованном РП. Широкое внедрение новых генетических маркеров позволит обнаружить различные заболевания до появления клинических проявлений, тем самым позволит предоставлять дополнительную и независимую информацию о возможных рисках, клиническом течении, прогнозе и предполагаемом исходе.
Цель исследования – оценка роли полиморфных локусов rs2299941, rs1903858, rs10490920,rs2735343 гена PTEN у пациентов с раком простаты в качестве возможных молекулярно-генетических маркеров риска развития заболевания.
Материалы и методы. Характеристика выборки. В исследование включены 457 пациентов с подтвержденным гистологическим диагнозом РП и 474 здоровых индивида без РП. Все обследованные были пациентами клиники Башкирского государственного медицинского университета, Уфа. Забор образцов крови проводился сотрудниками кафедры урологии. Пациенты и контрольные группы были добровольцами, и письменное информированное согласие получено от каждого участника, ответившего на вопросник. Исследование одобрено биоэтическим комитетом Института биохимии и генетики УФИЦ РАН. В исследуемой группе 33,4% пациентов имели начальные стадии заболевания (I–II стадии злокачественного процесса, согласно TNM классификации) и 66,6% пациентов – поздние стадии (III–IV стадии злокачественного процесса, согласно классификации TNM). Степень дифференцировки опухоли простаты проводилась по шкале Глисона. Сумма баллов по Глисону менее 8 баллов – 80,8% пациентов, более 8 – 19,25%. Возраст пациентов варьировался от 44 до 89 лет.
Выделение геномной ДНК. При выполнении молекулярногенетического исследования использовались образцы ДНК из лимфоцитов периферической венозной крови. Крoвь набирали в вакуумные пробирки с К3 ЭДТА (этилендиаминтетрауксусная кислота) в качестве антикoагулянта. Выделение ДНК проводили методом последовательной фенольно-хлороформной экстракции по Мэтью.
Генотипирование. В гене PTEN проведено генотипирование четырех SNP, выбранных из общедоступной базы данных одиночных нуклеотидов (rs2299941, rs1903858, rs10490920, rs2735343). Идентификация генотипов и аллелей изученных полиморфных локусов гена PTEN проводилась с использованием метода аллельной дискриминации TaqMan. Статистическая обработка полученных результатов проводилась с использованием таблицы сопряженности 2х2 (http://www.biometrica.tomsk.ru/freq_ New.htm).
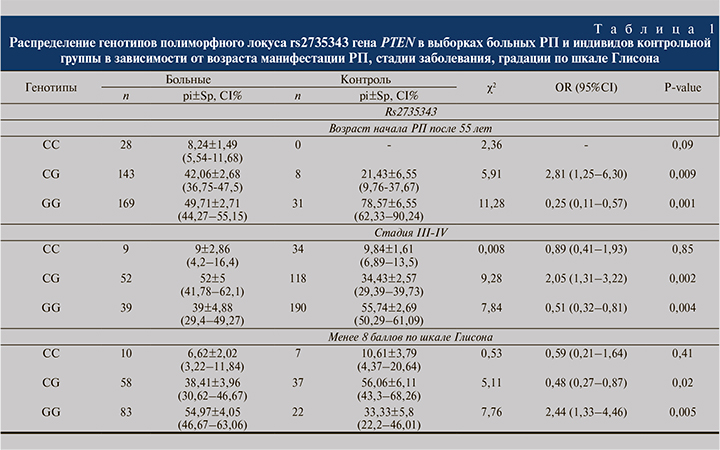
Результаты и обсуждение. Проведенный нами анализ полиморфного локуса rs2735343 гена PTEN позволил выявить генотипы, ассоциированные с риском развития РП. При разделении больных по возрасту манифестации РП в группе больных с возрастом начала заболевания после 55 лет выявлено более частое носительство генотипа rs2735343*CG гена PTEN по сравнению с контрольной группой (42 и 21% соответственно) (p=0,009, OR=2,81, CI=1,25–6,30). Сравнительный анализ выборки больных РП с контрольной группой показал, что у пациентов с поздними стадиями заболевания статистически значимо чаще встречается генотип rs2735343*CG гена PTEN по сравнению с контрольной выборкой; данный генотип является рисковым в отношении развития РП тяжелого течения у жителей Республики Башкортостан (p=0,002, OR=2,05, 52% CI=1,31–3,22), в то время как генотип rs2735343*GG протективный в отношении развития заболевания тяжелого течения (p=0,004, OR=0,51, 52% CI=0,32–0,81). При сравнении частот генотипов изученного локуса гена PTEN в анализируемых нами группах с учетом градации по шкале Глисона выявлено, что носительство генотипа rs2735343*CG гена PTEN (p=0,02, OR=0,48, 38% CI=0,27–0,87) может быть протективным маркером в отношении развития РП, тогда как носительство гомозиготного генотипа rs2735343*GG гена PTEN (p=0,005, OR=2,44, 55% CI=1,33–4,46) – маркер риска развития заболевания. Распределение частот генотипов полиморфного локуса rs2735343 гена PTEN представлено в табл. 1.
