Альфа1-адреноблокатор как эффективное средство лечения СНМП с позиции фармакологии
Три последовательных этапа предшествуют лечебному действию препарата альфа1-адреноблокатора (α1-АБ, ААБ): фармацевтический, фармакокинетический и фармакодинамический, которые складываются в «дорожную карту» препарата ААБ [1].
1. На первом фармацевтическом этапе от ААБ требуется длительно (2–3 года) сохранять свои свойства в составе таблетки/капсулы.
Пока ААБ находится в лекарственной форме – это химическое соединение, пока только потенциально обладающее полезными терапевтическими свойствами. Присутствует в виде активной фармацевтической субстанции (АФС), что позволяет поддерживать его физическую стабильность и химическое равновесие, сохранять устойчивость к агрессивным факторам – влажности, атмосферному кислороду и солнечной/тепловой энергии [2]. «Активность» ААБ в составе фармацевтического препарата определяется наличием в химической структуре ААБ реакционноспособных=активных группировок, таких как гидроксильная (-OH), аминогруппа (-NH-), атомы азот (N), в составе гетероцикла и др. (рис. 1). Кристаллическая структура (микрогранулы, микрокристаллы АФС) ограничивает возможность молекулы ААБ раньше времени перейти в растворимую форму и вступить в нежелательное фармацевтическое взаимодействие.
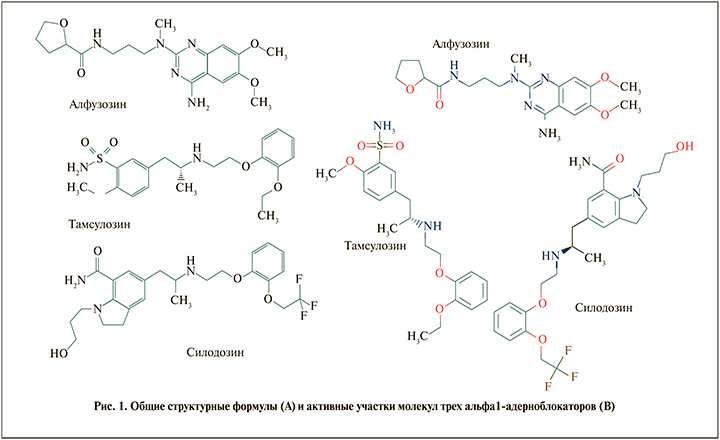
2. После высвобождение ААБ из состава таблетки/капсулы начинается второй – фармакокинетический – этап. На возможность абсорбции ААБ из желудочно-кишечного тракта (ЖКТ) влияют его физико-химические особенности: размер молекулы (молекулярный вес ААБ), проницаемость через бислойные фосфолипидные мембраны эпителиоцитов (показатель липофильности ААБ), наличие заряда молекулы при определенном значение рН (константа кислотности – рКа) в различных отделах ЖКТ.
В понятие «активность» ААБ на фармакокинетическом этапе входит возможность вступления в реакции печеночного метаболизма (ферменты системы цитохрома Р-450, конъюгации с глюкуроновой кислотой, глутатионом и др.). Метаболические превращения, комплексообразование с белками крови по-прежнему зависят исключительно от химической формулы ААБ и не зависят от его потенциальных лечебных свойств [3].
Наличие в химической структуре ААБ реакционноспособных=активных группировок является «приглашением» к метаболизму, позволяя «выхватывать и включать» молекулу ААБ в реакции метаболического превращения в различных компартментах гепатоцитов.
3. Строго говоря, только сейчас на третьем, фармакодинамическом, этапе, оккупируя рецептор, ААБ наконец становится альфа1-адреноблокатором в буквальном смысле слова. Это «только миг» в жизни молекулы: время полудиссоциации комплекса ААБ с рецептором при 37оС не превышает нескольких минут. Все остальное время жизни молекула ААБ находится в статусе ксенобиотика – химического соединения, чужеродного для организма, по отношению к которому стратегия организма определяется принципом «элиминация asap» [4].
Таким образом, разделение фармакологических свойств ААБ на «фармакодинамику» и «фармакокинетику» имеет глубокое основание. Фармакодинамика – результат непосредственного взаимодействия ААБ с терапевтической мишенью – альфа1-адренорецептором. Вне связи с рецептором молекула ААБ находится в фармакокинетическом «поле», описываемом терминами «всасывание», «распределение», «метаболизм» и «выведение».
