Актуальность. Рак предстательной железы (РПЖ), развивающийся из эпителия ее альвеолярно-клеточных элементов, считается одним из наиболее распространенных злокачественных новообразований у мужчин и вторым по показателю смертности заболеванием в этой популяции [1–3]. Ежегодно в мире регистрируют 1 млн 100 тыс. новых случаев РПЖ [4]. В Японии у трети больных РПЖ выявляют в старческом возрасте [5].
В Дании в 1980 г. зарегистрировано 1297 больных РПЖ, к 2012 г. количество больных выросло до 4315 при сравнительно высоких показателях смертности, особенно среди лиц старше 80 лет [6]. В Беларуси около 60% впервые выявленных случаев заболевания диагностируют на поздних (III–IV) стадиях, в Северной Америке и странах Западной Европы данный показатель варьируется от 15 до 35% [7].
К 2016 г. в Казахстане доля пациентов с РПЖ, диагностированным на начальных стадиях, составила 42,7%, в Узбекистане – 29,2%, в Кыргызстане – 27,8% [8].
Высокая смертность от РПЖ обусловлена контингентом больных, у которых заболевание было обнаружено на поздних стадиях. В связи с особенностями развития опухоль может долгие годы не сказываться на самочувствии больного или же проявляться ирритативными и/или обструктивными симптомами, не специфичными для РПЖ. В связи с этим успех лечения во многом определяется эффективностью ранней диагностики локализованного РПЖ, осуществляемой исключительно с помощью биопсии, что делает ее одной из наиболее распространенных урологических процедур. В США ежегодно выполняется свыше 500 тыс. биопсий простаты [9]. Трансперинеальный доступ исторически описан первым [10], хотя в настоящее время он используется реже, чем трансректальный доступ [11]. Причина в том, что трансперинеальная методика выполнения процедуры более инвазивна и технически сложна [12].
Мета-анализ данных литературы показал, что забора материала из 10–12 участков предстательной железы (ПЖ) трансректальным доступом под контролем трансректального УЗИ (ТРУЗИ) достаточно для первичной и повторной биопсии. Данная методика биопсии называется систематической, где максимально охватывается периферическая зона ПЖ [13].
Необходимо отметить, что в ранней дианостике локализованного РПЖ ключевую роль играет своевременно выполненная биопсия. Однако высокий процент истинно- и ложноотрицательных результатов первичной биопсии, а также нежелательные инфекционно-воспалительные осложнения, обусловленные техникой проведения процедуры, ставят перед исследователями вопрос о необходимости разработки оптимальных показаний к выполнению данной процедуры.
Цель исследования: улучшить результаты ранней диагностики РПЖ путем совершенствования показаний к выполнению биопсии ПЖ.
Материалы и методы. Проведен анализ результатов 251 первичной мультифокальной биопсии простаты, выполненной пациентам, обратившимся в РСНПМ «Центр урологии» по поводу симптомов нижних мочевыводящих путей в 2018–2019 гг. Пациенты были разделены на две группы в зависимости от объема предварительного клинического обследования. В первую группу вошли 189 пациентов, которым была выполнена первичная мультифокальная (систематическая корэ) биопсия простаты, основанием которой стало обнаружение повышенного содержания общего сывороточного простатического специфического антигена (ПСА) и/или наличие подозрительного очага в простате, по данным пальцевого ректального исследования (ПРИ) и ТРУЗИ простаты.
Вторую группу составили 62 пациента, которым кроме указанных исследований до биопсии выполняли мультипараметрическую магнитно-резонансную томографию (мпМРТ) простаты на аппарате Philips Ingenia 1.5 Tesla с оценкой полученных данных по шкале PI-RADS v2 (Prostate imaging reporting and data system), т.е. с определением степени риска выявления РПЖ [14, 15].
Возраст пациентов первой группы составил 68,54±0,54 (51–92) года, уровень общего ПСА в сыворотке крови – 75,21±9,88 (1,4–893,5) нг/мл, объем ПЖ – 72,36±2,29 (21–197) см3, во второй группе соответствующие показатели составили 67,58±1,07 (47–88) года, 86,90±18,65 (2,5 – 638,0) нг/мл, 66,50 ± 3,74 (17–174) см3.
Трансректальное УЗИ проведено всем пациентам с помощью ректального внутриполостного датчика с частотой 7,5 МГц (C9-4v, 42 Гц, динамический диапазон) на аппарате Philips Affinity 50 G (Голландия). Оценивали поперечный, переднезадний и сагиттальный размеры ПЖ, рассчитывали ее объем. При выявлении эхопатологии ткани ПЖ определяли ее размер, локализацию и структуру.
