Введение. Эректильная дисфункция (ЭрД) является составной частью проблемы сексуальных дисфункций, ограничивающих полноценность половой жизни – одно из важнейших компонентов, обеспечивающих высокий уровень не только качества жизни мужчины, но и ее продолжительности [1, 2]. Эректильная дисфункция имеет множество причин, но общим конечным патогенетическим путем ее формирования остается дисфункция эндотелиальных клеток, выстилающих кровеносные сосуды кавернозных тел, приводящая к снижению высвобождения эндотелиального оксида азота и нарушению вазодилатации [3].
В связи с этим ЭрД можно рассматривать как клиническое проявление генерализованного сосудистого заболевания. Данные крупных популяционных исследований показали, что ЭрД – значимый предиктор общей смертности наряду с сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями [4]. В связи с этим ЭрД у мужчин требует лечения с применением междисциплинарного подхода [5]. Повышенный интерес к этому вопросу связан еще и с тем, что эндотелиальная дисфункция (ЭД) функционально обратима и возможности ее коррекции у пациентов с ЭрД довольно широки [6]. Препараты группы ингибиторов фосфодиэстеразы 5-го типа (ФДЭ-5), в частности тадалафил, – мощные и достаточно безопасные инструменты в борьбе с ЭрД. Ингибиторы ФВЭ-5 обычно используются в качестве схемы лечения по требованию из-за их короткой продолжительности действия. Особенностью фармакологического действия тадалафила является продолжительность его действия, обусловленная длительным периодом полувыведения препарата. Тадалафил можно принимать регулярно, например 1 раз в день, что позволит пациентам вступать в половую связь в любое время, устраняя необходимость принимать дозу перед половым актом [7]. Постоянная концентрация лекарственного средства в крови позволяет сохранять спонтанность половых контактов, что безусловно оказывает положительное влияние на качество жизни и пациентов, и их партнерш.
Целью исследования: оценить эффективность и безопасность приема тадалафила в дозе 5 мг в сутки или 20 мг «по требованию» на состояние эндотелиальной функции, выраженность ЭрД и уродинамику у мужчин с легкой и умеренной степенями ЭрД.
Материалы и методы. В исследование были включены 60 пациентов мужского пола с доброкачественной гиперплазией предстательной железы (средний возраст – 55,75 [46, 60] года) с ЭрД и сердечно-сосудистой патологией (артериальная гипертензия [АГ], ишемическая болезнь сердца [ИБС]). Критерии исключения: стенокардия напряжения III–IV функциональных классов; хроническая сердечная недостаточность выше 2-го функционального класса; злокачественная АГ; состояние после острого нарушения мозгового крово-обращения, инфаркта миокарда, перенесенных менее чем за 6 мес.; жизнеугрожающие нарушения ритма сердца; выраженные нарушения функции печени, почек (хроническая болезнь почек стадии 4 и выше); сахарный диабет; ЭрД органического характера (посттравматическая, аномалии развития, тотальный кавернозный фиброз); андрогенный дефицит.
Все пациенты были разделены на 3 группы по 20 человек. Пациентам 1-й группы для лечения ЭрД был назначен тадалафил (Тадалафил СЗ, НАО «Северная Звезда») в режиме ежедневного приема в дозе 5 мг/сут. Мужчины 2-й группы принимали тадалафил 20 мг «по требованию», но не реже 1 раза в неделю. Третья группа, в которой тадалафил не назначался, служила контролем. Все пациенты, включенные в исследование, принимали препараты, рекомендованные для базисной терапии АГ и ИБС (допускалась любая сопутствовавшая терапия, кроме приема нитратов). Продолжительность исследования составила 4 нед.
