Актуальность. Трансуретральная резекция (ТУР) – «золотой» стандарт в лечении немышечно-инвазивного рака мочевого пузыря (НМИ РМП) [1–3]. Однако высокая (до 90%) частота рецидивов обусловливает необходимость поиска методов повышения радикальности лечения [3–5]. Одним из путей решения данной задачи является выполнение операции с применением дополнительных методов интраоперационного контроля: фотодинамического [6, 7], трансуретрального ультразвукового (ТУУЗ) [8–10], узкоспектровой цистоскопии [11–13] и оптической когерентной томографии [14–16]. Наиболее изучены ТУР под фотодинамическим и ТУУЗ-контролем. Однако публикации по сравнительному анализу этих двух методов малочисленны [17]. Другим способом повышения радикальности ТУР является адьювантная внутрипузырная химиотерапия (ВПХТ). К задачам ВПХТ относятся предупреждение имплантации опухолевых клеток и эрадикация резидуальной опухоли [18]. Впервые ВПХТ для лечения РМП в клинической практике в начале 1960-х гг. применили Jones и Swinney, используя препарат ТиоТЭФ [19]. Согласно рекомендациям Европейской ассоциации урологов, ранняя адьювантная ВПХТ показана пациентам с низким риском рецидива и как начальный этап химиотерапии в группе пациентов промежуточного и высокого риска [20, 21].
R. J. Sylvester et al. [22] считают, что длительная адьювантная ВПХТ эффективна во всех случаях после ТУР НМИ РМП. В том же исследовании показано, что митомицин С и доксорубицин проявляют одинаковый эффект, у ТиоТЭФа он несколько хуже. Другие авторы считают [23], что необходимости в длительной ВПХТ нет, а ее результаты сопоставимы с таковыми однократного введения химиопрепарата. Эффект ранней однократной ВПХТ сохраняется в течение первых 2 лет и повышает радикальность лечения [22, 24]. В то же время длительная поддерживающая ВПХТ изменяет частоту рецидива, но не влияет на прогрессировние заболевания [25].
Таким образом, несмотря на значительные успехи применения различных методов для снижения риска развития рецидива, необходим поиск путей повышения радикальности лечения пациентов с НМИ РМП.
Цель исследования: оценить эффективность дополнительных методов интраоперационного контроля ТУР в лечении НМИ РМП.
Материалы и методы. Проанализированы результаты лечения 138 пациентов, из них 92 мужчины, прооперированных в урологическом отделении ГАУЗ «Клиника медицинского университета» по поводу НМИ РМП в стадии Та–Т1N0M0. Средний возраст пациентов составил 59 лет. Монополярная ТУР выполнена 28 пациентам, ТУР под фотодинамическим контролем (ФДК) – 28, ТУР под интраоперационным ТУУЗ-контролем – у 26. Трансуретральная резекция с последующим ранним однократным внутрипузырным введением химиопрепарата (ранняя адьювантная химиотерапия – РАХТ) проведена 29 пациентам. Химиопрепарат – митомицин С 40 мг (n=5) и доксорубицин 50 мг (n=24) – вводили в первые 24 ч после ТУР. Длительную адьювантную внутрипузырную химиотерапию (ДАХТ) после ТУР получили 27 пациентов: в 6 случаях для инстилляции использовали митомицин С 40 мг, в 21 – доксорубицин 50 мг, которые вводили 1 раз в неделю в течение 6 нед., затем 1 раз в месяц до 12 мес.
Оценивали частоту и характер рецидивов в зависимости от метода лечения в течение 5 лет. Степень тяжести послеоперационных осложнений определяли согласно классификации Clavien–Dindo.
Статистическая обработка данных осуществлена с использованием пакета прикладных программ Statistica 7.0 и Microsoft Exel 2003.
Результаты. В группе монополярной ТУР рецидивы в целом возникли у 14 (50%) пациентов (см. таблицу), что говорит о недостаточной радикальности метода.
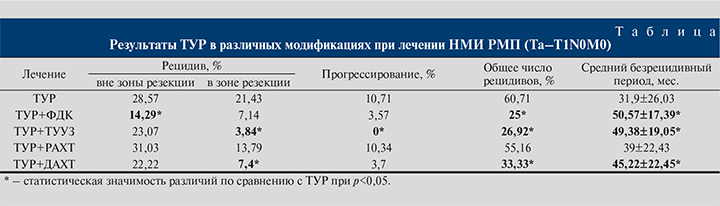
У 3 (10,71%) пациентов диагностировано прогрессирвание опухолевого процесса в мышечно-инвазивную форму. Общее чило рецидивов в данной группе за пятилетний срок наблюдения составило 17 (60,71%) случаев. Средний безрецидивный период в данной группе составил 31,9 мес.
При монополярной ТУР осложнения развились у 5 (17,86%) пациентов. Причиной кровотечения, возникшего в ближайшем послеоперационном периоде у 3 (13,63%) пациентов, был недостаточно эффективный интраоперационный гемостаз. Данное осложнение в 2 (7,14%) наблюдениях было ликвидировано консервативно (Clavien–Dindo II), 1 (3,57%) пациенту потребовалось хирургическое вмешательство: ревизия мочевого пузыря (Clavien–Dindo III). Перфорация стенки мочевого пузыря (Clavien–Dindo III) в 1 (3,57%) случае возникла в результате раздражения запирательного нерва и как следствие –неконтролируемой глубины резекции стенки мочевого пузыря. Воспалительные осложнения в виде обострения хронического пиелонефрита (Clavien–Dindo II) у 1 (3,57%) пациента обусловлены сопутствовавшей хронической инфекцией мочевыводящих путей.