Подготовка пациентов к биопсии включила прекращение приема антиагрегантов за 5–7 сут. до процедуры, начало приема ципрофлоксацина по 500 мг 2 раза в сутки накануне процедуры (с 2019 г. – парентеральное введение защищенных цефалоспоринов за 2 ч до процедуры), очистительную клизму за 1 ч до процедуры.
Материал для исследования во всех случаях получен трансректальным доступом под контролем ТРУЗИ на фоне местной анестезии с использованием геля с лидокаином (катеджель) и перипростатической блокады 2%-ным раствором лидокаина. Забор материала проведен с помощью биопсийного пистолета BIP-high speed multi иглой 18–20G, длиной 20 см, из 10–12 участков ПЖ с охватом периферической и апикальной зон. У 62 пациентов второй группы дополнительно осуществлен прицельный забор 2–4 столбиков из зоны интереса, выявленной при мпМРТ.
Статистическая обработка материала проведена с помощью программ MS Office Excel 2007, StatSoftStatistica 8.0 с использованием критериев Стьюдента, Фишера. Статистически значимыми считали различия при p<0,05.
Результаты. В первой группе по результатам первичных биопсий в 124 (65,6%) наблюдениях была верифицирована аденокарцинома, в 65 (34,4%) – доброкачественная гиперплазия ПЖ (ДГПЖ), аденоматозный вариант. Анализ результатов биопсий в зависимости от объема ПЖ показал следующую картину (табл. 1).
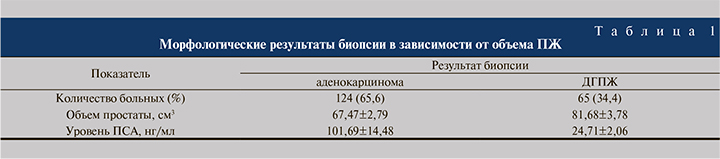
Результаты морфологического исследования материала простаты в зависимости от уровня общего ПСА показал, что повышенный уровень ПСА в значительной степени обусловливает выявляемость РПЖ (рис. 1).
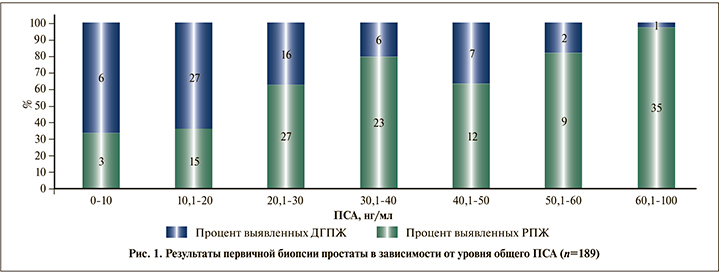
Как видно на рис. 1, наиболее высокая доля отрицательных результатов биопсии оказалась среди пациентов с уровнем ПСА менее 20 нг/мл (n=51) – 33 (64,7%).
Учитывая подобную картину низкой выявляемости РПЖ среди пациентов с уровнем ПСА менее 20 нг/мл, пациентов первой группы (n=189) мы разделили на две большие подгруппы: с уровнем ПСА менее 20 и более 20,1 нг/мл (табл. 2).
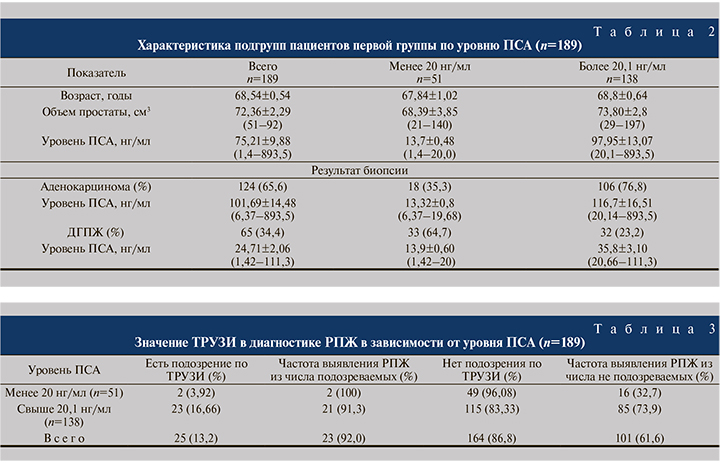
Как видно из табл. 2, среди пациентов с уровнем ПСА менее 20 нг/мл выявляемость РПЖ была низкой – 18 (35,3%) наблюдений, тогда как среди пациентов с уровнем ПСА выше 20,1 нг/мл РПЖ диагностировали статистически значимо чаще – 106 (76,8%) пациентов (p<0,05).
