Введение. Доброкачественная гиперплазия предстательной железы (ДГПЖ) – одно из наиболее распространенных заболеваний в урологической практике, вызывающее симптомы нижних мочевыводящих путей (СНМП) в пожилом возрасте [1]. Распространенность ДГПЖ прогрессивно увеличивается после 40 лет, таким образом к 90 года составляя более 90% [2], и значительно ухудшает качество жизни [3, 4]. По разным данным, к 80 годам каждый 4-й мужчина будет нуждаться в лечении по поводу ДГПЖ. Социальная значимость и актуальность этой проблемы подчеркиваются демографическими исследованиями Всемирной организации здравоохранения, свидетельствующими о росте населения планеты в возрасте старше 60 лет, причем его темпы существенно опережают рост численности населения в целом вне зависимости от страны.
Интравезикальная простатическая протрузия (ИПП) – относительно новый параметр, оценивающий интравезикальную обструкцию (ИВО) [5]. Связь ИПП с ИВО, а также ее влияние на выбор консервативной терапии ДГПЖ наглядно продемонстрированы в диссертационной работе А. Д. Болотова [6].
Одними из основных методов хирургического лечения гиперплазии простаты является биполярная трансуретральная резекция простаты (бТУРП) и позадилонная аденомэктомия (ПАЭ), а персонификация подхода к лечению пациентов в настоящее время крайне актуальна. Персонификация возможна путем выявления предикторов, влияющих на результат лечения.
Цель настоящей работы: оценить влияние интравезикальной простатической протрузии на функциональные результаты биполярной трансуретральной резекции простаты и позадилонной аденомэктомии.
Материалы и методы. Работа имеет ретроспективный характер и выполнена на базе Федерального государственного образовательного учреждения дополнительного профессионального образования «Российская медицинская академия непрерывного профессионального образования» Министерства здравоохранения Российской Федерации, университетской клинической больницы им. С. П. Боткина в соответствии с Хельсинкской декларацией Всемирной медицинской ассоциации «Этические принципы проведения научных медицинских исследований с участием человека» и Правилами клинической практики в Российской Федерации, утвержденными приказом № 266 Минздрава России от 19.06.2003. В основу данной работы легли результаты обследования и лечения отобранных сплошным методом 210 пациентов, обратившихся в урологическую клинику ГКБ им. С. П. Боткина с симптомами нижних мочевыводящих путей, вызванными инфравезикальной обструкцией, обусловленной доброкачественной гиперплазией предстательной железы, в период с сентября 2019 по декабрь 2021 г. Критерии включения: информированное согласие на участие в исследовании; отсутствие тяжелой соматической патологии по основным классам заболеваний (МКБ10); наличие симптомов нижних мочевыводящих путей, вызванных инфравезикальной обструкцией (IPSS>20 или Qmax<10), обусловленной гиперплазией простаты, неэффективность предшествовавшей терапии альфа-адреноблокаторами и ингибиторами 5α-редуктазы.
Критерии исключения: отказ от участия в исследовании, наличие тяжелой соматической патологии по основным классам заболеваний (МКБ-10), возраст менее 50 лет, наличие рака простаты, резистентный к терапии сахарный диабет или диабетическая нейропатия, наличие в анамнезе или при физикальном обследовании признаков неврологического заболевания, хирургических вмешательств или травм в тазовой области, наличие в анамнезе заболеваний, передаваемых половым путем, прием лекарственных средств, способных воздействовать на мочевой пузырь, наличие рубцовой деформации шейки мочевого пузыря.
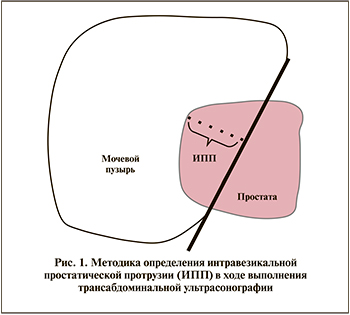
С учетом вышеописанных критериев хирургическое лечение гиперплазии простаты проведено 210 пациентам. Трансабдоминальная ультрасонография выполнялась на аппарате «Acuson XP 128/10» с использованием конвексного абдоминального датчика (рабочая частота 3–3, 5–5 МГц). Интравезикальная простатическая протрузия измерялась во время трансабдоминальной ультрасонографии предстательной железы по стандартному принципу, представленному на рис. 1. В зависимости от величины интравезикальной простатической протрузии (ИПП) каждая из групп была дополнительно разделена на подгруппы: подгруппа «а», где ИПП менее 5 мм, – Ia (n=49), IIa (n=53), и подгруппа «б», где ИПП более 5 мм, – Iб (n=52) и IIб (n=56).