С позиции лекарственной терапии цель фармакокинетики – обеспечить «в нужное время, в нужном месте присутствие действующего начала в терапевтическом диапазоне эффективных концентраций».
Применительно к фармакотерапии препаратом ААБ данная цель складывается из решения следующих задач:
a) «druggable» – фармацевтическая пригодность молекулы ААБ: способность высвобождаться из таблетки/капсулы с заданной кинетикой, проходить первый барьер на своем пути (клеточные мембраны энтерои колоноцитов) [5];
b) создавать высокие эффективные концентрации в ткани простаты, минимизируя присутствие в других органах и системах (простатотропные свойства ААБ) [6];
c) находить и прочно связываться с целевыми альфа1-адренорецепторами (рецепторселективность ААБ) [7].
Лечебные и побочные эффекты ААБ служат следствием того, как «четко и полно» ААБ выполняет поставленные задачи. Забегая вперед, следует сказать, что не существует «идеального» ААБ, а клиническая уроселективность решается в двух основных направлениях. Первый, фармакокинетический, путь, реализуемый преимущественно за счет простатотропности, характерен для алфузозина [8]. Напротив, тамсулозин и силодозин используют рецепторселективные свойства молекулы для того, чтобы сбалансировать желательные уродинамические эффекты и минимизировать возможное побочное действие [9].
Вернемся к перечисленным задачам и сформулируем особенности трех наиболее широко применяемых в урологической практике ААБ.
А. В табл. 1 приведены две фундаментальные характеристики молекулы ААБ – растворимость в воде (мг/мл) и липофильность (значение logP) [10].

Алфузозин и тамсулозин отнесены к классу I биофармацевтической классификационной системы, т.е. имеют самый благоприятный из возможных набор свойств с точки зрения фармацевтического этапа [11]. Важное уточнение: чтобы добиться этого, алфузозин и тамсулозин применяются в виде соли (гидрохлорида). Например, препарат Алфупрост® МР содержит 10 мг алфузозина гидрохлорида. Силодозин используется в форме base, возможно, это одна из причин необходимости повышения его общей дозы, несмотря на высокий аффинитет и селективность молекулы на рецепторном уровне в сравнении с другими ААБ.
B. В абсорбции ААБ важную роль играет рН ЖКТ, величина которого повышается с 4–5 (проксимальные отделы) до 8–8,5 (дистальные сегменты толстого кишечника) [12]. Абсорбции по механизму простой диффузии подвергаются только незаряженные молекулы ААБ, не несущие заряда. Следовательно, в зависимости от химической природы способность ААБ будет «динамично» меняться по мере пассажа таблетки/капсулы. Прием пищи способен изменять значения рН, а вместе с ним биодоступность ААБ. Ключевым фактором на этапе всасывания служит величина рКа – значение рН, при котором 50% молекул ААБ находятся в незаряженной форме, вторая часть – в ионизированной форме.
Значение рКа для алфузозина составляет 8,13 [10]; он относится к органическим основаниям (рКа>7). С практической точки зрения важно, что способность к абсорбции у алфузозина будет возрастать по мере продвижения по ЖКТ, а значит, лекарственные формы пролонгированного высвобождения имеют преимущества (Алфупрост® МР) по сравнению с таблетками с кинетикой немедленного высвобождения.
Тамсулозин характеризуется еще более выраженными основными свойствами, рКа=9,93 [10]. Все сказанное для алфузозина справедливо и для него.
Свойства силодозина описываются двумя значениями рКа: рКа1 и рКа2, соответственно 4.03 и 8.53 [13]. Это свидетельствует о наличии у ААБ «окна всасывания», лежащего в пределах указанных значений, что не требует дополнительных форм модифицированного высвобождения.
После приема внутрь силодозин хорошо всасывается, абсорбция пропорциональна дозе. Низкую величину абсолютной биодоступности силодозина (около 32%), по-видимому, определяет пресистемный метаболизм.