Пациентам проводили общеклиническое обследование (оценка общего состояния, анализ жалоб со стороны сердечно-сосудистой системы [ангинозные боли, повышение артериального давления [АД] и т.д.], обследование по основному урологическому заболеванию [наличие и выраженность симптомов нижних мочевыводящих путей [СНМП]), оценку роста, массы тела пациента с определением индекса массы тела. Проводили измерение АД на обеих руках в положении пациента, сидя по стандартной методике, подсчет частоты сердечных сокращений (ЧСС). Оценку степени ЭрД проводили по Международному индексу эректильной функции (анкета МИЭФ-5) [8]. Пациенты отвечали на вопросы анкеты, выбирая оценку, которая максимально верно отражала их состояние. При сумме баллов от 21 до 25 констатировали отсутствие ЭрД, от 16 до 20 диагностировали ЭрД легкой степени, от 11 до 15 – ЭрД умеренной степени, от 5 до 10 – выраженную ЭрД. Всем пациентам было проведено тестирование по опроснику IPSS для получения субъективной информации о выраженности СНМП и их влиянии на качество жизни анкетируемых мужчин [9]. Сумма баллов от 0 до 7 говорит о незначительных нарушениях мочеиспускания, от 8 до 19 – об умеренных нарушениях, от 20 до 35 – о тяжелых симптомах болезни.
Инструментальную оценку выраженности эндотелиальной дисфункции проводили фотоплетизмографическим способом с оценкой индеса жесткости (ИЖ) и отражения (ИО), показателя функции эндотелия (ПФЭ). Для оценки нарушений уродинамики нижних мочевыводящих путей проводили урофлоуметрическое исследование на урофлоуметре ANDROMEDA CONUS (Германия).
С целью исключения андрогенного дефицита исходно у всех пациентов определяли уровень общего тестостерона в сыворотке крови иммуноферментным методом (набор ООО «Компания Алкор Био», Россия).
Функцию сосудистого эндотелия оценивали с помощью аппарата Элдар-Эндо (ЗАО «Инженерно-медицинский центр "Новые приборы"», Россия). Кроме того, определяли уровень эндотелина-1 в сыворотке крови (Quantikine ELISA Endothelin-1 Immunoassay, R&D Systems, США) и оксида азота (NO) в сыворотке и плазме крови (нитраты и нитриты) методом иммуноферментного анализа («Total Nitric Oxide Assay Kit», США).
Исследование биохимических показателей (общий холестерин, холестерин липопротеинов высокой и низкой плотности, триглицериды, креатинин сыворотки крови, аспарагиновая и аланиновая трансаминазы, глюкоза крови натощак) проводили по общепринятым методикам на биохимическом анализаторе LEASYS-2 («AMS», Италия).
Все показатели оценивали исходно и через 4 нед. исследования. Статистическая обработка полученных данных проведена с помощью пакета статистических программ Statistica 6.0 (StatSoft Inc., США). Для проверки нормальности распределения показателей использовали критерий Шапиро–Уилка. Для количественной характеристики показателей использовали медиану с интерквартильным размахом (Ме [Q1; Q3]). Значимость различий между группами оценивали с помощью критерия Краскела–Уолиса, используемого для сравнения средних значений в несвязанных группах при непараметрическом распределении показателей. Корреляционный анализ между показателями проводили с помощью корреляции Пирсона. Статистически значимым считали различия при p<0,05.
Результаты и обсуждение. Исходно пациенты были сопоставимыми по возрасту, сопутствующей патологии и терапии, принимаемой по этому поводу, тяжести ЭрД и ЭД (табл. 1).