Урофлоуметрия проводилась на портативном аппарате УРОДИН 1000 фирмы ДАНТЕК. Заполнение опросников осуществлялось по правилам GCP (Good Clinical Practice), т.е. без участия врача.
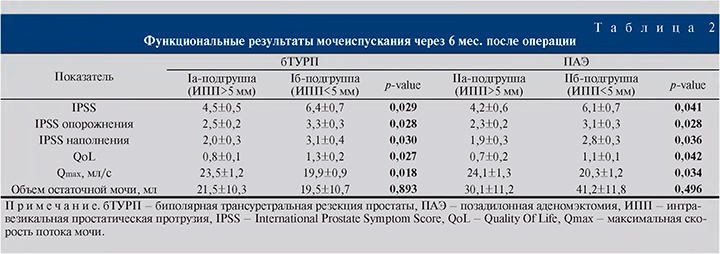
В зависимости от выбора метода хирургического лечения и объема простаты все пациенты были рандомизированы на две группы. В первую группу вошли больные с объемом простаты менее 80 см3, перенесших бТУРП (n=101). Вторую группу составили пациенты с объемом простаты более 80 см3, которым была выполнена стандартная ПАЭ (n=109).
Через 6 мес. после операции всем обследованным пациентам проводилось определение объема простаты, величины ИПП, максимальной скорости потока мочи (Qmax), объема остаточной мочи. Оценка результатов лечения осуществлялась путем анкетирования с помощью шкалы IPSS (дополнительно систематизированную на симптомы накопления и опорожнения) и шкалы качества жизни (QoL).
Обработка полученных данных выполнена в рамках пакета статистических программ Excel-2010 (среднее арифметическое, среднее квадратичное отклонение). Оценку репрезентативности выборки определяли в ходе ее проверки на нормальность распределения согласно критерию Колмогорова. В ходе обработки полученных данных рассчитывали долевые соотношения в процентах. Проверку гипотезы о различиях между долями проводили согласно критерию Стьюдента. Различия считали значимыми при p<0,05.
Результаты. Входящие параметры, за исключением объема простаты (менее 80 см3 в группе бТУРП и более 80 см3 в группе ПАЭ), не имели статистически значимых различий (табл. 1).
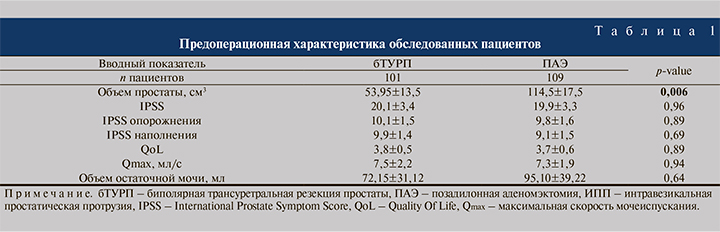
Функциональные результаты мочеиспускания через 6 мес. после операции представлены в табл. 2. При сравнении функциональных результатов качества мочеиспускания через 6 мес. после хирургического лечения методом биполярной ТУРП у пациентов с ИПП более 5 мм и ИПП менее 5 мм (подгруппы Iа и Iб соответственно), установлено достоверно значимое снижение баллов шкалы IPSS – 4,5±0,5 и 6,4±0,7 (p<0,05), в том числе как опорожнения (2,5±0,2 и 3,3±0,3; p<0,05), так и наполнения (2,0±0,3 и 3,1±0,4; p<0,05); снижение баллов шкалы QoL (0,8±0,1 и 1,3±0,2; p<0,05), улучшение максимальной скорости потока мочи пациентов (23,5±1,2 и 19,9±0,9; p<0,05). В отношении уменьшения объема остаточной мочи в вышеуказанных группах достоверных различий выявлено не было (21,5±10,3 и 19,5±10,7; p=0,89).