Значимым фармакокинетическим параметром, который позволяет оценивать простатотропные свойства ААБ, служит объем распределения (volume of distribution – Vd). Если ААБ равномерно распределяется во всех водных компартментах организма, значение Vd будет соответствовать значению 0,6–0,8 л/кг, т.е. сопоставимо с общим содержанием воды в теле – в среднем 70% (зависит от пола, веса, степени дегидратации, более выраженной с возрастом). Vd для силодозина равен 0,81 л/кг. Можно утверждать, что это еще одна причина несоответствия между предельно выраженными рецепторотропными свойствами молекулы и относительно высокой (8 мг) по сравнению с тамсулозином (0,4 мг) суточной дозой. Как ожидалось, тамсулозин имеет минимальное по сравнению с другими ААБ значение Vd, равное 0,2 л/кг, что указывает на то, что распределение силодозина, по-видимому, ограниченно внеклеточной жидкостью. Адренорецепторы расположены в цитоплазматических мембранах эффекторных клеток, чтобы ААБ связался с ними, нет необходимости проникать внутрь клетки [14]. «Уязвимость» молекулы тамсулозина выражается в тесной привязанности к объему внеклеточной жидкости, величина которой может меняться в различных ситуациях, повышая риск выйти из терапевтического коридора плазменных концентраций (обезвоживание, изменение онкотического давления плазмы крови и экстравазального пространства). Так, изменение буферной емкости альбумина (например, при гипоальбумиемии) может существенно влиять на концентрацию свободной фармакологически активной формы тамсулозина, повышая риск возможных ортостатических побочных эффектов (в норме связывание тамсулозина с белками плазмы – 99%).
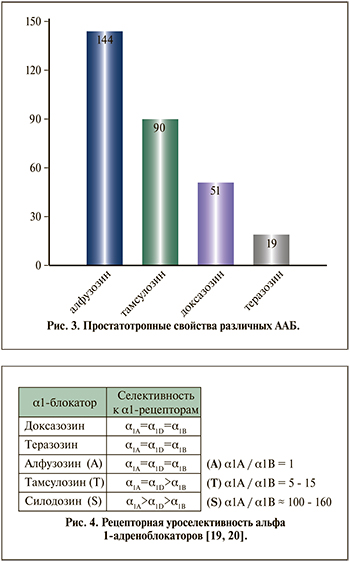
О чем свидетельствует высокое, 2,5 л/кг, значение Vd для алфузозина? Это указывает на выраженную способность ААБ выходить, «вымываться» из крови, накапливаясь в тканях НМП. Простатропные свойства алфузозина хорошо известны и детально описаны в литературе [8, 15]. С увеличением времени концентрация алфузозина в ткани простаты повышается в 2 раза по сравнению с плазменным уровнем (через 6 ч после введения алфузозина по сравнению с 1 ч) [16]. Как следует из данных, представленных на рис. 2, алфузозин обладает максимальным по сравнению с другими ААБ индексом простатоселективности [17].

Исследования, выполненные на клиническом материале, подтвердили, что наибольшую селективность к тканям простаты продемонстрировал алфузозин. Для тамсулозина данный показатель ниже в среднем на 38% [18]. У других изученных препаратов ААБ (доксазозин и теразозин) уровень простатотропности оказался значительно ниже (рис. 3).
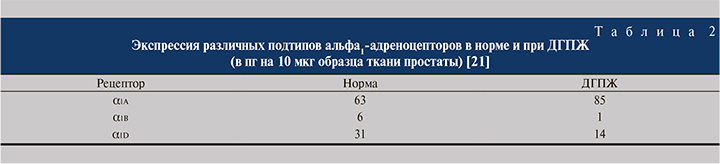
С. Эффективность фармакодинамического рецепторного этапа характеризуется тремя расчетными показателями. Аффинитет (сродство) к рецептору (количественно вычисляется в виде Кд, нМ). Рецепторная емкость (плотность рецепторов), вычисляемая как пмоль/кл или нмоль/г ткани. Соотношение сродства к различным типам адренорецепторов: альфа1А/альфа1В, альфа1А/альфа1D (рис. 4). Согласно результатам исследования in vitro, селективность силодозина в отношении aльфа1A-адренорецепторов по сравнению с aльфа1B-адренорецепторами примерно в 17 раз больше, чем у тамсулозина [6].