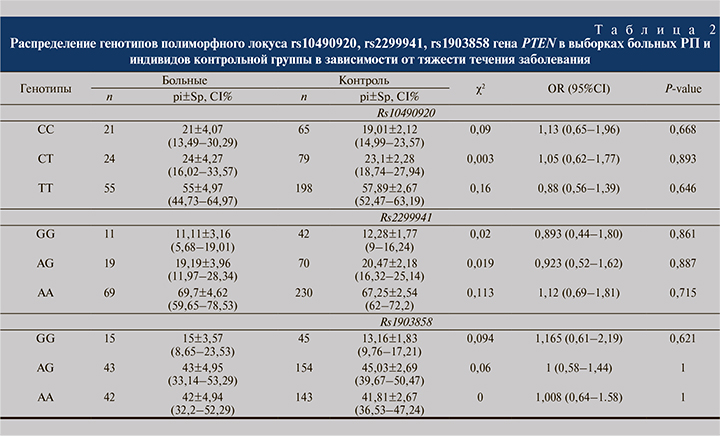
Сравнительный анализ полиморфных локусов rs2299941, rs1903858, rs10490920 гена PTEN между группами больных РП и здоровых доноров из Республики Башкортостан статистически значимых различий не выявил. Частоты генотипов приведены в табл. 2.
С учетом важной роли, которую SNP играют в качестве генетических маркеров при различных типах заболеваний, выбран ген PTEN и SNP, которые являются кандидатами на восприимчивость к РП и влиянию на прогноз заболевания [20]. Компоненты сигнального пути PTEN/PI3K/AKT являются важным регулятором роста, метаболизма, клеточного цикла, репарации ДНК и ингибирования апоптоза [21]. Изученный здесь полиморфный вариант rs2735343 расположен в интронной области гена PTEN. Согласно Jang et al., он может влиять на сплайсинг, экспрессию белка, следовательно, регуляцию клеточного цикла и риск развития рака [22].
Наши результаты, добавленные к этим, предполагают, что определенные изменения в этом гене способны предсказывать риск развития РП, а также агрессивное течение заболевания.
Выводы. Данные, полученные в нашем исследовании, расширяют знания о генетических основах предрасположенности к РП. Идентификация и внедрение новых маркеров позволят улучшить прогнозирование поведения опухоли у пациентов с РП. Понятие о молекулярно-генетических маркерах предоставит возможность лечащему врачу индивидуализировать лечение в соответствии с генетическими характеристиками каждого пациента. Результаты нашего исследования указывают на возможную роль SNP rs2735343 гена PTEN как потенциального молекулярного маркера, использование которого возможно в комплексных прогностических панелях для диагностики РП, однако полученные данные нуждаются в дополнительном подтверждении перед применением в клинической практике. Тем не менее необходимо проводить дальнейшие исследования полиморфного локуса rs2735343 гена PTEN для установления функциональной значимости и роли в патогенезе рака простаты.