Подобные функциональные результаты продемонстрированы и в группе пациентов, перенесших позадилонную аденомэктомию. Через 6 мес. после операции установлено достоверно значимое снижение баллов шкалы IPSS (4,2±0,6 и 6,1±0,7; p<0,05), в т.ч. как опорожнения (2,3±0,2 и 3,1±0,3; p<0,05), так и наполнения (1,9±0,3 и 2,8±0,3; p<0,05), снижение баллов шкалы QoL (0,7±0,2 и 1,1±0,1; p<0,05), улучшение максимальной скорости потока мочи (24,1±1,3 и 20,3±1,2; p<0,05) у пациентов с ИПП более 5 мм (IIа-подгруппа), чем у пациентов с ИПП менее 5 мм (IIбподгруппа). Кроме того, также нет достоверных различий в отношении объема остаточной мочи (30,1±11,2 и 41,2±11,8; p=0,50)
Сравнивая функциональные результаты бТУРП и ПАЭ с учетом ИПП >5 и ИПП <5 мм, т.е. сравнивая между собой Iaи IIaи Iби IIб-подгруппы соответственно, статистически значимых различий в значении IPSS (4,5±0,5 и 4,2±0,6, где p=0,70, 6,4±0,7 и 6,1±0,7, где p=0,751), в том числе IPSS наполнения (2,0±0,3 и 1,9±0,3, где p=0,813, 3,1±0,4 и 2,8±0,3, где p<0,549) и IPSS опорожнения (2,5±0,2 и 2,3±0,2, где p=0,481, 3,3±0,3 и 3,1±0,3, где p<0,638), QoL (0,8±0,1 и 0,7±0,2, где p=0,655, 1,3±0,2 и 1,1±0,1, где p=0,373), Qmax (23,5±1,2 и 24,1±1,3, где p=0,735, 19,9±0,9 и 20,3±1,2, где p=0,791), объема остаточной мочи (21,5±10,3 и 30,1±11,2, где p=0,573, 19,5±10,7 и 41,2±11,8, где p=0,175) выявлено не было, что позволяет сделать вывод о сопоставимости по эффективности вышеописанных хирургических методов лечения ДГПЖ.
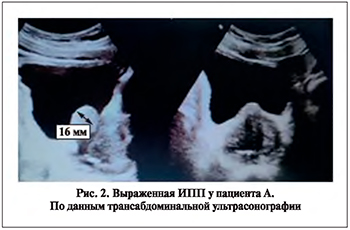
Клиническое наблюдение № 1 Пациент А. 65 лет. Жалобы на мочеиспускание вялой струей мочи, тяжесть в надлобковой области, чувство неполного опорожнения мочевого пузыря, ноктурию до 5 раз. Вышеуказанные симптомы отмечает в течение года. Амбулаторно получал комбинированную терапию α1a-адреноблокатором (Тамсулозин 0,4 мг 1 раз в сутки) и ингибитором 5α-редуктазы 1-го и 2-го типов (Дутастерид 500 мкг 1 раз в сутки) без эффекта. По данным дообследования: сумма баллов по шкале IPSS – 26, качество жизни (QoL) – 5, уровень простатспецифического антигена (ПСА) крови – 1,9 нг/мл. По данным пальцевого ректального исследования, предстательная железа без очагов уплотнения. По данным урофлоуметрии, Qmax 6,9 мл/с, за время исследования выделено 140 мл мочи. По данным трансабдоминальной ультрасонографии: объем простаты – 61 см3, ИПП – 16 мм (рис. 2).
Таким образом, с учетом наличия инфравезикальной обструкции предстательной железы, обусловленной ДГПЖ, пациенту выполнена биполярная трансуретральная резекция простаты. На вторые сутки после операции уретральный катетер удален с предварительным наполнением мочевого пузыря до умеренных позывов к мочеиспусканию физиологическим раствором в объеме 250 мл. Пациент повторно обследован через 6 мес. после операции: сумма баллов по шкале IPSS – 4 (из них IPSS наполнения – 2, опорожнения – 2), качество жизни (QoL) – 1, Qmax – 25 мл/с, остаточной мочи – 20 мл.
Клиническое наблюдение № 2. Пациент К. 67 лет. Жалобы на мочеиспускание вялой струей мочи, чувство неполного опорожнения мочевого пузыря, ноктурию до 3 раз более 5 лет. В течение 4 лет получал аналогичную вышеописанной в клиническом случае № 1 комбинированную терапию α1a-адреноблокатором (Тамсулозин 0,4 мг 1 раз в сутки) и препарат группы 5α-редуктазы 1-го и 2-го типов (Дутастерид 500 мкг 1 раз в сутки) с временным эффектом. Прогрессивное ухудшение качества мочеиспускания последние полгода. По данным дообследования: сумма баллов по шкале IPSS – 25, QoL – 5, ПСА крови – 1,5 нг/мл. По данным пальцевого ректального исследования, предстательная железа без очагов уплотнения. По данным урофлоуметрии, Qmax – 7,3 мл/с, за время исследования выделено 160 мл мочи. По данным трансабдоминальной ультрасонографии: объем простаты – 52 см3, ИПП – 4 мм (рис. 3).