Важно учитывать, что экспрессия различных подтипов альфа1-адреноцепторов при доброкачественной гиперплазии предстательной железы (ДГПЖ) существенно изменяется по сравнению с нормальными значениями (табл. 2).
Точная оценка перечисленных показателей, изучение закономерностей структура-эффект в ряду ААБ проводятся преимущественно в исследованиях in vitro. Предоставляя ценную научную информацию, необходимую в том числе для поиска и разработки новых перспективных ААБ, эксперименты in vitro имеют существенные ограничения [22]. Это «фармакодинамика в чистом виде», когда в «тепличных» лабораторных условиях, поддерживая постоянно длительно оптимальную концентрацию ААБ в пробирке/плашке планшета/флаконе, мы лишены возможности оценить фармакокинетический вклад в действии ААБ. Вступая в свои права в условиях in vivo, фармакокинетика вносит существенные изменения в концентрацию ААБ в месте действия. Так, в пробирке ААБ обычно не подвергается метаболизму, температура инкубации может быть ниже физиологической, составляя 25оС и даже 4оС, чтобы исключить все возможности клеточного метаболизма [23].
Создание эффективного и безопасного препарата ААБ обязательно учитывает особенности фармакокинетики и фармакодинамики активного начала. Наглядным примером сбалансированных фармакологических свойств ААБ является препарат Алфупрост® МР в виде таблеток пролонгированного действия на основе монолитной матриксной системы, содержащих по 10 мг алфузозина гидрохлорид (в составе гранул). Среднее значение относительной биодоступности составляет 104,4% по сравнению с применением алфузозина в лекарственной форме немедленного высвобождения (2,5 мг 3 раза в сутки). Максимальная концентрация алфузозина в плазме достигается через 9 ч после приема препарата по сравнению с 1 ч для формы немедленного высвобождения. Метаболиты алфузозина, образующиеся в печени, не обладают фармакологической активностью. По сравнению со здоровыми добровольцами среднего возраста у пациентов пожилого возраста (старше 75 лет) фармакокинетические показатели алфузозина не увеличиваются.
От активной молекулы к эффективной терапии: клиническая уроселективность
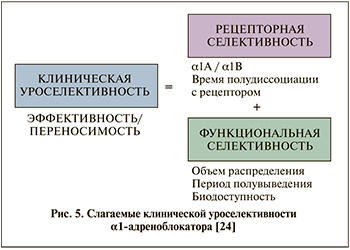
Клиническая уроселективность – показатель, характеризующий влияние препаратов на инфравезикальную обструкцию (ИВО) и симптомы нижних мочевыводящих путей (СНМП) при минимальном количестве побочных эффектов [18]. Клиническая уроселективность – самый важный критерий, определяющий соотношение выгоды и риска применения препарата [18]. Каждый ААБ решает вопросы уроселективности в своей манере – в соответствии с химическим строением и фармакологическими свойствами (рис. 5). Клиническая уроселективность препаратов алфузозина обеспечивается в основном уникальными фармакокинетическими/функциональными свойствами (объем распределения, простатотропность) [8, 15, 17], в то время как у тамсулозина и силодозина доминирует рецепторный/фармакодинамический компонент [7, 9, 19].
От международного непатентованного наименования «алфузозин» к лекарственному препарату
Разработка формуляции с модифицированным высвобождением должна основываться на хорошо установленной клинической необходимости (например, на повышении приверженности и(или) безопасности пациентов) и на единстве физиологических, фармакодинамических и фармакокинетических аспектов. Формы дозирования с пролонгированным высвобождением – это формы дозирования, обеспечивающие длительность высвобождения по сравнению с таковым у формы дозирования с немедленным высвобождением, вводимой тем же путем. Такая намеренная модификация достигается за счет специального дизайна формуляции и(или) методов производства.
Форма дозирования с пролонгированным высвобождением может быть приемлема, если действующее вещество способно оказывать желаемое клиническое действие, хотя фармакокинетический профиль в этом случае будет отличаться от достигаемого при применении формы с немедленным высвобождением.
Формуляция с пролонгированным высвобождением может иметь ряд преимуществ перед формой с немедленным высвобождением. Например, сниженными флуктуациями плазменной концентрации лекарства, способными обеспечить более постоянные эффекты и(или) сниженную частоту и(или) интенсивность нежелательных лекарственных реакций; меньшей частотой введения и тем самым потенциальным повышением приверженности пациентов.