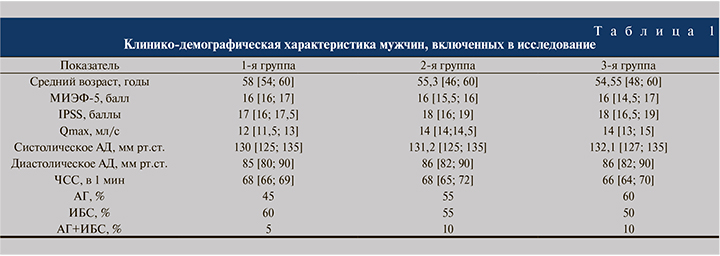
По данным проведенной инструментальной и лабораторной диагностики все пациенты с ЭрД имели проявления ЭД (табл. 2). Исходно легкая степень ЭрД присутствовала у 85, 75 и 65% пациентов 1-й, 2-й и 3-й групп соответственно, в остальных случаях диагностировали умеренную степень ЭрД. Выявлены корреляционные связи между выраженностью ЭрД по данным опросника МИЭФ-5 и показателями, характеризующими наличие дисфункции эндотелия: между суммарным баллом МИЭФ-5 и уровнем эндотелина-1 (r=0,47; р<0,05); между ответами на 2-й и 5-й вопросы анкеты МИЭФ-5 и содержанием эндотелина-1 (r=0,63, р<0,05 и r=-0,54, р<0,05 соответственно). Ответы на 3-й и 5-й вопросы анкеты МИЭФ-5 коррелировали с показателем функции эндотелия (ПФЭ) – r=0,49 и r=-0,50 (р<0,05 в обоих случаях) для 3-го и 5-го вопросов соответственно.
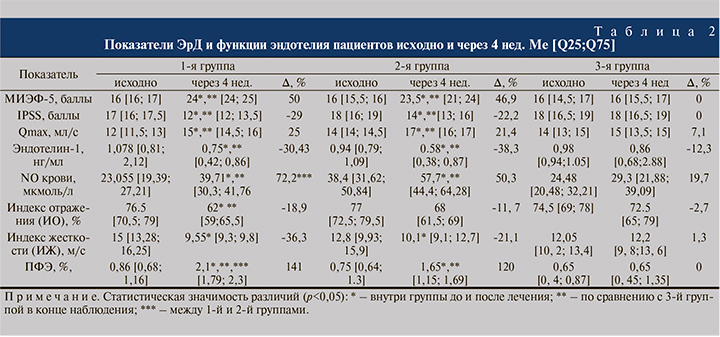
Проведенное нами исследование продемонстрировало значимое положительное влияние тадалафила на показатели ЭД по данным фотоплетизмографического исследования. Через 4 нед. приема тадалафила в обоих режимах достигнуто статистически значимое снижение индекса отражения (ИО), индекса жесткости (ИЖ), а также увеличение ПФЭ (табл. 2). В первой группе пациентов, принимавших 5 мг тадалафила ежедневно. ИЖ снизился с 15 до 9,55 м/с (р<0,05). При приеме 20 мг препарата «по требованию» с 12,8 до 10,1 м/с (р<0,05).
В группе контроля ИЖ практически не изменился. Обращает на себя внимание факт статистически значимого снижения ИО только в группе пациентов, постоянно принимавших препарат. Динамика ИО во 2-й и 3-й группах носила статистически незначимый характер. Через 4 нед. ПФЭ в 1-й группе пациентов возрос с 0,86% в начале исследования до 2,1% (Δ, % +141) vs 0,75% до 1,65% (Δ, %, +120) (р1,2<0,05; р1, 3< 0,05; р2, 3<0,05). В группе контроля ПФЭ не изменился (Δ, %, 0) При оценке лабораторных показателей, характеризующих функциональные возможности эндотелия, отмечено увеличение уровня NO как в 1-й, так и во 2-й группе (см. табл. 2), однако более значимым оно было в группе пациентов постоянного приема 5 мг тадалафила (72,2 против 50,3%, р<0,05). Уровень эндотелина -1 статистически значимо снизился только в группах приема тадалафила (Δ,% -30,43% в 1-й группе больных; Δ,% -38,3% во второй; р1, 3<0, р2, 3<0,05. При нарушении функции эндотелия в крови повышается концентрация эндотелина-1, который является вазоконстриктором, и снижается выработка NO, обладающего мощным вазодилатирующим влиянием на сосуды. Таким образом, выявленное в нашем исследовании достоверное снижение уровня эндотелина-1 на фоне повышения концентрации NO при двух режимах приема тадалафила имеет важное клиническое значение.