С учетом наличия инфравезикальной обструкции предстательной железы, обусловленной ДГПЖ объемом 56 см3, пациенту также выполнено оперативное лечение методом биполярной трансуретральной резекции простаты. Уретральный катетер удален на вторые сутки после операции с наполнением мочевого пузыря. Через 6 мес. после операции проведено контрольное обследование: сумма баллов по шкале IPSS – 6 (из них IPSS наполнения – 3, опорожнения – 3), QoL 2, Qmax – 19 мл/с, остаточной мочи – 25 мл.
Обсуждение. Поскольку совокупность хирургических методов лечения ДГПЖ, находящих применение в клинической практике, в настоящее время представляет собой внушительный список, для каждого из хирургических методов отсутствуют четкие показания. Выбор метода хирургического лечения, по актуальным рекомендациям Российского общества урологов, утвержденным Минздравом РФ [7] и Европейской ассоциацией урологов [8], зависит от объема простаты, сопутствующих заболеваний и возможности проведения анестезии, выбора пациента, оценки возможных осложнений, связанных с лечением, доступности хирургических методов и предпочтений хирурга в проведении определенных операций. Помимо этого Д. В. Еникеев и соавт. [9] произвел сравнение показаний к оперативному лечению ДГПЖ рекомендаций Европейского общества урологов, Американского общества урологов, Национального института здоровья и клинического совершенствования, где наглядно продемонстрировал гетерогенность показаний к выбору операции, что обусловливает актуальность выявления предикторов функциональных результатов оперативных методик с целью формирования персонифицированного подхода к выбору метода хирургического лечения ДГПЖ.
В последнее время растет интерес научного сообщества к интравезикальной простатической протрузии. Г. Г. Кривобородов и соавт. [5] в обзорной статье продемонстрировали, что интравезикальная простатическая протрузия (ИПП) является относительно новым показателем, который используется для оценки значимости интравезикальной обструкции. Также А. Д. Болотов [6] в рамках диссертационного исследования продемонстрировал влияние ИПП на консервативную терапию ДГПЖ.
В отношении пороговой величины ИПП существуют различные данные. Ряд источников [10–13] предлагает следующее распределение по степеням: I степень – менее 5 мм, II степень – от 5 до 10, III степень – более 10 мм. Так, Reis et al. [12] рассматривали пороговым значением наличия инфравезикальной обструкции величину ИПП в 5 мм с чувствительностью 95% и специфичностью 50%. Shin et al. [13] для ИПП, равной 5 мм, получили чувствительность 66,7% и специфичность 80,5%. А. Д. Болотов и соавт. [6] в рамках диссертационного исследования определили величину ИПП, равную 10 мм, с чувствительностью 67,4% и специфичностью 100% в отношении наличия инфравезикальной обструкции. Следует отметить, что все вышеописанные исследования так или иначе затрагивали влияние ИПП на консервативную терапию ДГПЖ, однако определения пороговых значений ИПП для оперативного лечения не предлагалось. Таким образом, пороговым значением разделения на подгруппы нами взято значение ИПП, равное 5 мм, однако определенно и с учетом полученных в настоящем исследовании данных целесообразно выполнение дальнейших исследований иными пороговыми значениями ИПП.
Выводы. С учетом гетерогенности данных и отсутствия четких показаний выбора метода хирургического лечения ДГПЖ можно сделать вывод, согласно которому существует проблема выбора метода оперативного лечения доброкачественной гиперплазии простаты, что позволяет формулировать концепцию персонифицированного подхода, элементы которого представлены в настоящей работе. Вышеописанные клинические наблюдения свидетельствуют, что пациенты с интрапузырной простатической протрузией выше 5 мм демонстрируют лучшие функциональные результаты на протяжении 6 мес. после биполярной трансуретральной резекции простаты, чем пациенты с интрапузырной простатической протрузией менее 5 мм. Выявлено достоверно более значимое снижение результатов шкалы IPSS, в особенности симптомов опорожнения, QoL и увеличение максимальной скорости потока мочи через 6 мес. у пациентов с интрапузырной простатической протрузией свыше 5 мм. Согласно сравнению биполярной трансуретральной резекции простаты и позадилонной аденомэктомии, последняя показала достоверно более значимое снижение вышеописанных показателей в группе с интрапузырной простатической протрузией свыше 5 мм, в то время как в группе с интрапузырной простатической протрузией менее 5 мм достоверных различий между показателями качества мочеиспускания выявлено не было.