Такими особенностями фармакокинетического профиля обладает ААБ Алфупрост® МР (алфузозин), лекарственная форма которого производится по запатентованной технологии модифицированного высвобождения [25]. Таблетка матричного типа препарата Алфупрост® МР состоит из гидрофильного матрикса, куда погружено действующее вещество алфузозин. Гипромеллоза, входящая в состав таблетки, используется как гидрофильный матричный агент, благодаря которому обеспечивается пролонгированное высвобождение действующего вещества. При попадании таблетки в жидкую среду гидрофильный матрикс способен впитывать массу воды без растворения с образованием гидрогеля. Модифицированное высвобождение алфузозина находит отражение в фармакокинетическом профиле препарата – отсутствие пиков концентрации препарата в сыворотке обеспечивает равномерное поступление алфузозина в сыворотку в течение 24 ч.
ДГПЖ как социально значимое заболевание
ДГПЖ одно из наиболее распространенных заболеваний мужской половины человечества старше 40 лет [26]. В Российской Федерации с 2000 г. заболеваемость ДГПЖ увеличилась в 1,5 раза, достигнув 12 млн мужчин [27]. В повседневной работе врача-уролога данное заболевание занимает второе место по распространенности (23%), уступая только инфекционным заболеваниям мочевыводящих путей (32%) [28, 29]. В течение последних 5 лет прирост заболеваний органов мочеполовой системы в России превысил таковую при патологии кровообращения, а ДГПЖ стала самым распространенным урологическим заболеванием мужчин пожилого и старческого возраста [30].
В эпидемиологическом исследовании S. J. Jacobsen et al. показано, что выраженность симптомов нижних мочевыводящих путей (СНМП), снижение максимальной скорости потока мочи (Qmax), увеличение размеров предстательной железы и пожилой возраст мужчины связаны с повышенным риском острой задержки мочи (ОЗМ) [31]. Группа из 2115 мужчин в возрасте от 40 до 79 лет была случайным образом отобрана с дальнейшей оценкой у них тяжести СНМП и измерением Qmax. Последующее наблюдение проводилось посредством ретроспективного анализа их медицинских карт для определения частоты случаев возникновения у этих пациентов ОЗМ за последующие 4 года. Результаты анализа показали, что среди мужчин без симптомов или с легкими симптомами (индекс симптомов Американской ассоциации урологов – 7 баллов или меньше) частота случаев ОЗМ увеличилась с 2,611 тыс. человеко-лет среди мужчин в возрасте от 40 до 49 лет до 9 311 млн человеко-лет среди мужчин в возрасте от 70 до 79 лет. Среди мужчин с умеренными и тяжелыми симптомами (индекс симптомов Американской ассоциации урологов больше 7 баллов) частота случаев ОЗМ увеличилась с 3,011,000 человеко-лет у мужчин 40–49 лет до 34,711,000 человеко-лет у мужчин в возрасте 70–79 лет. Мужчины со сниженной Qmax (менее 12 мл/с) имели в 4 раза выше риск ОЗМ по сравнению с мужчинами с Qmax и более 12 мл/с (95% ДИ: 2,3, 6,6). Мужчины с увеличенной предстательной железой (объемом более 30 мл3) подвергались 3-кратному увеличению риска частоты развития ОЗМ (95% ДИ: 1,0, 9,0, р=0,04).
ААБ как медикаментозная терапия первой линии СНМП при ДГПЖ
Согласно рекомендациям Европейской ассоциации урологов (ЕАУ), ААБ являются первой линией терапии расстройств мочеиспускания у мужчин, страдающих ДГПЖ [32]. В Российской Федерации используются следующие препараты данной группы: алфузозин, доксазозин, тамсулозин и силодозин. Косвенные и ограниченные прямые сравнения показали, что все ААБ имеют сопоставимую эффективность при применении в соответствующих дозах [33]. Хотя для достижения максимального улучшения симптоматики требуется несколько недель, статистически значимое преимущество над плацебо наблюдается уже в первые часы или дни приема [34]. В контролируемых исследованиях показано, что ААБ обычно снижают показатель IPSS (Международная шкала симптомов простаты) примерно на 30–40% и увеличивают Qmax примерно на 20–25% [35, 36]. В исследованиях с открытым приемом ААБ наблюдалось улучшение показателя IPSS до 50% и увеличение Qmax до 40% [10, 11]. ААБ позволяют уменьшить выраженность как накопительных, так и симптомов опорожнения. По данным исследований с наблюдением от менее 1 года до 3 лет, ААБ эффективны вне зависимости от размера предстательной железы (ПЖ), в то же время снижение показателя IPSS и улучшение Qmax на фоне терапии ААБ сохраняются в течение как минимум 4 лет [37–41]. Эффективность ААБ не зависит от возраста [39–41].