Далее в каждой подгруппе мы анализировали роль и информативность ТРУЗИ и ПРИ в диагностике РПЖ (табл. 3). Анализ показал, из 189 пациентов только у 25 (13,2%) в ходе ТРУЗИ обнаружены подозрительные очаги в ПЖ, из них у 23 (92%) выявлен РПЖ. Однако в целом данные ТРУЗИ позволили выявить заболевание лишь у 23 (12,2%) из 189 обследованных.
При этом среди пациентов с уровнем ПСА менее 20 нг/мл в подавляющем большинстве (96,08%) наблюдений ТРУЗИ не имело диагностической ценности при выявлении заболевания. Роль ТРУЗИ в подгруппе пациентов с уровнем ПСА более 20,1 нг/мл несколько больше (16,66%), но в данной подгруппе большему количеству пациентов была также выполнена биопсия из-за увеличения уровня ПСА. Следовательно, роль ТРУЗИ в ранней диагностике РПЖ среди пациентов с уровнем ПСА менее 20 нг/мл значительно меньше.
Анализ роли ПРИ простаты в ранней диагностике РПЖ показал (табл. 4), что она, к сожалению, возрастает только среди больных с высоким уровнем ПСА.

Из 189 пациентов у 62 (32,8%) были обнаружены участки уплотнения, подозрительные на РПЖ, и из числа подозреваемых выявляемость после биопсии достигла 55 (88,7%). В целом ПРИ позволило выявить заболевание у 55 (29,1%) обследованных.
Среди пациентов с уровнем ПСА менее 20 нг/мл только у 17,6% выявлены изменения при ПРИ и после биопсии РПЖ был верифицирован у 66,66% из числа подозреваемых.
Таким образом, роль ПРИ простаты в ранней диагностике РПЖ среди пациентов с уровнем ПСА менее 20 нг/мл также низкая – выявляемость 6 (11,76%) из 51.
Далее мы проанализировали результаты биопсии простаты у пациентов, у которых изменения, подозрительные на РПЖ, были выявлены как при ПРИ, так и по данным ТРУЗИ (табл. 5): по данным биопсии, РПЖ был выявлен в 100% наблюдений. Однако подобная комбинация методов исследований в подгруппе пациентов с уровнем ПСА менее 20 нг/мл оказалась информативной только у 1 (1,96%) пациента (см. табл. 5).
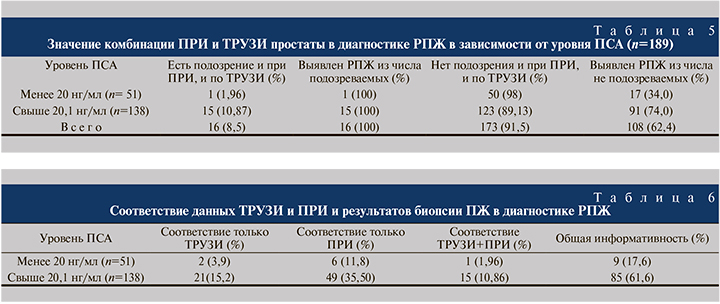
Проведенный анализ показал, что в первой подгруппе по сравнению со второй информативность ТРУЗИ и ПРИ была достоверно ниже – 9 (17,6%) против 85 (61,6%; р<0,001; табл. 6).
Таким образом, у большинства больных с уровнем ПСА менее 20 нг/мл отсутствуют характерные изменения в простате по данным ТРУЗИ и ПРИ; выявляемость РПЖ в данной подгруппе составила всего 35,3% (см. табл. 2).
 В свою очередь отрицательный результат имел место у 64,7% обследованных. Среди последних – пациенты с истинно отрицательным и ложноотрицательным результатом. Следовательно, часть из этих больных в динамике по показаниям будут подвергнуты повторной травматичной процедуре биопсии.
В свою очередь отрицательный результат имел место у 64,7% обследованных. Среди последних – пациенты с истинно отрицательным и ложноотрицательным результатом. Следовательно, часть из этих больных в динамике по показаниям будут подвергнуты повторной травматичной процедуре биопсии.
С учетом подобной картины для рационального выбора показаний к биопсии 62 пациентам второй группы была выполнена мпМРТ простаты. Пациентов распределили, исходя из риска выявления рака согласно PI-RADS v2, всем выполнили стандартную биопсию (10–12 столбиков) и прицельную биопсию из зон интереса (2–4 столбика).