В кавернозной ткани под действием специфической фосфодиэстеразы 5-го типа (ФДЭ-5) цГМФ переходит в неактивный 5’-гуанозинмонофосфат. При недостаточной выработке NO ишемизированным или поврежденным эндотелием концентрация цГМФ в гладкомышечных клетках сосудов снижается, вследствие чего не происходит увеличения притока крови к кавернозным телам и эффективной эрекции не наступает. Механизм действия ингибиторов ФДЭ-5 основан на блокаде гидролиза цГМФ, что приводит к резкому росту его концентрации, активации цГМФ-зависимой протеинкиназы с последующим фосфорилированием ионных каналов, вследствие чего снижается концентрация кальция в гладкомышечных клетках и возникает их расслабление [10]. Ингибиторы ФДЭ-5 не вызывают эрекции, а лишь облегчают ее развитие в результате действия эндогенного NO, который выделяется из нервных окончаний и эндотелиальных клеток, стимулируя синтез цГМФ ферментом гуанилатциклазой [11]. Эндотелий не только выполняет барьерную функцию между кровью и гладкой мускулатурой сосудов, но и вырабатывает вазоактивные вещества, регулирующие процессы пролиферации, гемостаза, миграцию клеток крови в сосудистую стенку, сосудистый тонус [12], а ЭД рассматривается как универсальное неспецифическое звено в патогенезе развития ЭрД [13].
В обеих группах приема тадалафила отмечено достоверное улучшение всех показателей, характеризующих ЭрД: повысился средний балл по шкале МИЭФ-5, при этом у всех пациентов обеих групп достигнут балл, позволяющий говорить об отсутствии ЭД (21–25 баллов). Обращает на себя внимание, что через 4 нед. в группе постоянного приема Тадалафила СЗ в дозе 5 мг в сутки максимальный балл (25 баллов) по МИЭФ-5 был достигнут 45% пациентов, тогда как в группе приема препарата «по требованию» в дозе 20 мг – только 10%. В группе контроля изменений максимального балла по МИЭФ-5 практически не произошло и к концу исследования доля пациентов с легкой и умеренной ЭрД составила 75 и 25% соответственно. Статистически значимые изменения отмечены как внутри, так и между 1-й и 2-й группами, а также по сравнению с группой контроля. В основе патогенеза эрекции (тумесценции) лежит механизм NO-цГМФ. Ведущий механизм ЭрД – недостаточность центральной или периферической выработки NO, приводящей к нарушению баланса между сокращением и расслаблением трабекулярных мышц corpus cavernosum полового члена, а использование ингибиторов ФДЭ-5 может нивелировать эти расстройства [14].
Проведенный корреляционный анализ продемонстрировал, что увеличение силы эрекции, согласно опроснику МИЭФ-5, коррелировало с изменением уровня эндотелина-1 (r=–0,53; р<0,05) в группе пациентов, принимавших тадалафил «по требованию». В группе контроля ответ на 2-й вопрос также коррелировал с уровнем эндотелина-1, но эта корреляция имела противоположное направление (r=0,52; р<0,05).
Согласно данным [15], выраженность СНМП по опроснику IPSS коррелирует с качеством эректильной функции [15].
С другой стороны, в исследовании [16] показано, что выраженность простатических симптомов у пациентов с нарушениями мочеиспускания коррелирует с выраженностью ЭД. Через 4 нед. приема тадалафила отмечено статистически значимое снижение выраженности СНМП (в пределах умеренной степени тяжести) на 29 и 22% в 1-й и 2-й группах соответственно (см. табл. 2). В группе контроля выраженность СНМП не только не изменилась, но у 15% пациентов ухудшилась. Отмеченная нами положительная динамика выраженности СНМП может быть опосредована положительным патогенетическим влиянием тадалафила на выраженность ЭД, играющей важную роль в формировании различных простатических симптомов [17, 18]. Следует отметить, что для пациентов 1-й группы установлена положительная сильная корреляционная связь между суммой баллов IPSS и изменением уровня эндотелина-1 (r=0,80; р<0,05), а увеличение уровня NO коррелировало с положительной динамикой практически всех простатических симптомов (r=-0,74; r=-0,51; r=-0,65; r=-0, 82; r=-0, 51, для всех р<0,05, 2–6-й вопросы опросника соответственно).