Эффективность и профиль безопасности наиболее назначаемых препаратов и группы α1-АБ были продемонстрированы в открытом рандомизированном сравнительном исследовании R. Manjunatha (2016) [42]. 90 пациентов с ДГПЖ и СНМП были рандомизированы в 3 группы по 30 человек в каждой для приема 10 мг алфузозина в форме пролонгированного высвобождения, тамсулозина 0,4 мг или силодозина 8 мг в течение 12 нед. Первичной конечной точкой была динамика баллов по IРSS, вторичной конечной точкой была фиксация жалоб пациентов, показатель качества жизни (QoL) и Qmax по сравнению с исходным уровнем. По результатам исследования, улучшение IPSS в группе алфузозина (на 62,14%) отмечено уже через 2 нед. лечения (р<0,001). Через 12 нед. терапии в группе алфузозина IPSS улучшилось на 88,18% по сравнению с 72,12% в группе тамсулозина и 82,23% в группе силодозина (р<0,001). Клинически значимое улучшение Qmax наблюдалось в группе алфузозина и тамсулозина (р=0,025 и р<0,001), но не силодозина (р=0,153). В группе алфузозина общее увеличение Qmax составило 25,34% по сравнению с исходным уровнем (р=0,025), а снижение ноктурии составило около 60% от начального показателя (р<0,001). Улучшение QoL составило более 75% во всех трех группах (р<0,001).
Эффективность применения алфузозина в форме пролонгированного высвобождения (10 мг/сут.)
Каждый из препаратов группы ААБ обладает рядом особенностей, что обусловливает их преимущества применения в реальной клинической практике. Основными клиническими особенностями, делающими алфузозин привлекательным для врачей-урологов, служат его «простатотропность» и форма таблетки с пролонгированным высвобождением действующего вещества, обусловливающими не только эффективность купирования СНМП, но и высокий профиль безопасности его использования коморбидными пациентами, в том числе с сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями [43].
Эффективность и безопасность применения алфузозина по сравнению с плацебо оценены в объединенном анализе, куда вошли три параллельных рандомизированных двойных слепых плацебо-контролируемых исследования пациентов с СНМП и клинически выраженной ДГПЖ [44]. Пациенты были рандомизированы для приема алфузозина 10 мг 1 раз/сут. (473 чел.) или плацебо (482 чел.), длительность терапии – 12 нед. Было продемонстрировано, что среднее улучшение суммы баллов по опроснику IPSS было более статистически достоверны (р<0,005) в группе алфузозина -6,0 (5,1), чем в группе плацебо -4,2 (5,7), при всех посещениях независимо от размера простаты.
Максимальная скорость потока мочи на 14-й, 28 и 84-й дни посещения была статистически достоверно выше (р<0,001) в группе алфузозина (среднее улучшение Qmax+2,3 (3,8) мл/с, чем в группе плацебо, +1,1 (3,1) мл/с независимо от размера простаты. Алфузозин хорошо переносился пациентами: количество абстинентных побочных эффектов было сопоставимым в обеих группах лечения: наиболее частым нежелательным явлением было головокружение (2,9% в группе плацебо, 6,1% в группе алфузозина); не было никаких существенных изменений в уровне кровяного давления по сравнению с плацебо, в том числе у пожилых пациентов и пациентов с гипертонической болезнью.