Пациентов с PI-RADS 1, по данным мпМРТ, не было выявлено. При PI-RADS 2 и PI-RADS 3 выявляемость РПЖ не превысила 20%, PI-RADS 4 и PI-RADS 5 она составила 87,5 и 92,3% соответственно (рис. 2).
Далее мы провели анализ результатов биопсии, исходя из уровня ПСА, распределив пациентов в две подгруппы аналогично тому, как это было сделано для первой группы (табл. 7).
Из 3 пациентов с PI-RADS 2 и уровнем ПСА менее 20 нг/мл ни у одного не подтвердился РПЖ, тогда как в подгруппе с уровнем ПСА более 20,1 нг/мл РПЖ выявлен у 1 (50%) пациента (см. табл. 7).

При PI-RADS 3 в первой подгруппе из 15 пациентов у 1 (6,67%) выявлен РПЖ, у 2 (13,3%) – HGPIN, тогда как из 8 пациентов второй подгруппы с такой же степенью РПЖ выявлен у 3 (37,5%; р=0,1).
При PI-RADS 4 в первой подгруппе выявляемость РПЖ выросла до 66,7%, во второй – до 100% (р=0,2).
При PI-RADS 5 в первой подгруппе выявляемость РПЖ выросла до 80%, во второй составила 95,2% (p=0,5).
Таким образом, в первой подгруппе пациентов со степенью риска 4 и 5 по PI-RADS v2, кому в обязательном порядке рекомендуется биопсия ПЖ, выявляемость РПЖ составила 75 против 35,3% аналогичной подгруппы, где мпМРТ не выполнялась (р<0,05; см. табл. 2).
Обсуждение. Ключевым событием в лабораторной дифференциальной диагностике заболеваний ПЖ на границе 1970–1980-х гг. стало выделение ПСА и определение его роли в выявлении РПЖ [16–18]. Так, в мета-анализах по результатам многочисленных исследований, посвященных информативности ПСА в ранней диагностике РПЖ, установлено, что чувствительность, специфичность и положительная предикативная ценность ПСА составляют соответственно 72,1, 93,2 и 25,1% [19, 20].
Введение определения ПСА в качестве скрининговой методики позволило в 2 раза увеличить выявляемость РПЖ на ранних стадия заболевания (Т1–Т2), в то время как ПРИ позволяло диагностировать РПЖ только в 30% гистологически подтвержденных случаев [21]. Мы в своем исследовании подтвердили данные литературы, согласно котрым из трех методов, принятых в качестве «золотого» стандарта исследования ПЖ (определение ПСА, ПРИ и ТРУЗИ ПЖ), уровень ПСА характеризуется наименьшим числом ложноотрицательных результатов [22].
По мнению некоторых авторов, использования уже ставших стандартными методов диагностики РПЖ, ТРУЗИ, МРТ, определения уровня общего ПСА в настоящее время недостаточно [23]. Достоверным методом диагностики является пункционная биопсия ПЖ, однако существует вероятность отрицательных результатов исследования, особенно среди лиц с низким уровнем ПСА. Мы в нашем исследовании также констатировали высокую долю отрицательных результатов среди пациентов с уровнем ПСА менее 20 нг/мл – 64,7%.
Магнитно-резонансная томография все шире входит в практику как объективный высокоэффективный метод исследования. По мнению многих авторов [24–28], МРТ, обладающую высокой мягкотканной контрастностью, следует включать в диагностический комплекс исследований ПЖ в качестве обязательного метода. По данным литературы, мпМРТ пациентов с РПЖ обладает большим преимуществом по сравнению с другими клиническими и лучевыми методами диагностики в определении локализации, истинных размеров опухоли и степени ее агрессивности [28]. Указанные авторы считают, что мпМРТ ПЖ необходимо проводить пациентам с отрицательными результатами биопсии (как первично, так и неоднократно) и/или с подозрительным уровнем ПСА, низким и/или в «серой» зоне (4–10 нг/мл). Однако мпМРТ ПЖ после отрицательного результата первичной или вторичной биопсии предпочтительно выполнять по крайней мерее через 4 нед. во избежание получения артефактов, поскольку сигнал от кровоизлияний в железе аналогичен сигналу от контрастного вещества [29].