В группе ТУР+ФДК отмечено снижение частоты рецидивов как вне, так и в зоне резекции (см. таблицу). Прогрессирование опухолевого процесса имело место только в 1 (3,57%) наблюдении. Средний безрецидивный период увеличился на 18,67 мес. по сравнению с контрольной группой монополярной ТУР, составив 50,57 мес. Применение ФДК в ходе ТУР немышечно-инвазивных форм новообразований мочевого пузыря позволило снизить общую частоту рецидивов в 2,4 раза. Послеоперационное течение у 2 (7,14%) пациентов осложнилось обострением хронического пиелонефрита (Clavien–Dindo II), после резекции устья мочеточника при локализации новообразования в данной области. В результате развился отек интрамурального отдела мочеточника, что привело к нарушению уродинамики верхних мочевыводящих путей. У 1 (3,57%) пациента на 4-й год наблюдения возникла стриктура мембранозного отдела уретры (Clavien–Dindo III).
Анализ результатов ТУР под динамическим ТУУЗ-контролем (ТУР+ТУУЗ) показал, что данная методика обеспечивает максимальный контроль радикальности в зоне резекции: рецидив в области оперативного вмешательства диагностирован лишь в 1 (3,84%) наблюдении. При этом не зафиксировано ни одного случая прогрессирования заболевания. Однако ТУУЗ-контроль не влияет на частоту рецидивов вне зоны резекции, так как по данному показателю группа была сопоставимой с группой ТУР (см. таблицу). К основным осложнениям ближайшего послеоперационного периода отнесены кровотечение (1 [3,85%] пациент; Clavien–Dindo II), обострение хронического пиелонефрита (3 [11,54%]; Clavien–Dindo II). Инфекционно-воспалительные осложнения возникли на фоне хронической инфекции мочевыводящих путей и неадекватной дренажной функции уретрального катетера, приведших к пузырно-мочеточниковому рефлюксу. Адекватная антибактериальная терапия во всех случаях позволила справиться с воспалительным процессом. В 1 (3,85%) случае интраоперационно произошла перфорация стенки мочевого пузыря в результате неадекватной визуализации зоны резекции опухоли передней стенки мочевого пузыря (Clavien–Dindo III). Осложнение выявлено с помощью ТУУЗ-контроля во время ТУР и потребовало повторного хирургического вмешательства: ревизии мочевого пузыря и ушивания перфорации.
В группе ТУР+РАХТ рецидив вне зоны резекции за 5 лет наблюдения выявлен у 9 (30,03%) пациентов. Рецидивы возникали к концу первого года после операции, и частота их достигла максимума к третьему году наблюдения. Рецидивы в зоне резекции развивались в первый год диспансерного наблюдения и не возникали в дальнейшем. Прогрессирование заболевания выявлено у 3 (10,34%) пациентов. Общее количество рецидивов и средний безрецидивный период статистически значимо не отличались от такового показателей группы ТУР (см. таблицу). Осложнением ТУР+РАХТ в 2 (6,9%) наблюдениях был острый цистит, в 1 (3,45%) – кровотечение, купированные консервативно (Clavien–Dindo II). В целом можно заключить, что ТУР с РАХТ не способствует снижению частоты рецидивов и ее применение сразу после операции нецелесообразно.
Анализ результатов ТУР+ДАХТ показал статистически значимое преимущество методики перед ТУР по всем показателям, кроме частоты рецидивов вне зоны резекции (см. таблицу). Осложнения в этой группе имели инфекционно-воспалительный характер (Clavien–Dindo II): острый цистит у 3 (11,1%) пациентов, активная фаза пиелонефрита у 1 (3,7%). Адекватная антибактериальная терапия с учетом чувствительности к антибиотикам по результатам бактериологического исследования мочи позволила ликвидировать воспалительный процесс и завершить курс длительной ВПХТ. Препараты группы α1-адреноблокаторов способствовали улучшению мочеиспускания, устранению дизурии, которая являлась нередким осложнением ВПХТ.
Длительная адьювантная ВПХТ после ТУР улучшает результаты лечения, повышая радикальность вмешательства путем профилактики рецидивов в зоне резекции в 2,9 раза, и увеличивает безрецидивный период до 45 мес.
Выводы
1. Анализ результатов лечения НМИ РМП и последующего диспансерного наблюдения показал, что наиболее радикальным способом лечения является ТУР под фотодинамическим контролем. Данный метод позволяет достоверно снижать общую частоту рецидивов и увеличивать безрецидивный период, преимущественно снижая частоту рецидивов вне зоны резекции.
2. Выполнение ТУР под ТУУЗ-контролем повышало радикальность путем снижения частоты рецидива в зоне резекции, обеспечивая профилактику прогрессирования, тем самым увеличивая длительность среднего безрецидивного периода.
3. При невозможности проведения интраоперационного контроля в качестве альтернативы целесообразно сочетать ТУР с длительной ВПХТ с целью повышения радикальности. Данный метод повышает радикальность лечения, увеличивает средний безрецидивный период, снижая частоту рецидива в зоне резекции.