Эффективность 3-летней монотерапии алфузозином с пролонгированным высвобождением 10 мг была оценена в крупнейшем европейском исследовании Alf-One [45]. Последнее включило 689 мужчин со средним возрастом к началу терапии 67,6 года. В результате лечения средний показатель динамики балла по шкале IPSS был 6,4, что статистически достоверно ниже чем до начала терапии (p<0,001). Улучшение более чем на 3 балла было достигнуто у 71,3% мужчин и более чем на 6 баллов у 47,2%. Среднее снижение эпизодов ноктурии было -0,8 (-25,5%), а также эпизодов ургентности -1,7 (-40,7%). В обоих случаях различия были статистически достоверны при сравнении с показателями до лечения (p<0,001). Вышеуказанные изменения отмечены с первых дней терапии и оставались стабильными в течение 3 лет терапии.
Профиль безопасности применения ААБ
Распределение рецепторов в нижних мочевыводящих путях, избирательность по подтипам рецепторов и особенности фармакокинетики обусловливают профиль переносимости каждого из ААБ. К наиболее частым побочным эффектам при приеме ААБ относят астению, головокружение и (ортостатическую) гипотензию. По данным мета-анализа, вазодилатирующее влияние наиболее выражено при применении доксазозина и теразозина, но встречается гораздо реже и сопоставимо при приеме алфузозина и тамсулозина [46]. Пациенты с сопутствующими сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями и/или сопутствующей терапией вазоактивными препаратами могут быть восприимчивы к вазодилатации, индуцированной ААБ [47]. В крупном ретроспективном когортном анализе мужчин в возрасте старше 66 лет прием ААБ сопровождался повышением риска падений (отношение риска [ОР]=1,14) или переломов (ОР=1,16), вероятнее всего, вследствие артериальной гипотензии [48].
Наличие побочных эффектов, связанных с адренорецепторной вазодилатацией, могут ограничивать применение ААБ в клинической практике [49]. Системный сосудистый эффект альфа-блокаторов был подтвержден в крупном исследовании ALLHAT, которое подтолкнуло к дальнейшему поиску ААБ для лечения СНМП при ДГПЖ с минимальным воздействием на сердечно-сосудистую систему, особенно у пожилых пациентов [50].
Несмотря на сходный профиль эффективности наиболее распространенных ААБ показатели безопасности для каждого препарата имеют свои особенности.
Кардиоваскулярная безопасность применения алфузозина в форме таблеток с пролонгированным высвобождением (10 мг/сут.)
В двойном слепом плацебо-контролируемом рандомизированном исследовании (N. Mondaini et al., 2006) оценено влияние алфузозина в дозе 10 мг на артериальное давление (АД) и частоту сердечных сокращений (ЧСС) у молодых здоровых добровольцев [51]. Мужчины (24–30 лет) были рандомизированы для приема в течение 1 нед. алфузозина (10 мг 1 раз в день) или плацебо. Было продемонстрировано, что между плацебо и группой алфузозина не наблюдалось достоверных различий в изменении систолического артериального давления (САД) и диастолического артериального давления (ДАД) или ЧСС от исходных показателей; эпизодов гипотензии (снижение САД>10%) во время терапии не зарегистрировано. Алфузозин не влиял на САД, ДАД или ЧСС у здоровых добровольцев.
В многоцентровом открытом обсервационном исследовании (Sánchez-Chapado et al., 2000) [52], куда вошли 3095 пациентов испанских клиник с СНМП при ДГПЖ, проведена оценка безопасности и эффективности 60-дневной терапии алфузозином с пролонгированным высвобождением (10 мг в сутки) в реальной клинической практике. Терапия алфузозином продемонстрировала отсутствие клинически значимого влияния на АД: АД снижалось в среднем на 5–6 мм рт.ст. (4%) во время лечения алфузозином; различия САД и ДАД не изменялись на протяжении всего периода наблюдения; бессимптомная постуральная гипотензия (снижение САД минимум на 20 мм рт.ст. и/или ДАД) зарегистрирована менее чем у 1% (у 28 пациентов); средняя ЧСС была в пределах нормы на протяжении всего исследования.