В 2007 г. международной рабочей группой, состоявшей из экспертов по МРТ ПЖ, совместно с Европейским обществом урогенитальной радиологии (ESUR) были опубликованы основополагающие принципы интерпретации результатов МРТ-исследований ПЖ в виде системы PI-RADS v.1 [30]. Система оказалась очень востребованной, и в 2015 г. была предложена вторая версия системы PI-RADS v.2 [31], где были исправлены и доработаны недостатки первой версии. Авторы считают, PI-RADS v.2 улучшает первичный диагностический процесс, позволяет оценивать риски и прогноз заболевания [32]. Концепция PI-RADS v.2 основана на представлении об анатомо-гистологическом строении ПЖ [33]. С помощью созданной карты можно наглядно локализовывать выявленные патологические изменения в структуре ПЖ и осуществлять визуальную поддержку планируемой таргетной биопсии [34].
Мы, впервые в Узбекистане, внедрили мпМРТ ПЖ с целью диагностики распространенного РПЖ, а также определения степени риска выявления заболевания и проведения первичной биопсии для ранней диагностики РПЖ.
К сожалению, в Узбекистане на сегодняшний день РПЖ в большинстве случаев диагностируют на поздних стадиях [8]. В связи с этим основной целью нашей работы стало улучшение ранней диагностики РПЖ. Для этого 62 пациентам была выполнена мпМРТ ПЖ до биопсии. Нас в большей степени интересовал результат пациентов с уровнем ПСА менее 20 нг/мл, у которых данные ПРИ и ТРУЗИ ПЖ были недостаточными для показаний к биопсии и малоинформативными в выявлении РПЖ.
Мы подтвердили данные литературы, согласно которым с нарастанием степени риска определения РПЖ по классификации PI-RADS v2, выявленной с помощью мпМРТ ПЖ, прямо пропорционально увеличивается и выявляемость РПЖ [14, 15, 30–34]. Согласно многоцентровому исследованию, биопсию необходимо выполнять при выявлении риска PI-RADS 3–5 [35].
Но при риске PI-RADS 3 выявляемость РПЖ значительно ниже и у разных авторов колеблется от 5 до 26% [36–39]. Данный показатель среди наших пациентов оказался 17,5% (рис. 2).
Проведенный нами анализ показал, на наш взгляд, очень важные в практическом отношении данные, что одна и та же степень риска по PI-RADS у разных пациентов имела разную диагностическую ценность, зависевшую от уровня ПСА. Следовательно, для улучшения ранней диагностики локализованной формы РПЖ при постановке вопроса о целесообразности выполнения биопсии ПЖ мы должны ориентироваться не только на степень риска по PI-RADS v2, но и на уровень ПСА. Таким образом мы можем избавить часть пациентов от дополнительных, повторных, инвазивных диагностических вмешательств.
Выводы
1. При первичной трансректальной мультифокальной биопсии простаты из 10–12 точек при объеме ПЖ 67,47±2,79 см3 выявляемость РПЖ составила 65,6%, среди пациентов с уровнем общего ПСА менее 20 нг/мл показатель составил 35,3%.
2. При определении показаний к биопсии среди пациентов с уровнем ПСА менее 20 нг/мл информативность ПРИ и ТРУЗИ ПЖ оказалась статистически значимо ниже (17,6%), чем у пациентов с уровнем ПСА выше 20,1 нг/мл (61,6%; р<0,001).
3. Выявляемость РПЖ при первичной трансректальной мультифокальной биопсии в сочетании с таргетной биопсией ПЖ среди пациентов с PI-RADS 4 и PI-RADS 5 была равной 91,2%. Выявляемость РПЖ среди пациентов с уровнем ПСА менее 20 нг/мл с PI-RADS 4 и PI-RADS 5 составила 75,0 против 35,3% в группе без мпМРТ (р<0,05).
4. Значение степени риска РПЖ по PI-RADS v2 отличается в зависимости от уровня ПСА. При 2-й и 3-й степенях риска по PI-RADS v2, уровне ПСА менее 20 нг/мл и отсутствии изменений по ТРУЗИ и ПРИ возможно наблюдение за пациентом в динамике без проведения биопсии. При аналогичной степени риска по PI-RADS v2 и уровне ПСА более 20,1 нг/мл предпочтительно выполнение биопсии. При 4–5-й степенях риска по PI-RADS v2 показано обязательное проведение биопсии ПЖ независимо от уровня ПСА.
5. Предварительное выполнение мпМРТ простаты перед биопсией у пациентов с уровнем общего ПСА менее 20 нг/мл без подозрительных участков в железе по данным ПРИ и ТРУЗИ простаты достоверно улучшает раннюю диагностику РПЖ и может избавить часть пациентов от повторных биопсий и нежелательных инфекционно-воспалительных осложнений, связанных с процедурой.