В группе пациентов, принимавших тадалафил «по требованию», изменение уровня эндотелина-1 коррелировало с ответом на вопрос о частоте неполного опорожнения мочевого пузыря после мочеиспускания (r=-0,55, р<0,05), а суммарный балл IPSS – с увеличением уровня NO (r=-0, 51, р<0,05).
Проведенное урофлоуметрическое исследование показало, что уродинамический показатель Qmax был снижен у пациентов всех групп (в норме у пациентов в возрасте 40–60 лет он не должен быть выше 18 мл/с [19]. Скорость мочеиспускания зависит от давления в мочевом пузыре (детрузор, натуживание), резистентности шейки/сфинктера. Одним из механизмов улучшения симптомов, обусловленных нарушениями уродинамики нижних мочевыводящих путей, может быть влияние тадалафила на выраженность ЭД [20, 21]. В ходе настоящего исследования отмечено достоверное повышение показателя Qmax, который составил 15 [11,5; 13] и 17 [16; 17] мл/с в 1-й и 2-й группах соответственно. В контрольной группе этот показатель практически не изменился (см. табл. 2). В группе ежедневного приема тадалафила отмечена корреляционная взаимосвязь между изменениями Qmax и уровнем эндотелина-1 (r= -0, 58, р<0,05) в ходе лечения.
Таким образом, проведенное исследование показало, что ежедневный прием тадалафила 5 мг/сут. более эффективен в долгосрочной перспективе при лечении ЭрД, что согласуется с ранее полученными данными, демонстрирующими, что низкие ежедневные дозы тадалафила безопасны и эффективны, обеспечивают стабильный уровень препарата, достаточный, чтобы положительно влиять на ЭрД [22]. Кроме того, показано, что ежедневный прием низких доз тадалафила может улучшать функцию эндотелия у пациентов с гиперплазией предстательной железы [23].
Нежелательных эффектов при приеме тадалафила СЗ как ежедневно по 5 мг, так и 20 мг «по требованию» в течение 4 нед. отмечено не было. Изменений показателей гемодинамики (АД, ЧСС), уровня трансаминаз, креатинина, глюкозы крови также не выявлено. Полученные нами результаты согласуются с мнением Д. Ю. Пушкаря и соавт. [24], которые в своем обзоре, посвященном эффективности и безопасности приема тадалафила 1 раз в сутки, подчеркнули, что данные современных клинических исследований свидетельствуют не только о высокой эффективности, но и о безопасности терапии тадалафилом в дозе 5 мг в сутки, а частота побочных эффектов сопоставима с таковой при приеме тадалафила в режиме по требованию, а также других ингибиторов ФДЭ-5. Кроме того, преимуществом ежедневного приема тадалафила является отсутствие психологической зависимости от времени приема препарата, что позволяет пациенту вести обычный образ жизни.
Выводы
1. Прием тадалафила в дозе 5 мг ежедневно или 20 мг «по требованию» в течение 4 нед. оказывает статистически значимое положительное влияние на показатели функции эндотелия и выраженность ЭрД.
2. Ежедневный прием 5 мг тадалафила по сравнению с режимом 20 мг «по требованию» более выраженно влияет на ЭД как патогенетический фактор, способствующий возникновению ЭрД.
3. Оба режима дозирования тадалафила безопасны для пациентов с заболеваниями сердечно-сосудистой системы.