В более позднем 6-месячном открытом проспективном исследовании (R. Hartung et al., 2006) [53], куда вошли 6523 мужчины с СНМП при ДГПЖ, средний возраст которых составил 64,7 года, оценено влияние алфузозина в форме таблеток с пролонгированным высвобождением (10 мг однократно в сутки) на АД, в том числе у пожилых пациентов и пациентов с АГ, ишемической болезнью сердца или диабетом, в том числе получавших антигипертензивные препараты (диуретики, бета-адреноблокаторы, ингибиторы ангиотензинпревращающего фермента, ингибиторы ангиотензина II и антагонисты кальциевых каналов). Было показано, что у мужчин без сопутствующей сердечно-сосудистой патологии или сопутствующей терапии антигипертензивными препаратами применение алфузозина сопровождалось отсутствием клинически значимого влияния на САД (среднее снижение на 2,6–2,8 мм рт.ст.) и ДАД (в среднем на 1,7–1,8 мм рт.ст.). У мужчин с сопутствующей сердечно-сосудистой патологией среднее значение снижения АД было также клинически незначимым: систолического на 3,5–5,8 мм рт.ст. и диастолического на 2,0–3,3. Постуральная гипотензия наблюдались редко – 0,7%. Авторы сделали вывод, согласно которому алфузозин в форме таблеток с пролонгированным высвобождением (10 мг 1 раз в сутки) эффективен и хорошо переносится, оказывает клинически незначимое влияние на АД, в том числе у пожилых пациентов и пациентов с АГ, ишемической болезнью сердца или диабетом, а также у пациентов, принимающих антигипертензивные препараты.
Эффективность и безопасность применения алфузозина в форме таблеток с пролонгированным высвобождением оценены в исследовании А. В. Кузьменко и соавт. [54]. Были отобраны и изучены амбулаторные карты 120 пациентов с ДГПЖ, которые находились на лечении в консультативно-диагностическом отделении больницы № 10 Воронежа с января 2000 по май 2021 г. Согласно амбулаторным картам, всем пациентам назначался препарат Алфупрост® МР в течение 12 нед. для лечения расстройств мочеиспускания, обусловленных ДГПЖ. Критерии включения в исследования: умеренная симптоматика по шкале IPSS, повышение АД или уже диагностированная АГ, объем простаты до 40 см3, снижение Qmax – 6-13 мл/с и отсутствие подозрений на рак ПЖ. Через 4 и 12 нед. терапии пациентам проводился контроль субъективных (IPSS, QoL) и объективных показателей (Qmax, объем остаточной мочи), контроль уровня АД и зарегистрированных нежелательных явлений (НЯ), связанных с проводимой терапией. Помимо анализа общей эффективности отдельное внимание было уделено динамике уровня АД у пациентов с АГ (АД до 160/100 мм рт.ст., 60 больных) и без нее, с повышенным нормальным АД по ВОЗ (АД до 130/80 мм рт.ст., 60 больных). Сопутствующая медикаментозная терапия по поводу АГ при этом не менялась. В результате ретроспективного анализа эффективности монотерапии препаратом Алфупрост® МР продемонстрировано уменьшение среднего балла по шкале IPSS на 30%, улучшение QoL в среднем на 1,8 балла, увеличение Qmax на 20,6% при отсутствии у пациентов остаточной мочи. Вышеуказанные данные коррелируют с ранее полученными результатами исследований с алфузозином в форме пролонгированного высвобождения (10 мг/сут.) и отражающих высокую эффективность препарата. В результате зафиксированного в амбулаторных картах мониторинга уровня САД и ДАД в начале, через 4 и 12 нед. терапии показано, что эти показатели варьировали в пределах 1 мм рт.ст. как в группе пациентов с АГ, так и среди пациентов с повышенным АД.
Заключение
Фармакологические свойства ААБ как лекарственного препарата определяется его фармакокинетикой, фармакодинамикой и лекарственной формой. Персонализированный подход к выбору препарата ААБ для медикаментозной терапии СНМП при ДГПЖ учитывает, с одной стороны, индивидуальные особенности пациента (наличие сопутствующих патологий: артериальная гипертензия, ишемическая болезнь сердца, сахарный диабет), с другой – индивидуальный фармакологический профиль ААБ, риск развития нежелательных лекарственных взаимодействий. По результатам обширного клинического опыта, в том числе данных современных клинических исследований, препарат Алфупрост® МР (алфузозин 10 мг в форме таблеток с пролонгированным высвобождением) продемонстрировал выраженную клиническую уроселективность: высокую эффективность купирования СНМП и кардиоваскулярную безопасность использования коморбидными пациентами, в том числе с сердечно-сосудистыми заболеваниями.



